How To Test For Celiac Disease At-home
 Welcome to the intricate world of managing Celiac Disease, a pervasive health condition that can significantly impact your quality of life. This article guides you on a journey to a better understanding of Celiac Disease, revealing the essential aspects that play a crucial role in detecting, diagnosing, and living with it. Embark on a voyage of exploration as we navigate the scientific complexities of Celiac Disease in comprehensible, layman terms, probing into its roots, symptoms, and contributing factors. We will then transition into the mechanics of At-Home Testing for Celiac Disease, a pivotal aspect that arms you with the knowledge and confidence to manage your health proactively. The final stop in our discourse will be the phase of Moving Forward After Diagnosis - a resourceful, empathetic guide to reclaiming your life post-diagnosis. Clarity is power, and we assure you - by the end of this, you will be sufficiently enlightened to better understand or manage this condition. Now, let us dive straight into our first cornerstone - Understanding Celiac Disease.
Welcome to the intricate world of managing Celiac Disease, a pervasive health condition that can significantly impact your quality of life. This article guides you on a journey to a better understanding of Celiac Disease, revealing the essential aspects that play a crucial role in detecting, diagnosing, and living with it. Embark on a voyage of exploration as we navigate the scientific complexities of Celiac Disease in comprehensible, layman terms, probing into its roots, symptoms, and contributing factors. We will then transition into the mechanics of At-Home Testing for Celiac Disease, a pivotal aspect that arms you with the knowledge and confidence to manage your health proactively. The final stop in our discourse will be the phase of Moving Forward After Diagnosis - a resourceful, empathetic guide to reclaiming your life post-diagnosis. Clarity is power, and we assure you - by the end of this, you will be sufficiently enlightened to better understand or manage this condition. Now, let us dive straight into our first cornerstone - Understanding Celiac Disease.Understanding Celiac Disease
Celiac disease, a prevalent yet often misunderstood condition, impacts millions worldwide. This article aims to shed light on three critical facets of this complex disease: the basics of Celiac disease, common symptoms and complications, and comparisons with gluten sensitivity. Our first focus will be on the fundamentals of Celiac disease—what it is, its causes and how it affects the digestive system. Following that, the article will enumerate its common symptoms and complications, offering a clearer perspective on how this disease manifests and the potential risks if left untreated. Lastly, we will differentiate between Celiac disease and gluten sensitivity, exploring the notable disparities, and discussing why these two often get mixed up. This comprehensive overview will provide a more profound understanding of Celiac disease, facilitating early detection and assistance in efficient management. As we transition into The Basics of Celiac Disease, let's first understand that it is an autoimmune disorder triggered by the ingestion of gluten, leading to an unexpected immune response in the small intestine.
The Basics of Celiac Disease
Understanding the basics of Celiac Disease is an essential starting point when looking into conducting an at-home test. Celiac Disease is an inherited autoimmune disorder, affecting approximately 1% of the population worldwide. It is characterized by the body's adverse reaction to gluten, a protein found in grains like wheat, rye, and barley. When individuals with Celiac Disease consume gluten, their immune system mistakenly identifies this protein as a threat and launches an attack against it. Interestingly, this autoimmune response primarily targets the small intestines. The small intestines are lined with villi, small finger-like projections that aid in nutrient absorption. When the immune response damages these villi, the affected individual suffers from nutritional deficiencies due to decreased absorption capacities, resulting in symptoms such as chronic diarrhea, abdominal bloating, weight loss, fatigue, and anemia. To further complicate matters, Celiac Disease is notorious for its broad symptom spectrum. Some affected individuals may experience severe symptoms while others may have none at all, a condition referred to as "silent" celiac disease. What's even more concerning is that the latter group, despite their lack of visible symptoms, can still suffer from the internal damage caused by the disease. In the broader picture, Celiac Disease is not just a gastrointestinal disorder. It is systemic, meaning it can affect other parts of your body. Unmanaged Celiac Disease can lead to a myriad of health problems, such as osteoporosis, infertility, nerve damage, and even certain types of cancer. This highlights the paramount significance of early detection and effective management of Celiac Disease, ensuring the prevention of its adverse long-term health effects. Another pivotal fact to underline is the genetic aspect of the disease. Celiac Disease tends to run in families, indicating a hereditary predisposition. This doesn't mean, though, that everyone inheriting the genes will develop the disease; environmental triggers also play a crucial role. In essence, understanding the basics of Celiac Disease underscores the rationale behind the vigilance for its symptoms and the urgency for its diagnosis. With this understanding, you can make informed decisions regarding at-home testing and subsequent treatment, if necessary.
Common Symptoms and Complications
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder where the ingestion of gluten leads to serious damage in the small intestine. Once triggered, celiac disease is a lifelong labeled disorder that affects both adults and children alike. Recognizing the common symptoms and complications associated with the disease is the first step to managing and potentially alleviating the pain inflicted. Typically, symptoms can be drastically diverse, fluctuating from digestive issues to stern headaches. One of the most common symptoms is diarrhea, often accompanied by stomach pain and bloating. These digestive symptoms can lead to substantial weight loss over time because your body isn't properly absorbing nutrients from the food you are eating. Others experience itchy, blistery skin rashes known as dermatitis herpetiformis, which can arise in conjunction with the other symptoms or completely on their own. The exhaustive list of possible symptoms also includes bone loss, joint pain, acid reflux, heartburn, and migraines. Alarmingly, some people might not have any symptoms but can still develop complications over time due to repeated autoimmune attacks on the small intestine. Speaking of complications, if not treated early or efficiently, celiac disease can lead to severe health issues. Malnutrition is a major concern, as the damaged small intestine is not able to absorb necessary nutrients (malabsorption). Over time, this can lead to a deficiency of nutrients like iron, calcium, folate, and vitamins B12, D, and K. Additionally, celiac disease has been linked to neurological conditions like seizures and cognitive impairment due to nutrient deficiencies. The constant inflammation and damaging of the small intestine also increase the risk of intestinal cancer over time. It becomes clear how early detection and lifestyle adjustments are crucial for individuals who have or might have celiac disease. Learning to recognize these symptoms and complications can make a significant difference in the overall health trajectory for many. It's important to note, factors such as family history, presence of other autoimmune disorders, or an existing diagnosis of Down Syndrome can increase your risk of developing celiac disease. Therefore, sensitivity towards your body's signals and regular check-ups are indispensable. Increasing awareness around this disorder is specifically crucial because an at-home test is available for celiac disease. It is a scientifically-validated test that screens for certain antibodies in your blood that are often elevated in people with celiac disease. Remember, early detection can prevent many future complications and furnish a better quality of life.
Celiac Disease vs Gluten Sensitivity
While both Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity involve the human body reacting negatively to the presence of gluten, the specific reactions and implications for the individual's health vary significantly. Celiac Disease is an autoimmune disorder, and when a person afflicted with this disease consumes gluten, their body misinterprets it as a threat and launches an immune reaction that primarily attacks the small intestine. The antibodies produced in response to gluten consumption damage the villi, which are small, finger-like projections lining the small intestine responsible for nutrient absorption. Continued damages to these villi can lead to malnutrition and a host of other health problems such as infertility, nerve damage, and seizures. On the other hand, Gluten Sensitivity—also known as non-celiac gluten sensitivity—does not involve an autoimmune attack on the small intestine. People with gluten sensitivity may experience symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and fatigue immediately after consuming gluten, but while these symptoms are extremely uncomfortable, they do not cause long-term damages to the intestines. It is significant to note that diagnosis of gluten sensitivity often occurs by the process of elimination—after ruling out celiac disease and wheat allergy. A precise understanding of these two conditions not only highlights the seriousness of Celiac Disease, but also ties into the need for an at-home testing. While immediate symptoms of gluten sensitivity are uncomfortable, the long-term effects of undiagnosed, and therefore unmanaged, celiac disease can be far more serious, necessitating a means of identifying the condition beyond symptom comparison. Therefore, learning to differentiate Celiac Disease from Gluten Sensitivity can help individuals make informed decisions about their health.
At-Home Testing for Celiac Disease
In the world of medical advancements, the possibility of at-home testing for Celiac disease is emerging as an enticing prospect, providing convenience and privacy to those in need. In this comprehensive overview, we will explore three key aspects of at-home testing for Celiac disease. To start, we will delve into an overview of the various at-home test kits currently available on the market, evaluating their effectiveness and ease of use. Next, we will guide you through the step-by-step procedure for carrying out these tests at home, ensuring you have all necessary information at your fingertips. Finally, we will help you understand the implications of your results, demystifying the process and offering insight on what to do next depending on the outcome. Such an understanding could be crucial to manage your health proactively and take timely steps if you identify a potential celiac disease risk. Now, let's begin our exploration with the various at-home test kits available, their features, pros, and cons, and how you can choose the right one for you.
Overview of Available At-Home Test Kits
With the recent advancements in medical technology, a wide array of at-home test kits are now readily available for consumers. These innovative tools offer an efficient and accessible way to monitor, diagnose, and manage various health conditions, including Celiac Disease. Fundamentally, celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder induced by the intake of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. A continuous and regular ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine, causing various symptoms, including diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, bloating, and anemia, among others. With at-home test kits, anyone suspected of having celiac disease can take proactive measures even from the comfort of their own homes. These kits provide a practical and non-invasive solution, perfect for individuals who prefer a DIY approach to health management or those who might find clinic visits inconvenient or anxiety-inducing. At-home celiac disease tests work by detecting antibodies produced by your body in response to gluten. The usual procedure involves a sample collection—typically a finger-prick blood sample—which is then sent back to a laboratory for analysis. Several tests are available from different companies, each with distinct features and benefits. Some tests may provide comprehensive antibody profiles, allowing for more accurate diagnosis, while others may offer quicker results. They all, however, aim to empower individuals to take control of their health, providing the crucial first step in managing a potentially life-long condition such as celiac disease. It is essential to remember that while these kits can give a good indication, they aren't substitutes for a medical diagnosis from a professional health care provider. False positives or negatives can occur, so any results indicating celiac disease should always be followed up with a trip to your doctor for a definitive diagnosis. Ultimately, the emergence of at-home test kits represents a significant shift in healthcare, bringing diagnostic capabilities directly into patient's hands. This promotes early detection, better management, and increased awareness of conditions like Celiac Disease, prioritizing public health and personal wellbeing.
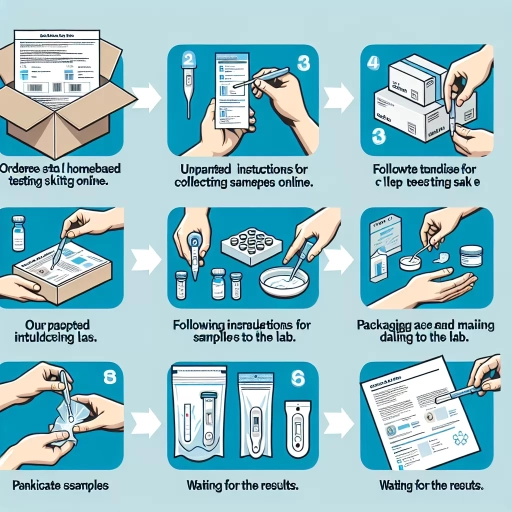
Procedure for Testing at Home
Testing for Celiac Disease at home has become increasingly convenient and accessible over the years. It's a rather straightforward process and should alleviate some of the stresses that come with determining if the disease is present. The subtleties within the procedure are crucial to ensure the veracity of the result, so an emphasis on understanding every step is imperative. To begin, you would order a Celiac Disease home testing kit from a reliable source. Once you receive your kit, it should contain a lancet for finger-pricking, a blood collection tube, a pre-paid envelope or package for sending the sample to the lab, and an instruction pamphlet. Before starting, read the instructions thoroughly to avoid any missteps or inaccuracies during the test. Ensure your hands are clean and warm, this aids in having a better blood flow for the testing. Now, to collect the blood sample, you would have to prick your finger with the provided lancet in the kit. It might be more comfortable to prick the side of your fingertip rather than the centre. Squeeze your finger gently to encourage a few good-sized drops of blood, then collect the blood in the collection tube up to the mark specified in the instruction pamphlet. Once the blood sample is collected, it should be stored correctly. Usually, the collection tube is sealed, placed in a biohazard bag, and then stored in a secure, cool place until you're ready to send it. Packaging and sending the sample according to the instructions will expediently get your sample to the laboratory for testing. While awaiting your results, be patient and continue with your current diet unless your doctor advises you otherwise. This is because changing diet can potentially affect the test results. At-home Celiac Tests are beneficial as they provide a private and convenient way to set your nerves at ease or take the first steps towards addressing a potential health issue. However, regardless of your results, consult with a healthcare professional to ensure a comprehensive understanding of your health and what steps to take thereafter. It is essential to keep in mind that these tests should not replace a full medical diagnosis, but they can offer insights and guide you on your next steps. Thus, at-home testing for celiac disease is a viable option for initial screenings, offering both convenience and veracity if steps are followed as directed. It is the first step in your journey to wellness, equipping you with knowledge and power over your wellbeing. The increasing popularity and acceptance of at-home testing kits make it easier than ever to take health into your own hands. From this perspective, the adage 'knowledge is power' truly makes sense.
How to Interpret the Test Results
Interpreting the results of an at-home test for Celiac disease does not have to be a daunting process. While the test can be a significant step towards understanding your health, the results should always be analyzed in conjunction with a medical professional's advice. If you find your test result is positive, it indicates the presence of certain antibodies typically associated with Celiac disease. But remember, the diagnosis is not confirmed yet, and it just signifies the need for further investigation by a healthcare provider. A negative test result, on the other hand, suggests the absence of these specific antibodies. Nonetheless, it doesn't entirely exclude the possibility of having Celiac disease, especially if you are already on a gluten-free diet or if the test was taken during an 'in-active' period of the disease. The condition might remain dormant and asymptomatic for a time, resulting in false negatives. The presence of uncertainty is why, irrespective of the results, individuals should always consult their healthcare professional. They are well-equipped to understand the subtleties and nuances involved. They may ask for additional testing, such as genetic tests or intestinal biopsies, which are deemed more reliable and conclusive. They can also consider your overall health, medical history, symptoms, and other factors in making a comprehensive analysis. Moreover, it's crucial not to alter your diet following the testing without the guidance of a medical expert. Abrupt dietary changes can interfere with future tests and possibly worsen the symptoms. So, while at-home testing for Celiac disease can be valuable for early detection, the results should ideally open a dialogue between you and your healthcare professional rather than be the sole determinant in diagnosing the disease. In conclusion, accurate interpretation is key when dealing with at-home testing results for Celiac disease. Always consult with a professional before making any significant health decisions, but use these kits as a tool to better understand your body, its reactions, and to spur on early conversations about the possible presence of Celiac disease.
Moving Forward After Diagnosis
Being diagnosed with Celiac Disease can surely be daunting, but it doesn't signal the end of the world. Rather, it grants a new beginning, an opportunity to create healthier habits and to prioritize your well-being. Moving forward after the diagnosis, there are three key areas of focus to ease this shift in your lifestyle - firstly, actively connecting with healthcare professionals, deploying a gluten-free diet, and finally, managing Celiac disease steadily in the long term. Each step will aid your progress and help you live a full, energetic life. The first, and perhaps one of the most important steps includes actively engaging with healthcare professionals. Physicians, dieticians, and therapists can provide useful knowledge, support, and encouragement, creating a sturdy foundation for your journey forward. By building strong relationships with these professionals, you establish a support network devoted to your health, which is crucial in the early stages after diagnosis. This active connection with healthcare professionals sets the ground for the following steps: beginning a gluten-free diet and learning long-term disease management techniques. The healthcare professionals are there to guide you every step of the way, ensuring your transition after diagnosis is as smooth and stress-free as possible.
Connecting with Healthcare Professionals
Connecting with Healthcare Professionals It is crucial to manage a celiac disease diagnosis effectively, and key to this process is establishing a well-navigated partnership with healthcare professionals. The importance of this connection is undeniable, as they play a pivotal role in the journey towards recovery and maintaining a healthier lifestyle. They are the storehouses of medical information, filled with years of experience and understanding, capable of guiding you through the maze of queries and concerns that often accompany this condition. Your healthcare team will provide essential clarifications on celiac disease, offering precise answers about how your body reacts to gluten, and insights on symptoms you might experience. More than just pivotal consultants, they aid in the interpretation of test results, simplifying complex medical jargon, and making the understanding of your own health more accessible. The professional advice extends beyond understanding your ailment, too. They help tailor the most suitable diet plan that meets your nutritional needs while avoiding gluten. Dietitians, in particular, are trained to develop personalized meal plans, guaranteeing that you neither miss out on taste nor nutritional viability. Furthermore, healthcare professionals can provide you with practical strategies to manage your gluten-free diet while outside of the comfort of your home. Whether it's navigating restaurant menus or managing awkward social settings, they can equip you with the right tools to handle these situations. This guidance, peppered with their deep understanding of celiac disease, ensures that you live a full life while also managing your health effectively. Emotional support is another important aspect of dealing with celiac disease. Physicians, therapists, and support groups can become dependable pillars of emotional strength. They can help parse through the anxiety, frustrations, and occasional loneliness that comes with such a diagnosis, facilitating overall mental well-being. Establishing a relationship with healthcare professionals is hence, not just about moving forward after a celiac disease diagnosis. It's about pacing forward with renewed knowledge, confidence and the reassurance that your health is in experienced hands. The collaboration isn't just beneficial; it's indispensable for leading a health-centric, gluten-free life. So, connect, consult, and walk forward hand-in-hand with these healthcare professionals, employing their expertise to your advantage to mitigate the impacts of celiac disease.
Starting a Gluten-Free Diet
Starting a gluten-free diet can seem daunting after your recent celiac disease diagnosis, but it's an essential step towards recovery and wellness. The complete exclusion of all gluten from your meal plan might feel restrictive or overwhelming; however, with a strategic approach and a positive perspective, you can turn this challenge into a springboard towards healthier eating habits. Firstly, acquiring a clear understanding of gluten and its sources is critical. Gluten is a group of proteins found in grains like wheat, barley, and rye. So, not only does bread and pasta need to be avoided, but also, processed foods often have hidden sources of gluten like in sauces, dressings, and seasonings. The next stride is refining your typical grocery list or diet with gluten-free alternatives - a conscious move to whole foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and gluten-free grains. Each new addition to your diet should be deliberate and thoughtful. Remember that 'gluten-free' doesn't always mean 'healthy', so veer away from processed gluten-free foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats. Cooking at home becomes the new norm on a gluten-free journey. It gives you control over your ingredients, ensuring gluten doesn't sneak into your meals. Expanding your culinary skills can become a surprising, enjoyable aspect of this lifestyle change. Be patient, knowing that it might take some time to adapt to the new diet fully. Foods that you didn't know you were sensitive to may reveal themselves once they are removed. New flavours, ingredients, and textures introduced into your diet may present novel culinary experiences. Lastly, share your journey. Many people have walked this path before and provide support, creative meal ideas, and tips to ease the process. Join gluten-free forums, follow gluten-friendly food bloggers, or engage with celiac disease support groups. Being part of a community can offer reassurance that you are not alone in this endeavour. With courage and consistent commitment, adjusting to a gluten-free diet becomes manageable over time. Not only will it eventually improve your celiac disease symptoms, but it presents an opportunity to redefine your relationship with food. Embrace it as a transition towards a healthier lifestyle rather than a restrictive hurdle. Remember, your health is vital and worth every effort.
Managing Celiac Disease in the Long Term
Celiac disease is a long-term condition that requires careful attention and management to avoid complications. Therefore, after receiving a positive diagnosis, one needs to look forward and begin the journey of managing Celiac Disease in the long term. The management of celiac disease requires an informed dietary overhaul primarily, given that the disease primarily affects the digestive system. Adherence to a strict gluten-free diet becomes the cornerstone of this long-term management strategy. However, this is not just about avoiding bread and pasta; gluten can also be found in seemingly safe foods like soups, sauces, and even some medications. As such, one needs to become an expert label-reader and vigilant food shopper, scrutinizing every product for potential gluten content. Moreover, long-term management of Celiac disease also depends on understanding the condition and regularly monitoring its progression. Medical appointments become a routine part of life. Regular check-ups will help monitor intestinal damage, nutritional deficiencies, and the possible onset of related conditions like osteoporosis, infertility, and other autoimmune diseases. The journey also includes paying attention to metal wellness as Celiac disease, like any long-term condition, can be emotionally challenging to manage. Consequently, measures such as joining a celiac support group or seeking counselling can provide an emotional haven and help to better manage the psychological effects of the disease. Additionally, reintroducing physical exercises into your routine can be beneficial for people managing celiac disease in the long term. Many a time, physical activities are sidelined due to this debilitating condition, but as the gluten-free diet aids with recovery and provides an energy boost, it's crucial to gradually return to an active lifestyle. This will not only help with weight management but also enhance overall mood and energy levels, which often take a beating due to celiac disease. Moving forward after a Celiac disease diagnosis is a transformative journey, one marked by dietary changes, lifestyle adjustments, and a new perspective on health. This journey is a testament to resilience and strength, where each day marks a step towards improved health and well-being, making the management of celiac disease a constant but rewarding progression in the long term.