How To Draw A Brain
Understanding the Basics of Brain Anatomy
An Introduction to Brain Structure
The human brain, often described as one of the most complex objects in the universe, is an intricate network of billions of nerve cells connected by trillions of synapses. It's the control center for everything we think, feel, and do, both consciously and subconsciously. To understand how to draw a brain accurately, we first need to familiarize ourselves with the structure of the brain. It's not as complex as it might initially appear - the brain can be broadly divided into specific regions, each of which carries out distinct functions.
Identifying Major Brain Parts
While the brain is made up of many different parts, there are a few key areas that can be readily identified and are essential for any drawing of the brain: the cerebral cortex, the cerebellum, and the brain stem. The cerebral cortex, which appears as a large, wrinkled structure at the top of the brain, is responsible for most of our high-level cognitive functions, including memory, attention, and thought. The cerebellum, located at the back of the brain, helps control voluntary movements like balance and coordination. The brainstem, connected to the spinal cord, controls essential involuntary functions like breathing and heart rate.
Understanding the Brain's Unique Appearance
The brain's appearance is as unique as its capabilities. It is made up of winding folds and grooves, called gyri and sulci, respectively. These give the brain its characteristic wrinkled look. Understanding the pattern and layout of these grooves can help in producing an accurate and detailed drawing.
Mastering the Art of Brain Drawing
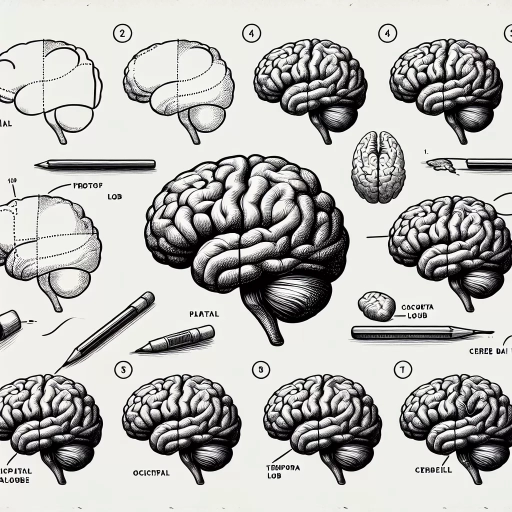
Sketching the Brain's Outline
The first step to drawing the brain is to create a rough outline. The overall shape of the brain is somewhat similar to a large oval but with a more intricate structure. The sketch should form the basic shape of the brain, including the bulging cerebral cortex, the smaller, spherical cerebellum and the protruding brain stem. Remember to keep the lines light in case any adjustments are necessary as you start to add details.
Adding Details to the Brain
The next step in drawing the human brain involves adding the intricate details. Start shading in the folds (gyri) and crevices (sulci) of the brain, keeping in mind the specificity of each section. The cerebral cortex has a convoluted, maze-like pattern, while the cerebellum has a more tree-like, or arborized appearance, called the 'arbor vitae'. The brain stem should be represented as a somewhat rectangular structure connected to the base of the cerebrum and cerebellum.
Perfecting Your Brain Drawing
Finally, you should refine your sketch, making sure to accurately represent the unique features of each part of the brain. Feel free to use references to ensure the accuracy of your drawing. This stage is also where you can work on the intricacies of shading and depth to give the brain a 3D appearance. Remember that the brain's appearance can vary greatly between individuals, so there is quite a bit of room for artistic interpretation. Keep practicing, adjusting, and refining, and in time, you'll master the art of drawing the human brain.
Digital Tools for Brain Drawing
Utilization of Digital Drawing Tools
Modern technology offers a variety of digital tools that can make the task of drawing the human brain easier and more accurate. Tools like digital styluses, tablets, and drawing software allow for a higher degree of precision and control, making them excellent options for both beginners and more experienced artists.
Drawing the Brain in 3D
With the aid of digital tools, we can go beyond a simple 2D representation of the brain to create a more realistic 3D model. Tools like Blender, 3DMax, or any software with 3D capabilities, let you rotate, zoom in and out, and see the brain from any angle. This can be particularly helpful when trying to grasp and draw the complex structure of the human brain.
The Role of Technology in Drawing and Understanding the Brain
Not only can digital tools make the task of drawing the brain easier, but technology also plays a crucial role in our understanding of the brain's structure and functions. For example, advanced imaging techniques like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provide extremely detailed views of the brain, providing valuable resources for both scientists and artists. Additionally, numerous digital resources, including online tutorials, courses, and image databases, can help guide anyone who wishes to draw or study the human brain.