How To Make Rubber
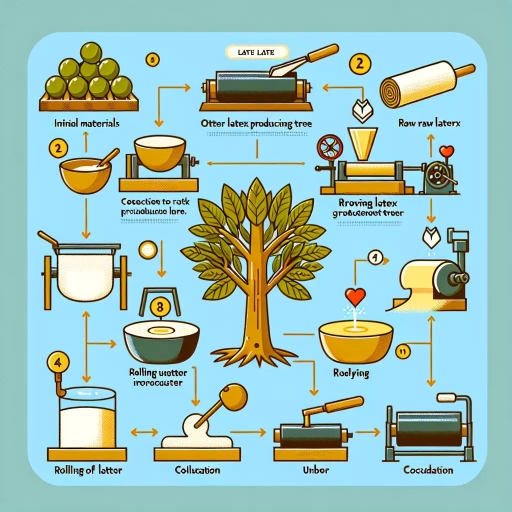
Here is the introduction paragraph: Rubber is a versatile and widely used material found in various products, from tires and gloves to medical devices and toys. However, have you ever wondered how rubber is made? The process of creating rubber involves several steps, from understanding the basics of rubber to preparing the necessary materials and equipment, and finally, the manufacturing process itself. To make rubber, it is essential to comprehend the fundamental properties and types of rubber, which will be discussed in the section "Understanding the Basics of Rubber." This knowledge will serve as a foundation for the subsequent steps, including preparing the required materials and equipment, and the actual manufacturing process. By grasping these concepts, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of how rubber is produced and appreciate the complexity involved in creating this essential material. With this foundation, we can delve into the world of rubber manufacturing, starting with the basics.
Understanding the Basics of Rubber
Rubber is a versatile and widely used material that has been a crucial component in various industries for centuries. Understanding the basics of rubber is essential to appreciate its significance and applications in our daily lives. From its unique properties to its diverse types and uses, there's a lot to explore about this fascinating material. In this article, we'll delve into the world of rubber, discussing its properties, types, and common applications. First, we'll examine the fundamental characteristics of rubber, including its elasticity, durability, and resistance to various environmental factors. By grasping what rubber is and its inherent properties, we can better understand its versatility and widespread adoption. Let's start by exploring the question, what is rubber and what makes it so unique?
What is Rubber and Its Properties
What is Rubber and Its Properties Rubber is a versatile and widely used material that is known for its unique properties. It is a polymer that is made up of long chains of molecules, which are cross-linked to create a three-dimensional network. This network gives rubber its elasticity, allowing it to stretch and deform without breaking. Rubber is also highly resistant to abrasion and wear, making it a popular choice for applications where durability is important. In addition to its physical properties, rubber is also resistant to many chemicals and can withstand extreme temperatures. There are two main types of rubber: natural rubber and synthetic rubber. Natural rubber is derived from the sap of the rubber tree, while synthetic rubber is made from petroleum-based materials. Both types of rubber have their own unique properties and are used in a variety of applications. Some of the key properties of rubber include its elasticity, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion and wear. It is also a good insulator and can be used to reduce vibration and noise. Rubber is used in a wide range of applications, including tires, belts, hoses, seals, and gaskets. It is also used in the production of adhesives, coatings, and other materials. Overall, rubber is a highly versatile material with a wide range of properties that make it an essential component in many industries.
Types of Rubber: Natural and Synthetic
Rubber is a versatile material that can be categorized into two main types: natural and synthetic. Natural rubber, also known as cis-1,4-polyisoprene, is derived from the sap of the rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). It is a biodegradable and renewable resource that has been used for centuries in various applications, including tires, gloves, and medical devices. Natural rubber is prized for its excellent elasticity, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion. On the other hand, synthetic rubber is man-made and produced from petroleum-based materials, such as styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and nitrile rubber (NBR). Synthetic rubber is more resistant to heat, oil, and chemicals than natural rubber, making it suitable for use in harsh environments, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries. There are also various types of synthetic rubber, including neoprene, butyl rubber, and ethylene-propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, each with its unique properties and applications. Understanding the differences between natural and synthetic rubber is crucial in selecting the right type of rubber for specific uses, ensuring optimal performance, and minimizing environmental impact.
Common Applications of Rubber
Rubber is a versatile material with a wide range of applications across various industries. One of the most common applications of rubber is in the automotive industry, where it is used to manufacture tires, belts, hoses, and seals. The unique properties of rubber, such as its elasticity, durability, and resistance to abrasion, make it an ideal material for these applications. In addition to the automotive industry, rubber is also widely used in the construction industry, where it is used to manufacture roofing materials, flooring, and insulation. Its water-resistant properties make it an excellent material for use in wet environments, such as bathrooms and kitchens. Rubber is also used in the manufacturing of sporting goods, such as basketballs, footballs, and tennis balls, due to its ability to absorb shock and provide a comfortable grip. Furthermore, rubber is used in the medical industry, where it is used to manufacture medical gloves, tubing, and other equipment. Its biocompatibility and resistance to chemicals make it an ideal material for use in medical applications. Other common applications of rubber include its use in the aerospace industry, where it is used to manufacture seals, gaskets, and other components, and in the consumer goods industry, where it is used to manufacture a wide range of products, such as toys, adhesives, and coatings. Overall, the unique properties of rubber make it a versatile material with a wide range of applications across various industries.
Preparing the Materials and Equipment
Preparing the materials and equipment is a crucial step in the rubber manufacturing process. To produce high-quality rubber products, it is essential to gather the right raw materials, select the appropriate equipment, and ensure safety precautions are in place. Gathering raw materials, such as rubber compounds and additives, is the first step in this process. This involves sourcing high-quality materials that meet the required specifications and standards. Selecting the right equipment, including mixers, molds, and vulcanizers, is also critical to ensure that the rubber is processed correctly. Additionally, ensuring safety precautions, such as wearing protective gear and providing adequate ventilation, is vital to prevent accidents and injuries. By carefully preparing the materials and equipment, manufacturers can ensure a smooth and efficient production process. In this article, we will explore the importance of gathering raw materials, starting with the selection of rubber compounds and additives.
Gathering Raw Materials: Rubber Compounds and Additives
The production of rubber compounds and additives requires the gathering of various raw materials. Natural rubber is obtained from the sap of the rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis), which is native to the Amazon rainforest. The sap, also known as latex, is collected through a process called tapping, where the bark of the tree is incised and the latex is allowed to flow out. Synthetic rubber, on the other hand, is produced from petroleum-based materials such as styrene and butadiene. These materials are derived from crude oil and natural gas through a process of refining and cracking. Other raw materials used in the production of rubber compounds and additives include carbon black, silica, and calcium carbonate, which are used as reinforcing fillers to improve the strength and durability of the rubber. Additional additives such as sulfur, zinc oxide, and stearic acid are also used to enhance the properties of the rubber, including its vulcanization, curing, and resistance to heat and chemicals. The quality and consistency of these raw materials are crucial in determining the final properties of the rubber compound, and therefore, it is essential to source them from reliable suppliers.
Selecting the Right Equipment: Mixers, Molds, and Vulcanizers
Here is the paragraphy: When it comes to selecting the right equipment for making rubber, it's essential to consider the specific needs of your project. Mixers are a crucial piece of equipment, as they help to combine and blend the rubber compound ingredients. There are several types of mixers available, including internal mixers, external mixers, and planetary mixers. Internal mixers are ideal for large-scale production, while external mixers are better suited for smaller batches. Planetary mixers are versatile and can be used for a variety of applications. Molds are another critical piece of equipment, as they shape the rubber into its desired form. There are various types of molds available, including compression molds, transfer molds, and injection molds. Compression molds are suitable for simple shapes, while transfer molds are better suited for complex geometries. Injection molds are ideal for high-volume production. Vulcanizers, also known as curing presses, are used to apply heat and pressure to the rubber compound, causing it to cross-link and cure. There are several types of vulcanizers available, including hydraulic, pneumatic, and electric models. Hydraulic vulcanizers are ideal for large-scale production, while pneumatic vulcanizers are better suited for smaller batches. Electric vulcanizers are versatile and can be used for a variety of applications. When selecting equipment, it's essential to consider factors such as the size and complexity of your project, the type of rubber compound being used, and the desired level of precision and accuracy. Additionally, it's crucial to ensure that the equipment is properly maintained and calibrated to ensure optimal performance and safety. By selecting the right equipment, you can ensure that your rubber-making process is efficient, effective, and produces high-quality results.
Ensuring Safety Precautions: Protective Gear and Ventilation
Ensuring safety precautions is a crucial step in the rubber-making process. To prevent injuries and exposure to hazardous materials, it is essential to wear protective gear and maintain proper ventilation. A pair of heat-resistant gloves, safety glasses, and a face mask should be worn at all times when handling chemicals and operating equipment. The gloves will protect your hands from burns and chemical splashes, while the safety glasses and face mask will shield your eyes and respiratory system from harmful fumes and particles. Additionally, a well-ventilated workspace is vital to prevent the accumulation of toxic gases and particles. Open windows, use exhaust fans, or install a ventilation system to ensure a safe and healthy working environment. By taking these precautions, you can minimize the risks associated with rubber production and ensure a successful and safe manufacturing process.
The Rubber Manufacturing Process
The rubber manufacturing process is a complex and multi-step procedure that involves transforming raw materials into a versatile and durable product. From tires and seals to gloves and medical devices, rubber is an essential component in various industries. The process begins with the creation of a customized rubber formula, which is achieved through compounding and mixing. This critical step sets the stage for the entire manufacturing process, as it determines the final product's properties and performance. The rubber mixture is then shaped and vulcanized to give it the desired form and strength. Finally, the finished product undergoes rigorous quality control measures to ensure it meets the required standards. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the rubber manufacturing process, starting with the crucial step of compounding and mixing, where the rubber formula is created.
Compounding and Mixing: Creating the Rubber Formula
Compounding and mixing are critical steps in the rubber manufacturing process. Compounding involves combining various ingredients, such as rubber polymers, fillers, plasticizers, and curatives, to create a unique rubber formula. The goal of compounding is to achieve the desired physical and chemical properties in the final product. The rubber formula is developed based on the intended application, performance requirements, and cost considerations. For example, a rubber compound for tire manufacturing would require a different formula than one for medical gloves. The compounding process typically involves a series of tests and iterations to ensure the formula meets the required specifications. Once the formula is finalized, the ingredients are mixed together in a specific order and ratio to create a uniform blend. The mixing process can be done using various methods, including internal mixing, where the ingredients are mixed together in a large batch, or continuous mixing, where the ingredients are fed into a mixer in a continuous stream. The mixing process is critical to ensure that the ingredients are evenly distributed and that the final product has consistent properties. The mixed compound is then processed into a form that can be used in the manufacturing process, such as a sheet, pellet, or powder. The quality of the compound and the mixing process can significantly impact the final product's performance, durability, and safety. Therefore, it is essential to carefully control the compounding and mixing processes to ensure that the rubber formula meets the required specifications and performance standards. By combining the right ingredients in the right proportions and mixing them correctly, manufacturers can create a wide range of rubber products with unique properties and applications.
Shaping and Vulcanizing: Transforming the Rubber Mixture
The rubber manufacturing process involves several stages, from compounding to vulcanization. After the rubber mixture is prepared, it undergoes a process called shaping, where the mixture is transformed into the desired form. This can be done through various methods, including extrusion, molding, and calendaring. Extrusion involves forcing the rubber mixture through a die to create a specific shape, while molding involves pouring the mixture into a mold and allowing it to cure. Calendaring, on the other hand, involves passing the mixture through a series of rollers to create a sheet or film. Once the rubber mixture has been shaped, it is then vulcanized, a process that involves heating the rubber under pressure to cross-link the molecules and create a strong and durable material. Vulcanization can be done through various methods, including compression molding, transfer molding, and injection molding. The vulcanization process can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours, depending on the type of rubber and the desired properties. The resulting vulcanized rubber is then removed from the mold and undergoes additional processing, such as cutting, grinding, and finishing, to create the final product. Throughout the shaping and vulcanizing process, quality control measures are taken to ensure that the rubber meets the required specifications and standards. This includes testing for properties such as tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to heat and chemicals. By carefully controlling the shaping and vulcanizing process, manufacturers can produce high-quality rubber products that meet the needs of various industries, from automotive to medical.
Finishing and Quality Control: Inspecting the Final Product
Here is the paragraphy: Finishing and quality control are the final stages of the rubber manufacturing process. After the rubber product has been molded, cured, and removed from the mold, it undergoes a series of inspections and tests to ensure it meets the required standards. The product is visually inspected for any defects, such as cracks, bubbles, or uneven surfaces. It is also checked for its dimensions, weight, and color to ensure it conforms to the specifications. Additionally, the product may undergo various tests, such as tensile strength, hardness, and abrasion resistance, to ensure it can withstand the intended use. The product may also be subjected to environmental testing, such as exposure to extreme temperatures, chemicals, or UV light, to ensure it can withstand the conditions it will be exposed to. Any products that fail to meet the required standards are removed from the production line and recycled or scrapped. The finished products are then packaged and prepared for shipping to customers. Throughout the finishing and quality control process, manufacturers may use various tools and equipment, such as calipers, micrometers, and spectrophotometers, to ensure accuracy and precision. By implementing a rigorous quality control process, manufacturers can ensure that their rubber products meet the required standards and are safe for use.