$33 An Hour Is How Much A Year
 Understanding the nuances of salary conversion can be critical to getting a real sense of your income. In this illuminating article, we delve deeper into the underlying dynamics of the question: how much is $33 per hour in a year? Embarking on this monetary journey, we'll first navigate the broader waters of converting salaries from hourly to yearly figures, providing clarity on the calculations involved. With a $33 hourly wage as our point of reference, we're going to scrutinize the details of this specific rate, including its value in terms of overtime and periodic raises. Lastly, we'll put the spotlight on comprehensive comparisons between a $33 hourly wage and national averages. By dissecting these pivotal factors, we hope to unravel the financial implications of earning $33 an hour and provide a benchmark for evaluating job offers. Let's set sail by Understanding the Salary Conversion: From Hour to Year, for a more hands-on perspective.
Understanding the nuances of salary conversion can be critical to getting a real sense of your income. In this illuminating article, we delve deeper into the underlying dynamics of the question: how much is $33 per hour in a year? Embarking on this monetary journey, we'll first navigate the broader waters of converting salaries from hourly to yearly figures, providing clarity on the calculations involved. With a $33 hourly wage as our point of reference, we're going to scrutinize the details of this specific rate, including its value in terms of overtime and periodic raises. Lastly, we'll put the spotlight on comprehensive comparisons between a $33 hourly wage and national averages. By dissecting these pivotal factors, we hope to unravel the financial implications of earning $33 an hour and provide a benchmark for evaluating job offers. Let's set sail by Understanding the Salary Conversion: From Hour to Year, for a more hands-on perspective.
Understanding the Salary Conversion: From Hour to Year
Understanding the salary conversion from hourly to yearly is essential for anyone seeking a clear picture of their financial status. This article simplifies the complexities of this calculation, unfolding the seemingly puzzling question of how a myriad of hours turns into an annual wage. Primarily, we will underscore the significance of being knowledgeable about your annual income, demystifying the arithmetic that connects an hour's wage to yearly earnings. Next, we will untangle the puzzle that is salary conversion, providing a step-by-step guide on how you can calculate your yearly salary based on your hourly wage. Last but not least, we'll delve into the key variables that can affect this conversion, from overtime to varying work weeks. As we transition to our first point, there's a common query that echoes in many minds - why is it so important to know your annual salary? Let's delve into that intricate discussion.
The Importance of Knowing Your Annual Salary
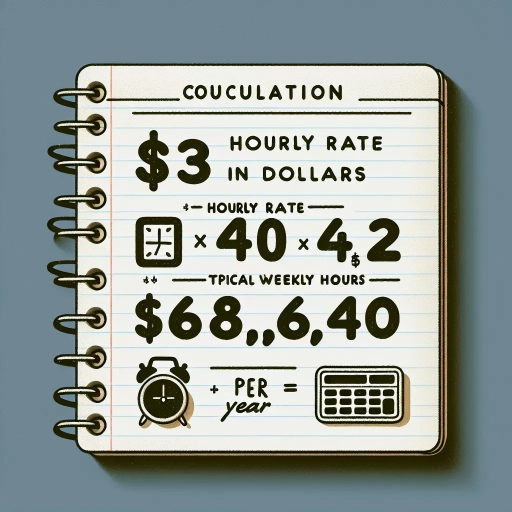
Knowing your annual salary is important for a multitude of reasons and provides a comprehensive, tangible breakdown of your earning potential. An annual salary offers deeper insights into your financial picture than hourly wages. It helps in long-term financial planning, giving you a clearer path for managing your monthly expenses, saving for future goals, or investing purposefully. Understanding the conversion of your hourly wage to an annual salary is not only beneficial, but critical. For instance, if you're making $33 an hour, you may wonder how much it equates to per year. Typically, the calculation is done based on the assumption that a full-time employee works roughly 2,080 hours per year, considering around 40 hours per week. Based on this premise, an hourly wage of $33 would convert to an annual income of around $68,640 before tax and deductions. Knowing your annual salary, therefore, allows you to budget better and generally feel more secure about your income. It also allows you to negotiate better when you are discussing salary with current or potential employers. Moreover, it becomes relatively easier to compare different job offers, giving you the power to make informed decisions regarding your professional future. Understanding your annual salary also provides an enhanced perspective about your professional worth. Comparing your annual salary with the competitive pay scales in the industry allows you to identify where you stand in the job market and whether you are being adequately compensated for your skills and experience. Financial stability also plays a key role in personal satisfaction and mental well-being. Knowing your annual salary and thereby, having a clear understanding of your financial capabilities, drives financial independence, providing you with the freedom to make autonomous decisions and the sense of self-confidence that comes with it. In conclusion, knowing your annual salary extracted from your hourly wage gives you a more robust understanding of where you stand financially. This involves not just evaluating the present but also effectively planning for the future. It equips you to handle financial hurdles, reach financial goals and ultimately leads you towards a financially secure life. So if someone asks, "33 an hour is how much a year?", you'll know how to make the conversion and grasp the value of the underlying information.
Decoding the Puzzle: How an Hourly Wage Translates to an Yearly Salary
Decoding the puzzle: How an hourly wage translates to an annual salary can often seem like a convoluted conundrum. The calculation is more than just multiplying hourly pay by the standard working hours of a year. There are several factors that are vital to consider for an accurate extrapolation. These factors include federal and state taxes, healthcare costs, retirement contributions, and bonuses, which all greatly affect the conversion of hourly to annual income. The standard method for translating an hourly wage to a yearly salary involves multiplying your hourly pay by the hours worked per week, then multiplying that total by 52, which represents the number of weeks in a year. For instance, if you earn $33 an hour and work 40 hours a week, your annual pre-tax earnings would approximate to $68,640. This figure, though, is pre-tax and does not include other employment benefits and potential costs. Federal and state taxes subtract a significant portion from your salary. For example, someone in the 22% tax bracket would see a significant reduction in their take-home pay. This makes the process of translation from hourly to yearly wage a bit more complex as one has to consider tax brackets, deductions, and credits. Healthcare costs and retirement contributions are other crucial factors to consider. Depending on your employer or the state you reside in, a percentage of your salary might go towards healthcare and retirement plans. Offerings like these are substantial components of an employee's overall compensation package. Bonuses also play into the equation, especially when it comes to an annual salary. Many employers offer performance bonuses, end-of-year bonuses, or sales commission, which can dramatically escalate your annual income. Understanding the salary conversion from hour to year, crucially involves understanding these elements that affect the transition from an hourly wage to an annual salary. The decoding of this puzzle reveals the importance of having a comprehensive view of one's hourly wage and the financial implications it holds. A seemingly simple numeric conversion unveils a multi-faceted financial picture that provides a holistic view of an individual’s entire compensation package, including the money you take home, your healthcare benefits, retirement savings and bonuses. Therefore, considering all these factors is integral to accurately understanding the salary conversion from hour to year.
Key Factors Affecting the Conversion
Key factors affecting the conversion of salary from an hourly rate to a year's earnings require a robust understanding, as they greatly impact one's total compensation. The principal element in this conversion is the number of hours worked per week. Typically, a full-time working week comprises 40 hours, yet this can fluctuate, especially in roles demanding overtime or with fluctuating schedule needs. Beyond the basic calculation of multiplying the hourly wage by the number of hours worked, several other elements factor into the equation. These include the number of workdays in a year and the possible variations such as working on weekends, holidays, or choosing to take unpaid time off. Moreover, the frequency of paid breaks during one's workday can impact the yearly estimate. If these breaks are deducted from the 40 hours, one would see a different annual figure than if their breaks were paid. Similarly, the existence of bonus hours or penalty rates can also significantly affect the annual income. In addition, the individual's tax status, including their 'tax-free allowance', is a crucial factor in the calculation of take-home salary from hourly rates. This usually involves considering whether the individual is an employee or a contractor, their marital status, and possible eligibility for adjustments and deductions. Lastly, the presence of benefits like health insurance, retirement contributions, performance bonuses, and other forms of compensation must also be accounted for. These elements, often overlooked in a simple hour-to-year conversion, can add significant value to an annual package. Understanding these key factors is crucial when converting a hourly rate to an annual salary, providing a comprehensive income overview and enabling more informed financial planning and decision-making. It's important to remember that the annual salary figure yielded from an hourly rate is an approximate, not an absolute – a reflection of potential earnings rather than a guaranteed sum. Navigating the complexities of wage conversion can be complex, yet when done right, promotes an optimal understanding of one's earning potential.
A Closer Look at an Hourly Wage of $33 Per Hour
As you’ll discover, earning an hourly wage of $33 is not only noteworthy, but it can also open the door to new financial possibilities and security. This multifaceted analysis will lead you through three salient concepts related to this salary range, each designed to help you understand and navigate the monetary landscape. First, we will explore various careers that offer an enticing $33 per hour wage, setting the foundation for your exploration into professions that can provide this advantageous salary. Following this, the focus will shift towards crafting a monthly and yearly budget with a $33 per hour salary. This segment is integral for understanding the dynamics of financial planning associated with this income bracket. Lastly, an in-depth look at the impact of taxes and benefits on your wage will present an essential reality check and guide you towards making informed decisions. Every salary has its pros and cons, its perks and deductions, and understanding these particulars can help you leverage your earnings in the best possible way. Now, let's delve deeper by turning our attention to careers that offer an hourly wage of $33, an excellent starting point for our journey to financial acumen.
Careers That Offer an Hourly Wage of $33
An hourly wage of $33 may sound quite appealing, as it equates to $68,640 per year based on a standard full-time employment. Let's delve deeper into different careers that offer this lucrative wage. Predominantly seen in the healthcare sector, occupations such as registered nurses, clinical laboratory technologists, and diagnostic medical sonographers command this wage tier. Specialized skills and education in medical technology and nursing put these careers into the realm of high-paying jobs. Registered nurses not only tend to patients but also provide critical insight into their health conditions, whereas medical sonographers use special imaging equipment to create images or to conduct tests that assist physicians in diagnosing various ailments. Stepping outside healthcare, we encounter mid-level industries, notably project management roles in various sectors. Handsome salaries are accorded to project managers as their role is pivotal in coordinating tasks, managing teams, and optimizing strategies to ensure project success. Another thriving field offering around $33 per hour is the realm of information technology. Database administrators ensure the secure collection, storage, and retrieval of data, a task of growing importance in the era of big data and digital information. Industries such as aerospace, mechanical, and civil engineering aren't left out either. While entry-level positions in these fields may start with a lower income bracket, with significant experience, professionals can expect to draw an hourly wage close to $33. In essence, roles that offer an hourly wage of $33 are often demanding jobs requiring specialized skills, education, and experience. Each possesses a unique set of challenges and responsibilities – from healthcare to project management to IT to engineering. Optimizing these skills and expanding on these avenues can help pave the path towards a rewarding career that offers both financial satisfaction and professional fulfillment.
Creating a Monthly and Yearly Budget with a $33 Per Hour Salary
Creating a monthly and yearly budget with a $33 per hour salary is an empowering endeavor that fosters financial independence and security. This journey begins by understanding your net income. At $33 per hour, assuming a 40-hour work week, your gross annual income comes out to $68,640. With standard tax deductions, the net income could reduce to around $52,000 per year. This equates to around $4300 per month, providing a foundation for your budget formation. Crafting a monthly budget necessitates consideration of your fixed and variable expenses. Fixed expenses, which may include rent or mortgage, utilities, insurances, and other recurring payments, are often non-negotiable. However, variable expenses like groceries, clothing, entertainment, and ad-hoc privileges offer a level of flexibility. This is where strategic planning can make a significant impact on wealth accumulation and financial stability. Creating a yearly budget greatly mirrors the monthly process, although it incorporates annual commitments and long-term financial goals. Be mindful about yearly expenses such as insurance premiums, car maintenance, and home repairs. Accounting for these once-a-year expenditures helps to prevent unforeseen financial stressors. Implementing a conservative rule-of-thumb, like the 50/30/20 budgeting method, can make this task more manageable. This principle suggests that 50% of your net income should be allocated towards necessities, 30% towards wants, and the remaining 20% towards savings. So, on a $52,000 net income, $26,000 would be for essentials, $15,600 for personal pleasures, and $10,400 towards elevating your financial future. Keeping track of your income and spending habits with these considerations can offer a clear perspective on your financial standing. It enables you to make informed decisions about spending, saving, and investing. Your $33 per hour wage does not only promise a comfortable lifestyle but also cultivates a pathway towards a secure financial future when managed well. A well-planned budget serves as a financial compass, guiding you towards sustainable wealth and prosperity.
Understanding the Impact of Taxes and Benefits on Your $33 Per Hour Wage
Understanding the impact of taxes and benefits on a $33 per hour wage is crucial in assessing the overall financial health and outlook of an individual earning such an income. Taxes and benefits are usually a significant part of paycheck calculations and have a dramatic impact on the net earning of an employee. Working full-time with a wage rate of $33 per hour, the gross annual income before taxes is roughly $68,640, assuming a standard 40-hour work week throughout the year without any vacations or holidays. However, this figure doesn't account for taxes or the value of benefits, which can significantly vary based on a variety of factors. Firstly, there's the federal income tax. The U.S tax system operates on a progressive scale, with the rate increasing as an individual's income elevates. Currently, someone earning $68,640, if filing as a single tax filer, would fall into the 22% federal tax bracket. However, it's critical to understand that this rate only applies to the income above the previous tax bracket's maximum, which essentially means the effective tax rate would be lower. After deductions for federal and possibly state and local taxes, Social Security, and Medicare, the remaining money typically results in an amount quite less than the originally assumed annual gross pay. Net income, or take-home pay, after these deductions, can provide a more realistic perspective of financial capabilities. Moreover, one must also consider the value of employment benefits in the wage analysis. Benefits like health insurance premium contributions, retirement plan matches, tuition assistance, and others can vastly improve the value of a $33 per hour pay rate. For instance, an employer-paid healthcare plan can translate into thousands of dollars per year, reducing out-of-pocket healthcare costs for the employee. In conclusion, comprehending the impact of taxes and benefits on a $33 per hour wage necessitates a deeper analysis of the comprehensive tax structure, deduction impacts, and the quantifiable value of benefits. A simple gross income calculation doesn't offer a complete picture of the actual financial status of an individual. Hence, to truly understand earnings, it's fundamental to account for these critical factors.
Comparing the $33 an Hour Wage Against National Averages
In the grand pursuit of measuring income stability and earning potential, an intriguing question arises – How does a $33 per hour wage fare in relation to the nation's financial barometer? To analyze this critically, we shall delve into three core areas. First, we will place that wage against the national minimum, a sector synonymous with the foundational survival income for American workers. Unpacking this comparison will yield insights into the palpable differences in lifestyle and financial security. Then, we'll assess how a $33 an hour paycheck stacks against the average American wage, providing a direct lens into relative earning power and societal standing. Finally, we'll explore the real-life implications of living on a $33 per hour wage, thus painting a vivid picture of the daily realities, challenges, and opportunities. Each segment imbues us with a piece of a larger narrative, starting with an in-depth comparison of the $33 per hour wage to the U.S. minimum wage. Hence, let's embark on this enlightening financial journey.
Comparing $33 Per Hour to the Minimum Wage
When comparing a $33 an hour wage to the minimum wage, a significant disparity emerges that's worth investigating further. The federal minimum wage in the United States is currently set at $7.25 per hour, with some states allowing for a higher minimum wage. This figure, however, pales in comparison to a wage of $33 per hour, which translates to an annual salary of about $68,640, assuming a 40-hour work week without vacation. For an individual earning the current federal minimum wage and assuming a full-time employment, the annual salary would be just over $15,080 before taxes - a staggering $53,560 less than what a person making $33 per hour earns. This gap widens even further when cost-of-living adjustments are factored in. Even when compared to the median wages in the US, which according to Bureau of Labor Statistics was $20.17 per hour in 2020, the $33 per hour wage stands as a strong earning potential. This person outperforms over half of the working population in terms of hourly wage. However, this comparison isn't to undermine the value of minimum wage jobs or those earning around the national average. It's rather an illumination of the potential earning spectrum within the modern employment landscape. The $33 per hour wage symbolizes a level of financial stability and upward mobility that unfortunately, the minimum wage does not currently offer. Moreover, when contrasting these wage rates, it's crucial to consider the nature of jobs that come with a $33 per hour wage. These positions often require a higher level of education or specialized skills, something not typically expected from minimum wage positions. The gap highlights the critical role of education and skill-building in achieving financial success and stability. Conclusively, understanding wage disparities such as these can encourage discussions about income inequality, the value of skills and education, and the need for considerations in policy-making to elevate the earnings of those on the lower end of wage spectrum.
How $33 an Hour Stacks Up Against the Average American Wage
At $33 an hour, an individual earns considerably more than the average American does in an hourly wage. According to the U.S Bureau of Labor Statistics, as of Q4 in 2020, the median average wage in America is $25.72 per hour. By rough comparison, someone earning $33 per hour is making about 28.4% more than the median wage earner. And when you extrapolate that $33 wage into an annual salary presuming full-time work, it totals to a gross income of roughly $68,640, a significant step up from nation's median salary which rests at around $53,490. Delving deeper into this comparison, the amount one earns per hour is highly dependent on factors such as location, industry, and level of education. For instance, highly populated states with a high cost of living like New York, California, and Massachusetts typically report higher average wages, and industries like Tech, Medicine, or Law often exceed the average hourly wage. Therefore, a $33 per hour wage might not stretch as far in these areas or occupations as it could in regions with lower living costs or in industries with lower average wages. Despite these regional and industrial differences, it's important to note that a $33 per hour wage far exceeds the federal minimum wage of $7.25, and also outpaces the highest state-level minimum wage of $14 in California and Washington D.C. In fact, at $33 an hour, even part-time work could potentially earn more than a full-time job at minimum wage. In conclusion, a $33 an hour wage, which equates to an approximate yearly income of $68,640 for full-time work, places a worker well above the national averages. This demonstration not only reveals the earning potential of higher-paying occupations, but it also underscores the vast disparities that can exist within the U.S. wage structure.
Exploring the Consequences of Living with a $33 Per Hour Wage
Living with a $33 per hour wage significantly impacts an individual's financial standing, thereby affecting the quality of life, investment potential, and social status. Usually considered a substantial hourly wage, earnings of $33 an hour translate to roughly a gross annual income of $68,640, assuming a standard 40-hour work week throughout the year. This places such earners notably above the national median wage, which is approximately $19.33 per hour or $40,198 a year according to data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics in 2020. This signifies a significant disparity. Beyond the mere numeric difference, this wage gap implies various consequences for living standards and financial security. For individuals earning $33 an hour, there are unique benefits and challenges. First, these individuals potentially enjoy an enhanced standard of living. They may afford larger homes in safer neighborhoods, healthy and diverse foods, high-quality healthcare, and personal luxuries. In addition, this wage also opens up opportunities for investment, further enabling wealth accumulation. However, a $33 per-hour wage is not without implications. It incurs a higher tax burden compared to lower income earners, thereby reducing net income. Plus, a stronger financial standing may impose an unintentional pressure to maintain certain lifestyle standards, which could potentially lead to excessive spending and less savings. In conclusion, living with a $33 per hour wage leads to a noticeably different lifestyle compared to the national average. While a higher wage brings apparent benefits, like improved living standards and greater investment opportunities, it also comes with higher tax liabilities and potential lifestyle inflation.