How To Propagate Zz Plant
Understanding ZZ Plant Propagation
The Basics of ZZ Plant Propagation
The ZZ plant, also known as Zamioculcas zamiifolia, is a popular houseplant native to East Africa. It's admired for its hardy nature and its striking, shiny foliage. Propagation of the ZZ plant is a relatively simple process that requires a few key steps. The most common methods include division, leaf cuttings, and stem cuttings. Understanding the process of propagation goes beyond just copying the plant; it involves nurturing the cuttings or divisions until they establish into a new plant. This understanding is crucial in successfully yielding a healthy, thriving ZZ plant.
Methods of ZZ Plant Propagation
There are various methods to propagate a ZZ plant, each with its unique techniques and success rates. Division is arguably the most straightforward method where the root ball of a mature plant is divided into several parts, and each part, which already has some roots, is planted separately. Leaf cuttings are another method in which a leaf is cut from the plant, allowed to dry for a day or so, and then partially buried in moist, well-draining soil. Stem cuttings involve cutting a stem from the parent plant and placing it in water or soil to initiate root development. Each method has its merits, and the choice ultimately depends on the plant's health and the gardener's preference.
Optimal Conditions for ZZ Plant Propagation
The ZZ plant is renowned for its resilience, but it still requires certain conditions for successful propagation. These include optimum temperature, adequate light, the right soil mix, and appropriate water level. ZZ plants do well in indoor temperatures of around 65 to 79 degrees Fahrenheit and need bright, indirect light. While they can tolerate low light conditions, growth may be slower. The soil mix should be well-draining to prevent waterlogging, as ZZ plants are susceptible to root rot. Lastly, while ZZ plants are drought-tolerant, they require watering whenever the soil has dried out during the propagation process.
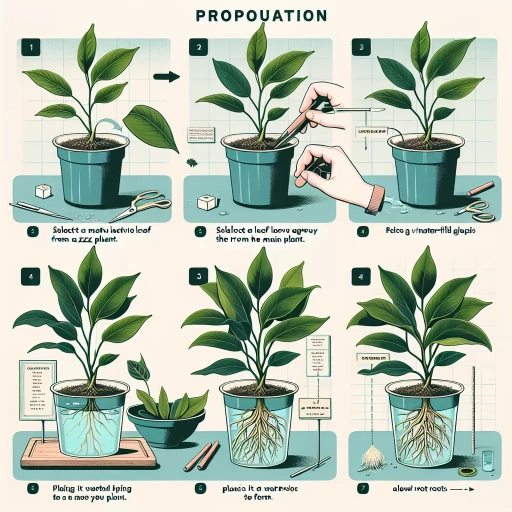
Step-by-Step Guide to ZZ Plant Propagation
Propagating ZZ Plant by Division
Division is the quickest way to propagate a ZZ plant as it already involves root sections. To do this, you'll first need to remove the plant from its pot gently. Shake off the soil to expose the roots and use a sharp, sterile knife to divide the root ball into sections, each with at least two or three stems. These sections can be planted in individual pots filled with fresh, well-draining soil. Water each newly potted plant thoroughly and place them in a warm spot that gets bright but indirect light. This method typically has a high success rate as the divisions already have roots.
Propagating ZZ Plant by Leaf Cuttings
Propagating a ZZ plant with leaf cuttings takes longer but is still relatively easy. You need to select a healthy, mature leaf and cut it off at the base of the stem. Allow the cutting to dry for a day or two until a film forms over the cut area. Plant the leaf cutting in a pot with moist, well-draining soil, ensuring that about half of the leaf is below the soil surface. Place the pot in a warm, well-lit place and wait for a few weeks until a new stem forms. This method may require patience, but it's a straightforward way to achieve plant propagation on a smaller scale.
Propagating ZZ Plant by Stem Cuttings
For stem cuttings, choose a healthy stem of a mature plant and cut from the base with a sharp, sterile tool. Allow the cutting to dry for a day or two before placing in water or planting it in well-draining soil. If using the water propagation method, make sure only the bottom part of the stem is submerged in water. Replace the water every week or so and transfer the cutting to a pot with soil once the roots develop. Stem cuttings propagate more quickly than leaf cuttings, usually within a few weeks, making it an alternative for those who prefer a quicker propagation method.
Tips and Warnings for ZZ Plant Propagation
Be Patient and Persistent
Propagation of the ZZ plant isn't always an overnight success. It takes time, whether you're propagating by division, leaf cuttings, or stem cuttings. Patience is fundamental since the plant can take several weeks to a few months to develop new growth. But the rewards are worth the wait. In addition to patience, persistence is key. Not every cutting or division may be successful, so don't be discouraged if your first few attempts fail. Persistence and observing proper horticultural practices will significantly increase the chances of success.
Ensure Optimal Conditions
As resilient as the ZZ plant is, it still requires an environment with the right conditions for propagation. Bright, indirect sunlight, warm temperatures, and well-draining soil mix are crucial elements that can't be compromised. Moreover, establishing a proper watering routine is fundamental since both over-watering and under-watering can impair the plant's growth. For successful propagation, it's critical to understand these needs and provide the appropriate care.
Beware of ZZ Plant's Toxicity
One important warning about the ZZ plant is its toxicity. All parts of the plant are toxic if ingested, and can also cause skin irritation in some people. Therefore, it's recommended to wear gloves while handling the plant and to wash your hands thoroughly afterwards. Keep the plant out of reach from children and pets to ensure safety. Despite its toxicity, the ZZ plant is generally safe to grow in the home if caution is exercised.