How Does A Printer Work
Here is the introduction paragraph: The world of printing has come a long way since the invention of the first printing press. Today, printers are an essential tool in our daily lives, allowing us to produce high-quality documents, images, and other materials with ease. But have you ever wondered how a printer actually works? From the basics of printer technology to the advanced features and modern printing capabilities, there's a lot to explore. In this article, we'll delve into the inner workings of a printer, starting with the fundamentals of printer technology. We'll examine the printing process, from digital to physical, and explore the advanced features that make modern printing possible. By understanding how a printer works, you'll gain a new appreciation for the technology that brings your digital creations to life. So, let's start by understanding the basics of printer technology. Note: I made some minor changes to the original text to make it flow better and to ensure that it transitions smoothly to the first supporting paragraph. Let me know if you'd like me to make any further changes!
Understanding the Basics of Printer Technology
Here is the introduction paragraph: In today's digital age, printing technology has become an essential part of our daily lives, from printing documents and photos to creating 3D models and prototypes. The evolution of printing technology has been remarkable, transforming from traditional methods to modern digital printing. To fully appreciate the capabilities of printers, it's essential to understand the basics of printer technology. This includes exploring the history of printing, from its humble beginnings to the current state-of-the-art technology. Additionally, knowing the different types of printers and their functions can help individuals choose the right printer for their needs. Furthermore, understanding the key components of a printer, such as inkjet or laser technology, can provide insight into how printers work and how to troubleshoot common issues. By understanding the basics of printer technology, individuals can unlock the full potential of their printers and take advantage of the many benefits they offer. Note: I made some minor changes to the original text to make it flow better and to ensure that it transitions smoothly to the three supporting paragraphs. Let me know if you'd like me to make any further changes!
The Evolution of Printing Technology
. The evolution of printing technology has been a remarkable journey, transforming the way we produce and disseminate information. From the early days of hand-copied manuscripts to the high-speed digital printers of today, printing technology has undergone significant advancements. The first major breakthrough came with the invention of the movable-type printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century, which enabled mass production of printed materials. This was followed by the development of lithography in the 18th century, which allowed for the printing of images and text on a large scale. The 20th century saw the introduction of offset printing, which further increased printing speeds and reduced costs. The advent of digital printing in the 1960s revolutionized the industry, enabling the production of high-quality prints with unprecedented speed and accuracy. Modern printing technology has continued to evolve, with the development of inkjet and laser printers, 3D printing, and digital press technologies. Today, printing technology plays a vital role in various industries, including publishing, advertising, and packaging, and continues to shape the way we communicate and access information. As printing technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative and efficient solutions to emerge, further transforming the way we live and work. Understanding the basics of printer technology is essential to appreciating the complexity and sophistication of modern printing systems, and how they have transformed the way we produce and disseminate information.
Types of Printers and Their Functions
. There are several types of printers, each with its unique functions and characteristics. Inkjet printers are the most common type, using a combination of ink and water to produce high-quality text and images. They are ideal for home use, printing documents, and photos. Laser printers, on the other hand, use a laser beam to produce high-quality text and images, making them suitable for high-volume printing, such as in offices and commercial settings. Dot matrix printers use a print head that moves back and forth, striking an ink ribbon against the paper to create characters, and are often used for printing multi-part forms and documents. 3D printers use melted plastic to create three-dimensional objects, layer by layer, and are commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. Thermal printers use heat to produce images on special heat-sensitive paper, and are often used for printing labels, receipts, and barcodes. Solid ink printers use a solid ink stick that is melted and applied to the paper, producing vibrant colors and are often used for printing graphics and images. Line printers use a print head that moves horizontally, printing a line of text at a time, and are often used for printing large volumes of text, such as in data centers and mainframe environments. Each type of printer has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of printer depends on the specific printing needs and requirements. Understanding the different types of printers and their functions is essential for selecting the right printer for a particular task or application.
Key Components of a Printer
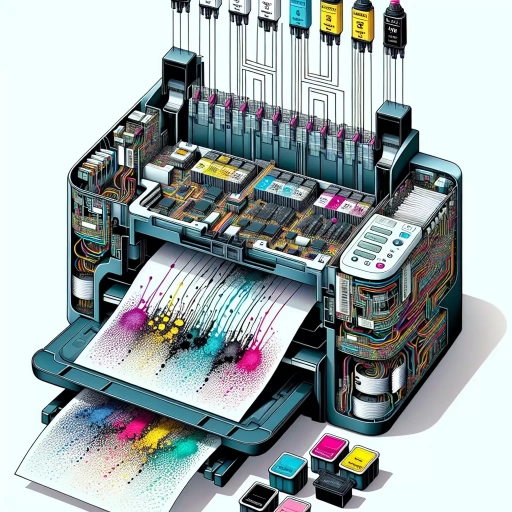
. A printer's functionality relies on several key components working in harmony. At the heart of the printer lies the print head, which is responsible for applying ink or toner onto the paper. The print head is typically made up of a series of tiny nozzles that spray ink or toner droplets onto the paper, creating the desired image. The print head is usually mounted on a carriage that moves back and forth across the paper, allowing for precise control over the printing process. Another crucial component is the paper feed system, which is responsible for feeding paper into the printer and aligning it properly for printing. This system typically consists of a paper tray, a paper feed roller, and a paper sensor that detects the paper's presence and orientation. The printer's control system, which includes the printer's CPU, memory, and firmware, plays a vital role in managing the printing process. It receives print jobs from the computer, interprets the print data, and sends instructions to the print head and other components to produce the desired output. Additionally, the printer's power supply provides the necessary power to the various components, while the printer's casing and chassis provide structural support and protection for the internal components. Finally, the printer's user interface, which may include buttons, LEDs, and a display screen, allows users to interact with the printer, select print options, and monitor the printing process. By understanding the key components of a printer, users can better appreciate the complex process involved in producing high-quality printed output.
The Printing Process: From Digital to Physical
Here is the introduction paragraph: The printing process is a complex and fascinating sequence of events that transforms digital files into physical documents. From the moment a print job is sent to a printer, a series of intricate steps unfolds, involving the receipt and processing of the job, the application of ink or toner, and the final output of the printed page. In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of the printing process, exploring how printers receive and process print jobs, the crucial role of ink or toner in bringing digital images to life, and the precise mechanisms by which printers apply ink or toner to the paper. By understanding these fundamental aspects of the printing process, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the technology that underlies it, and transition seamlessly into understanding the basics of printer technology.
How Printers Receive and Process Print Jobs
. When a print job is sent to a printer, it undergoes a complex process to transform digital data into a physical printout. The journey begins when a user sends a print command from their device, such as a computer or mobile phone, to the printer. The printer receives the print job through a communication protocol, such as USB, Wi-Fi, or Ethernet, and stores it in its memory buffer. The printer's control system, typically a microprocessor or application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC), then interprets the print job and breaks it down into smaller, manageable chunks. This process is called rasterization, where the digital data is converted into a series of tiny dots that will eventually form the printed image. The printer's firmware, a set of pre-programmed instructions, then takes over to manage the printing process, including paper handling, ink or toner management, and print head movement. As the print job is processed, the printer's sensors and feedback mechanisms continuously monitor the printing process, making adjustments as needed to ensure optimal print quality. Finally, the printed page is ejected from the printer, and the process is complete. Throughout this process, the printer's control system and firmware work in tandem to ensure that the print job is executed efficiently and accurately, resulting in a high-quality printout that meets the user's expectations.
The Role of Ink or Toner in the Printing Process
. The role of ink or toner in the printing process is multifaceted and crucial. Ink or toner is the substance that is transferred onto the paper or printing material to create the desired image or text. In inkjet printers, ink is stored in cartridges and is sprayed onto the paper through tiny nozzles, creating a pattern of tiny droplets that form the image. In laser printers, toner is a dry powder that is electrostatically charged and attracted to the paper, where it is fused into place using heat and pressure. The quality of the ink or toner used can greatly affect the final print quality, with factors such as color accuracy, vibrancy, and durability all playing a role. Additionally, the type of ink or toner used can also impact the environmental sustainability of the printing process, with some options being more eco-friendly than others. Overall, the ink or toner is a critical component of the printing process, and its selection and use can have a significant impact on the final product.
How Printers Apply Ink or Toner to the Paper
. The printing process involves a series of intricate steps that ultimately result in the application of ink or toner to the paper. In inkjet printers, the process begins with the print head, which is comprised of a series of tiny nozzles that spray ink onto the paper. The nozzles are controlled by a sophisticated system that ensures the precise amount of ink is released at the exact moment it is needed. As the paper moves through the printer, the print head moves back and forth, depositing ink onto the paper in a precise pattern. The ink is then absorbed into the paper, creating the desired image or text. In laser printers, the process is slightly different. Instead of using ink, laser printers use toner, a dry powder that is electrostatically charged and attracted to the paper. The toner is applied to the paper through a process called electrostatic transfer, where the toner is drawn to the paper by an electrostatic charge. The toner is then fused to the paper using heat and pressure, creating a permanent image. In both cases, the result is a high-quality print that is crisp, clear, and vibrant. Whether it's a document, photo, or artwork, the printing process is a remarkable feat of technology that brings digital images to life.
Advanced Features and Modern Printing Capabilities
Here is the introduction paragraph: The world of printing has undergone a significant transformation in recent years, with advancements in technology leading to the development of advanced features and modern printing capabilities. Gone are the days of basic printing, as today's printers offer a wide range of innovative features that cater to diverse needs and preferences. From wireless and mobile printing options that enable users to print on-the-go, to high-quality printing and resolution options that produce stunning visuals, modern printers have evolved to meet the demands of a rapidly changing world. Additionally, specialized printing features and technologies, such as 3D printing and variable data printing, have opened up new possibilities for creative expression and business applications. As we explore the advanced features and modern printing capabilities of today's printers, it's essential to first understand the basics of printer technology, which will be discussed in the next section, Understanding the Basics of Printer Technology.
Wireless and Mobile Printing Options
. Here is the paragraphy: The world of printing has evolved significantly with the advent of wireless and mobile printing options. Gone are the days of being tethered to a printer via a physical connection. With the rise of smartphones, tablets, and laptops, the need for convenient and flexible printing solutions has become increasingly important. Wireless printing allows users to print documents and images from their devices without the need for cables or wires. This technology uses Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity to establish a connection between the device and the printer, enabling seamless printing from anywhere within range. Mobile printing takes this concept a step further, allowing users to print from their mobile devices using specialized apps or cloud-based services. For example, Google Cloud Print and Apple AirPrint enable users to print from their Android or iOS devices, respectively, without the need for a physical connection. Additionally, many printers now come equipped with NFC (Near Field Communication) technology, allowing users to print by simply tapping their device on the printer. These wireless and mobile printing options have revolutionized the way we print, providing greater flexibility, convenience, and ease of use. Whether you're printing documents, photos, or emails, wireless and mobile printing options make it easier than ever to get the job done.
High-Quality Printing and Resolution Options
. Here is the paragraphy: High-quality printing and resolution options are essential for producing crisp and vibrant images. Modern printers offer a range of resolution options, including 300, 600, and 1200 dots per inch (dpi), which determine the level of detail and clarity in the printed output. The higher the resolution, the more detailed and precise the print will be. For example, a 1200 dpi printer can produce extremely fine lines and intricate details, making it ideal for printing high-quality photographs, graphics, and text. Additionally, some printers offer advanced features such as variable dot size and grayscale printing, which allow for even more precise control over the printing process. These features enable printers to produce a wide range of tonal values and subtle color gradations, resulting in prints that are rich in detail and depth. Furthermore, some printers also offer specialized printing modes, such as photo printing or draft printing, which allow users to optimize the printing process for specific types of documents or images. Overall, the combination of high-quality printing and advanced resolution options enables modern printers to produce outstanding prints that meet the demands of even the most discerning users.
Specialized Printing Features and Technologies
. Here is the paragraphy: Specialized printing features and technologies have revolutionized the printing industry, enabling the creation of high-quality prints with unique characteristics. One such feature is spot varnishing, which involves applying a glossy finish to specific areas of the print, creating a striking visual effect. Another technology is metallic ink printing, which uses special inks that contain metallic particles to produce prints with a shimmering, reflective finish. Additionally, some printers offer white ink printing, which allows for the creation of prints with white text or images on colored or transparent backgrounds. Furthermore, some advanced printers feature raised printing, also known as tactile printing, which creates a three-dimensional effect by raising certain areas of the print. This technology is often used in packaging and labeling applications to create Braille text or other tactile elements. Moreover, some printers offer scented printing, which involves infusing the print with fragrances or scents, creating a multisensory experience for the viewer. These specialized printing features and technologies enable businesses and individuals to create unique and eye-catching prints that stand out from the crowd, making them ideal for applications such as marketing materials, packaging, and fine art printing. By leveraging these advanced features, printers can produce prints that not only look amazing but also engage the viewer on multiple levels, making them a valuable asset for any business or creative endeavor.