Composting Toilet How It Works
Here is the introduction paragraph: Composting toilets are an innovative and eco-friendly solution for managing human waste, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional flush toilets. But have you ever wondered how they work? In this article, we will delve into the world of composting toilets, exploring what they are, how they function, and the essential considerations for installation, maintenance, and safety. From the basics of composting toilet technology to the practical aspects of using and caring for these systems, we will cover it all. So, let's start with the fundamentals: what is a composting toilet?
What is a Composting Toilet?
Composting toilets are an innovative solution for managing human waste in an environmentally friendly manner. These toilets use natural processes to decompose waste, reducing the need for water and minimizing the amount of waste sent to landfills. But what exactly is a composting toilet, and how does it work? In this article, we will delve into the definition and explanation of composting toilets, explore the various types available, and discuss the benefits of using these eco-friendly toilets. By understanding the ins and outs of composting toilets, individuals can make informed decisions about their waste management options and contribute to a more sustainable future. So, let's start by defining what composting toilets are and how they function.
Definition and Explanation of Composting Toilets
Composting toilets are a type of dry toilet that uses natural processes to decompose human waste, typically without the use of water. These toilets work by using microorganisms to break down the waste into a composted material that can be safely disposed of or reused as fertilizer. Composting toilets are often used in areas where access to water is limited, such as in remote or rural areas, or in areas where traditional sewage systems are not available. They are also used in environmentally conscious households and communities that aim to reduce their water usage and minimize their impact on the environment. Composting toilets can be self-contained, meaning that they have their own composting chamber, or they can be centralized, meaning that they are connected to a larger composting system. Some composting toilets also use additional features, such as heat, oxygen, and carbon-rich materials, to enhance the composting process and reduce odors. Overall, composting toilets offer a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional toilets, and can be an effective solution for managing human waste in a variety of settings.
Types of Composting Toilets Available
There are several types of composting toilets available, each with its unique features and benefits. Self-contained composting toilets are compact, all-in-one units that combine the toilet seat, composting chamber, and ventilation system in a single unit. These toilets are ideal for small spaces, such as RVs, boats, or tiny homes. Centralized composting toilets, on the other hand, have a separate composting unit that is connected to the toilet seat via a pipe. This type of toilet is suitable for larger households or commercial applications. Vermicomposting toilets use worms to break down human waste, while bokashi toilets use microorganisms to ferment the waste. Incinerating toilets use electricity to burn human waste, reducing it to a small amount of ash. Finally, urine-diverting dry toilets (UDDTs) separate urine from feces, allowing for more efficient composting and reducing odors. Each type of composting toilet has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which one to use depends on factors such as space constraints, user preferences, and local regulations.
Benefits of Using Composting Toilets
Using a composting toilet can have numerous benefits for individuals, communities, and the environment. One of the most significant advantages is the reduction of water consumption, as composting toilets do not require water for flushing, unlike traditional toilets. This can be especially beneficial in areas where water is scarce or in regions prone to droughts. Additionally, composting toilets can help reduce the amount of wastewater generated, which can pollute waterways and harm aquatic life. By composting human waste, these toilets also produce a valuable nutrient-rich compost that can be used as fertilizer, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and promoting sustainable agriculture. Furthermore, composting toilets can help mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with traditional wastewater treatment processes. They also provide a unique opportunity for individuals to take control of their waste management, promoting a sense of self-sufficiency and environmental stewardship. Overall, composting toilets offer a sustainable, eco-friendly, and cost-effective solution for managing human waste, making them an attractive option for those looking to reduce their environmental footprint.
How Does a Composting Toilet Work?
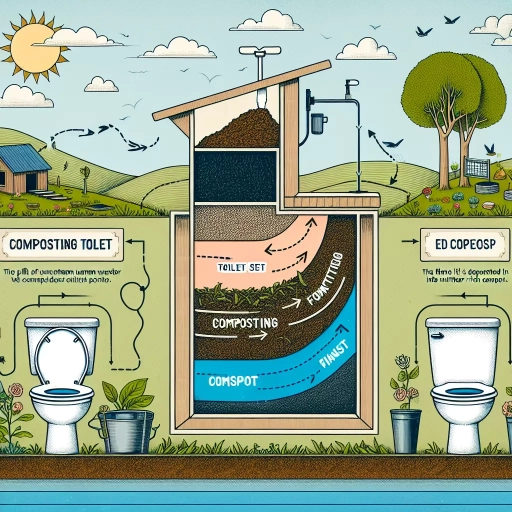
A composting toilet is a type of toilet that uses natural processes to decompose human waste, reducing the need for water and minimizing environmental impact. Composting toilets work by using microorganisms to break down waste into a composted material that can be safely disposed of or reused as fertilizer. But how does this process work, and what are the key components involved? To understand the inner workings of a composting toilet, it's essential to delve into the composting process, which involves breaking down waste into its constituent parts. Additionally, it's crucial to examine the key components of a composting toilet system, including the toilet itself, the composting chamber, and the aeration system. Furthermore, managing moisture and odors is critical to maintaining a healthy and efficient composting process. By exploring these aspects, we can gain a deeper understanding of how composting toilets work. Let's start by examining the composting process, which is the foundation of a composting toilet's functionality.
The Composting Process: Breaking Down Waste
The composting process is a natural, biological process that breaks down organic waste into a nutrient-rich soil amendment. It involves the decomposition of organic materials, such as food scraps, yard trimmings, and human waste, by microorganisms like bacteria and fungi. These microorganisms feed on the organic matter, breaking it down into simpler compounds that can be easily absorbed by plants. The composting process requires a combination of "green" materials, such as food scraps and grass clippings, which are high in nitrogen, and "brown" materials, such as dried leaves and twigs, which are high in carbon. The ideal mix of green and brown materials is typically 2/3 brown materials and 1/3 green materials. The composting process also requires adequate moisture, oxygen, and heat. As the microorganisms break down the organic matter, they release heat, which can reach temperatures of up to 160°F (71°C). This heat helps to kill off pathogens and weed seeds, making the compost safe to use. The composting process can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on the size of the compost pile, the mix of materials, and the environmental conditions. The end result is a dark, crumbly, and earthy-smelling compost that is rich in nutrients and can be used to improve soil structure, fertility, and overall health.
Key Components of a Composting Toilet System
A composting toilet system typically consists of several key components that work together to break down human waste into a safe and usable compost. The first component is the toilet itself, which is designed to collect and store human waste in a controlled environment. This can be a self-contained unit or a central composting system that serves multiple toilets. The toilet is usually equipped with a ventilation system that helps to remove odors and moisture from the waste. The second component is the composting chamber, where the waste is broken down into compost. This chamber is typically a large, insulated container that is designed to maintain a consistent temperature and moisture level, ideal for microbial growth. The composting chamber is usually equipped with aeration pipes or turners that help to introduce oxygen and speed up the decomposition process. The third component is the carbon-rich bulking agent, such as coconut coir or sawdust, which is added to the composting chamber to absorb excess moisture and provide a food source for the microorganisms. The fourth component is the microorganisms themselves, which are responsible for breaking down the organic matter into compost. These microorganisms can be introduced to the composting chamber through the addition of compost tea or effective microorganisms. Finally, the fifth component is the finished compost, which is the end product of the composting process. This compost is safe to handle and can be used as a nutrient-rich fertilizer for plants. Overall, a well-designed composting toilet system requires careful consideration of these key components to ensure efficient and effective waste management.
Managing Moisture and Odors in Composting Toilets
Managing moisture and odors is crucial in composting toilets to ensure a healthy and efficient decomposition process. Excess moisture can lead to anaerobic conditions, creating unpleasant odors and hindering the composting process. To manage moisture, composting toilets often employ a combination of techniques, including ventilation systems, absorbent materials, and careful monitoring of liquid inputs. Adequate ventilation helps to evaporate excess moisture, while absorbent materials like coconut coir or peat moss absorb liquids and maintain a dry environment. Regular monitoring of liquid inputs, such as urine and water, is also essential to prevent over-saturation. Additionally, some composting toilets incorporate features like urine diverters, which separate urine from feces, reducing moisture levels and odors. By controlling moisture, composting toilets can minimize odors and create a favorable environment for microorganisms to break down organic matter. Effective odor management also relies on maintaining a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, ensuring adequate aeration, and regularly turning or aerating the compost pile. By implementing these strategies, composting toilets can efficiently manage moisture and odors, producing a valuable compost product while minimizing environmental impacts.
Installation, Maintenance, and Safety Considerations
When it comes to composting toilets, there are several key considerations that must be taken into account to ensure a safe, efficient, and environmentally friendly experience. The installation of a composting toilet is a critical step in the process, and it requires careful site selection and preparation to ensure optimal performance. Regular maintenance tasks are also essential to prevent odors, pests, and other issues that can arise if the toilet is not properly cared for. Additionally, health and safety precautions must be taken to minimize the risk of disease transmission and other hazards associated with composting toilets. By understanding these important considerations, individuals can ensure a successful and sustainable composting toilet experience. In this article, we will explore these key considerations in more detail, starting with the critical step of installing a composting toilet, including site selection and preparation.
Installing a Composting Toilet: Site Selection and Preparation
When installing a composting toilet, site selection and preparation are crucial to ensure proper functioning and minimize potential issues. The ideal location for a composting toilet is a well-ventilated area with adequate space for the unit and any additional components, such as a composting chamber or urine-diverting system. It's essential to choose a location that is easily accessible for maintenance and emptying, as well as being close to a water source for cleaning and flushing. The site should also be level and stable to prevent the unit from shifting or toppling over. Additionally, it's recommended to install the composting toilet in an area with a consistent temperature between 40°F and 90°F (4°C and 32°C) to facilitate optimal composting conditions. Before installation, the site should be prepared by ensuring the floor is level and secure, and any necessary electrical or plumbing connections are made. It's also important to check local building codes and regulations regarding composting toilets and obtain any necessary permits before commencing installation. By carefully selecting and preparing the site, homeowners can ensure a successful and trouble-free composting toilet installation.
Regular Maintenance Tasks for Composting Toilets
Regular maintenance tasks for composting toilets are crucial to ensure optimal performance, hygiene, and safety. One of the most important tasks is adding bulking agents, such as coconut coir or sawdust, to the composting chamber to absorb excess moisture and maintain aeration. This should be done regularly, ideally every 1-2 weeks, depending on usage. Additionally, the composting toilet's ventilation system should be checked and cleaned regularly to ensure proper airflow and prevent odors. This includes inspecting and cleaning the vent pipes, fans, and filters. It is also essential to monitor the composting toilet's temperature, as it should be within the optimal range of 131°F to 140°F (55°C to 60°C) to facilitate efficient decomposition. Furthermore, the composting toilet's compost should be turned or aerated regularly to maintain oxygen levels and prevent matting. This can be done manually or with the help of automated systems. Regular maintenance also involves inspecting the toilet's electrical components, such as the heating element and sensors, to ensure they are functioning correctly. Moreover, the composting toilet's drain system should be checked regularly to prevent clogs and ensure proper drainage. By performing these regular maintenance tasks, composting toilet owners can ensure their system operates efficiently, effectively, and safely, producing high-quality compost and minimizing odors and pests.
Health and Safety Precautions When Using Composting Toilets
When using composting toilets, it is essential to take health and safety precautions to minimize the risk of disease transmission and ensure a safe and hygienic environment. One of the primary concerns is the potential for pathogen transmission, particularly from fecal matter. To mitigate this risk, it is crucial to follow proper installation, maintenance, and operation procedures. This includes ensuring that the toilet is installed in a well-ventilated area, away from living spaces and water sources, and that it is regularly maintained to prevent the buildup of pathogens. Additionally, users should always wash their hands thoroughly after using the toilet, and any cleaning or maintenance tasks should be performed while wearing protective gloves and eyewear. It is also important to note that composting toilets are not suitable for households with infants or young children, as they may be more susceptible to disease transmission. Furthermore, individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, should exercise extreme caution when using composting toilets. By taking these health and safety precautions, users can minimize the risks associated with composting toilets and enjoy a safe and sustainable sanitation solution.