How Do Eels Reproduce
Understanding the Eel's Unique Life Cycle
The Migratory Habits of Eels
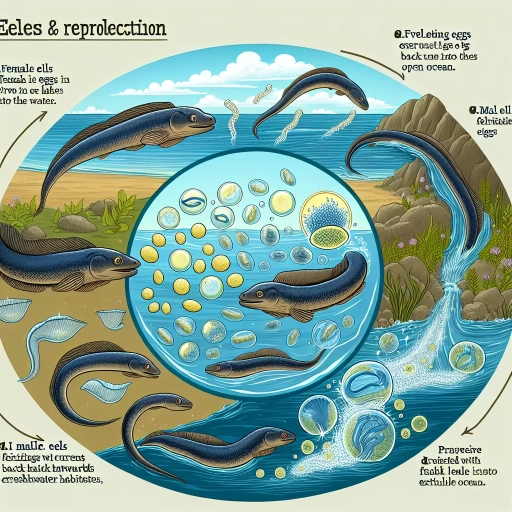
Eels are renowned for their unique migration patterns, typically traveling from their freshwater or brackish-water habitats into the open ocean for reproduction. This migration process is a crucial part of the eel's life cycle and plays a significant role in their reproductive strategy. Eels, such as the European eel and the American eel, are known to travel thousands of kilometers, from Europe and North America's coastlines to the Sargasso Sea, to spawn and lay eggs. This journey is particularly remarkable considering the extreme distance and the inherent perils associated with it, including predation and harsh environmental conditions. Nevertheless, eels make this migration annually, underscoring the species' adaptive prowess and resilience.
The Spawning Process
Once eels reach their spawning grounds in the Sargasso Sea, the females release their eggs, and males fertilize them externally. This spawning process usually occurs deep beneath the ocean's surface, where water temperatures are typically cooler. The females can release millions of eggs per season, and once fertilized, these eggs gradually rise to the ocean's surface, where they hatch into larvae. The larval stage of an eel's life is particularly interesting because these young eels, also known as leptocephali, have a flat and transparent body shape, significantly different from the cylindrical and opaque morphology typically associated with adult eels.
The Return Migration
Following the hatching, the leptocephali begin a new migratory journey back to the freshwater habitats. Here, they develop into "glass eels" before reaching the "elver" stage, and finally maturing into adult eels. The return migration is, in many ways, as spectacular and complex as the outward journey to the Sargasso Sea. The larval eels must navigate a diverse range of environments - from the open ocean, through estuaries, and into freshwater bodies. Various factors influence this migratory behavior, including water temperature, salinity, and even geomagnetic fields. Upon reaching their destination, the adult eels will then reproduce and the cycle continues.
The Mysteries Surrounding Eel Reproduction
The Elusive Spawning Grounds
Despite the extensive knowledge about the migratory patterns and the general life cycle of eels, there still exists a shroud of mystery surrounding the exact location of their spawning grounds. Although it's widely accepted that eels spawn in the Sargasso Sea, no one has ever directly observed eels spawning in the wild. This elusiveness has mostly been attributed to the depth at which eels spawn, coupled with the challenge of tracking them across their colossal migratory route.
Eel Reproduction in Aquaria
Another fascinating aspect of eel reproduction is the fact that it is nearly impossible to reproduce their breeding conditions in captivity. Many attempts to do so have resulted in failure or only partial success. Certain factors like water temperature, pressure, salinity, and even light conditions must be just right to induce eels to breed. To this day, successful eel breeding in captivity remains a challenging feat that only a handful of aquarists and researchers have achieved.
The Role of Pheromones
While direct observation of eel spawning has remained elusive, scientists believe that pheromones play a significant role in eel reproduction. Pheromones are chemicals that animals emit to communicate with others of the same species. Eels likely use pheromones to coordinate spawning events and to lead other eels to the spawning grounds. Given that these spawning grounds can be thousands of kilometers away, the ability to communicate via chemical signals underscores the eel's remarkable adaptability and survival strategy.
The Future of Eels
Conservation Challenges
Eels, like many aquatic species, are facing significant conservation challenges today. Population decline has been particularly notable in eel species like the European eel, where numbers have dramatically fallen over the past few decades. This decline is attributed to a number of factors, including overfishing, habitat degradation, and potentially, changes in ocean currents due to climate change. These challenges underscore the urgent need for effective conservation strategies for eels.
The Role of Aquaculture
Aquaculture, the farming of aquatic species in controlled environments, has often been proposed as a solution to the decline in eel populations. However, given the unique life cycle of eels and the difficulties associated with breeding them in captivity, aquaculture is not a straightforward solution. Despite these challenges, progress has been made in countries like Japan, where the culture of Japanese eels has become a booming industry. Continued research and development in this field will be a critical component for the future conservation of eels.
Public Awareness and Protection Measures
A key element in the conservation of eels is public awareness. In many parts of the world, eels are still considered a culinary delicacy, and demand for eel meat puts pressure on wild populations. By raising awareness about the plight of eels and promoting sustainable fishing practices, we can help to mitigate the pressures on these extraordinary creatures. Additionally, by ensuring the enforcement of laws and regulations aimed at protecting eel habitats and banning the illegal trade in eels, we can ensure the survival of these fascinating animals for generations to come.