How Many Feet In A Fathom
Here is the introduction paragraph: When it comes to measuring depth, particularly in nautical and maritime contexts, two units of measurement are commonly used: fathoms and feet. But have you ever wondered how many feet are in a fathom? Understanding the relationship between these two units is crucial for various applications, from navigation and sailing to engineering and construction. In this article, we will delve into the basics of fathoms and feet, explore a step-by-step guide on how to convert fathoms to feet, and examine the real-world applications of these conversions. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to work with fathoms and feet. So, let's start by understanding the basics of fathoms and feet.
Understanding the Basics of Fathoms and Feet
Understanding the basics of fathoms and feet is crucial for various applications, including navigation, construction, and scientific research. To grasp the fundamentals of these units of measurement, it is essential to explore their definitions, historical uses, and standardization across different regions. This article will delve into the world of fathoms and feet, starting with the definition of fathoms and their relationship to feet. We will also examine the historical use of fathoms in measurement, highlighting their significance in the past. Additionally, we will discuss the standardization of fathoms across different regions, shedding light on the variations and similarities in their usage. By understanding these aspects, readers will gain a comprehensive knowledge of fathoms and feet, enabling them to apply this knowledge in various contexts. To begin, let's define fathoms and their relationship to feet, exploring the intricacies of these units of measurement.
Defining Fathoms and Their Relationship to Feet
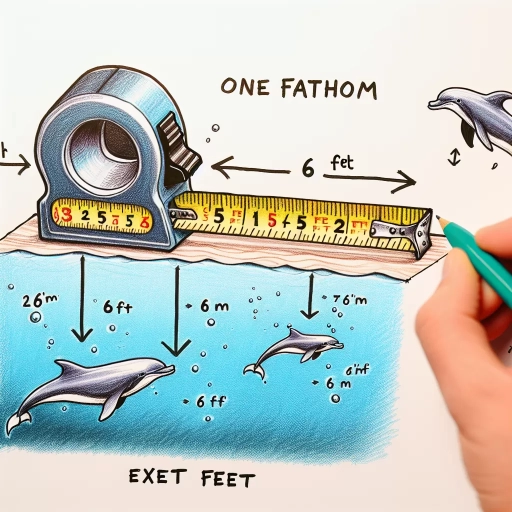
A fathom is a unit of length equal to six feet, primarily used to measure the depth of water. The term "fathom" is derived from the Old English word "fæðm," which means "the length of the outstretched arms." Historically, fathoms were used to measure the depth of water by throwing a weighted line, known as a sounding line, into the water and measuring the length of the line that was submerged. This method was used by sailors and fishermen to determine the depth of the water and navigate safely. In modern times, fathoms are still used in various fields, including navigation, marine biology, and underwater construction. The relationship between fathoms and feet is straightforward: one fathom is equal to six feet, making it a convenient unit of measurement for calculating depths and distances. For example, if a diver descends to a depth of three fathoms, they are at a depth of 18 feet. Understanding the relationship between fathoms and feet is essential for anyone working with water depths, whether it's for recreational or professional purposes.
Historical Use of Fathoms in Measurement
A fathom has been a unit of measurement for thousands of years, with its origins dating back to ancient civilizations. The word "fathom" is derived from the Old English word "fæðm," which referred to the length of the outstretched arms from fingertip to fingertip. This method of measurement was used by sailors and fishermen to measure the depth of water, as well as the length of ropes and cables. In ancient Greece and Rome, the fathom was used as a standard unit of measurement for building and construction projects. The fathom was also used in medieval England as a unit of measurement for land and property, with the "fathom" being equivalent to 6 feet. The use of fathoms as a unit of measurement continued well into the 19th century, particularly in the shipping and maritime industries. Today, while the fathom is no longer a widely used unit of measurement, it remains an important part of our cultural and historical heritage, and is still used in some specialized contexts, such as in the measurement of water depth and in the construction of ships and boats.
Standardization of Fathoms Across Different Regions
The standardization of fathoms across different regions has been a topic of interest for centuries. Historically, the length of a fathom varied significantly between countries and even within regions. In the United Kingdom, for instance, a fathom was equivalent to 6 feet, while in the United States, it was standardized to 6 feet in 1959. Similarly, in Canada, a fathom was defined as 6 feet under the Weights and Measures Act of 1970. In Australia, the length of a fathom was standardized to 6 feet in 1972, as part of the country's metrication process. In contrast, some countries, such as Germany and the Netherlands, used a fathom equivalent to 6.25 feet, while others, like France, used a fathom of 6.1 feet. The lack of standardization led to confusion and errors in navigation, trade, and other fields that relied on precise measurements. To address this issue, the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recommended the adoption of a standardized fathom of 6 feet in 1959. Today, the IHO's standard is widely accepted and used across the globe, ensuring consistency and accuracy in measurements involving fathoms. Despite this, some countries still use their traditional definitions, highlighting the need for continued education and awareness about the importance of standardization in measurement.
Converting Fathoms to Feet: A Step-by-Step Guide
Converting fathoms to feet is a crucial task in various fields such as navigation, engineering, and construction. To ensure accuracy and precision, it is essential to understand the conversion process thoroughly. In this article, we will delve into the step-by-step guide of converting fathoms to feet, exploring the conversion factor between the two units, providing practical examples, and highlighting common mistakes to avoid. By understanding the conversion factor between fathoms and feet, we can establish a solid foundation for accurate conversions. This knowledge will enable us to tackle complex calculations with confidence, making it easier to navigate through various applications. Let's start by understanding the conversion factor between fathoms and feet.
Understanding the Conversion Factor Between Fathoms and Feet
Understanding the conversion factor between fathoms and feet is crucial for accurate calculations in various fields such as navigation, engineering, and construction. A fathom is a unit of length equal to six feet, and this conversion factor is widely used in different applications. To convert fathoms to feet, you can simply multiply the number of fathoms by six, as one fathom is equivalent to six feet. For example, if you have a measurement of five fathoms, you can convert it to feet by multiplying five by six, which equals thirty feet. This conversion factor is essential for ensuring precision in calculations, especially in situations where small errors can have significant consequences. By understanding the relationship between fathoms and feet, you can make accurate conversions and avoid potential mistakes in your work.
Practical Examples of Converting Fathoms to Feet
Converting fathoms to feet is a common task in various fields such as navigation, engineering, and construction. Here are some practical examples that illustrate the conversion process. For instance, if a sailor needs to measure the depth of the water in a harbor, they might use a sounding weight that measures 5 fathoms. To convert this to feet, they would multiply 5 fathoms by 6 feet, resulting in a depth of 30 feet. Similarly, a construction engineer might need to calculate the length of a pipe that needs to be laid underwater. If the pipe is 10 fathoms long, they would convert this to feet by multiplying 10 fathoms by 6 feet, giving a length of 60 feet. In another example, a scuba diver might need to measure the distance to a underwater landmark. If the landmark is 3 fathoms away, they would convert this to feet by multiplying 3 fathoms by 6 feet, resulting in a distance of 18 feet. These examples demonstrate how converting fathoms to feet is a straightforward process that can be applied in a variety of real-world situations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Fathom to Feet Conversions
When converting fathoms to feet, it's essential to be aware of common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate results. One of the most common errors is forgetting to multiply the number of fathoms by 6, as there are 6 feet in a fathom. This simple oversight can result in a conversion that is off by a factor of 6. Another mistake is using the wrong conversion factor, such as using 5 or 7 feet per fathom instead of the correct 6 feet. This can lead to a significant error, especially when working with large numbers. Additionally, it's crucial to ensure that the units are consistent, as mixing units can lead to confusion and incorrect conversions. For example, if you're converting fathoms to feet, make sure you're not accidentally using a conversion factor for a different unit, such as yards or meters. By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can ensure accurate and reliable conversions from fathoms to feet.
Real-World Applications of Fathoms and Feet Conversions
The use of fathoms and feet conversions is a crucial aspect of various real-world applications, including maritime and underwater measurements, engineering and construction, and everyday situations. In the maritime industry, fathoms are used to measure the depth of water, which is essential for navigation and safety. Accurate conversions between fathoms and feet are necessary to ensure that vessels can safely navigate through waters with varying depths. In engineering and construction, precise conversions are required to ensure that buildings and structures are designed and built to withstand various environmental conditions. Furthermore, in everyday situations, such as measuring the depth of a pool or the height of a building, fathoms to feet conversions are necessary to obtain accurate measurements. This article will explore the real-world applications of fathoms and feet conversions, starting with the use of fathoms in maritime and underwater measurements.
Use of Fathoms in Maritime and Underwater Measurements
The use of fathoms in maritime and underwater measurements is a long-standing tradition that dates back to ancient times. A fathom is a unit of length equal to six feet, and it has been widely used in the maritime industry for measuring the depth of water, the length of ropes and chains, and the size of ships and boats. In the past, sailors and fishermen used fathoms to measure the depth of the water to determine the best fishing spots or to avoid shallow waters that could damage their vessels. Today, fathoms are still used in various maritime applications, including navigation, hydrography, and offshore construction. For example, fathoms are used to measure the depth of the water in ports and harbors, as well as the height of waves and tides. In underwater construction, fathoms are used to measure the length of pipelines and cables, and to determine the depth of underwater excavations. In addition, fathoms are also used in the offshore oil and gas industry to measure the depth of wells and the length of pipelines. Overall, the use of fathoms in maritime and underwater measurements is an important part of ensuring the safety and efficiency of various maritime operations.
Importance of Accurate Conversions in Engineering and Construction
Accurate conversions are crucial in engineering and construction to ensure the safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of projects. In these fields, small errors in measurement can have significant consequences, such as structural failures, delays, and budget overruns. For instance, a miscalculation in the conversion of fathoms to feet can lead to incorrect calculations of water depth, which can affect the design and construction of offshore platforms, bridges, or tunnels. Similarly, in construction, incorrect conversions can result in improper material quantities, leading to waste, rework, and increased costs. Furthermore, accurate conversions are essential for compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards, such as building codes and safety protocols. Inaccurate conversions can lead to non-compliance, resulting in fines, penalties, and reputational damage. Therefore, engineers and construction professionals must prioritize accurate conversions to ensure the success and integrity of their projects. By using reliable conversion tools and techniques, they can minimize errors, optimize designs, and deliver high-quality results that meet the required standards.
Everyday Situations Where Fathoms to Feet Conversions Are Necessary
Fathoms to feet conversions are necessary in various everyday situations, particularly in industries and activities that involve measuring depths or lengths in water or underwater environments. For instance, in offshore oil and gas exploration, fathoms are used to measure the depth of water at drilling sites, and converting these measurements to feet is crucial for determining the appropriate drilling equipment and techniques. Similarly, in marine construction, fathoms are used to measure the depth of water at construction sites, and converting these measurements to feet is necessary for designing and building structures such as bridges, piers, and seawalls. In addition, fathoms to feet conversions are also necessary in recreational activities such as scuba diving and snorkeling, where divers need to measure their depth to avoid exceeding safe limits and to navigate underwater environments safely. Furthermore, in fishing and aquaculture, fathoms are used to measure the depth of water in fishing nets and aquaculture cages, and converting these measurements to feet is necessary for determining the appropriate gear and equipment. Overall, fathoms to feet conversions are an essential part of various everyday situations that involve measuring depths or lengths in water or underwater environments.