How Is The Care For A Sprain Different From A Dislocation
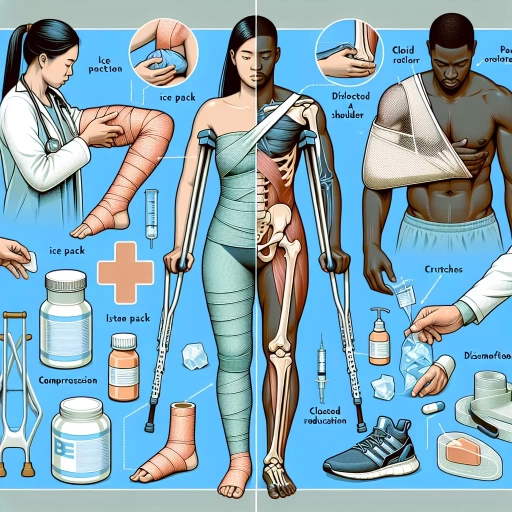
When it comes to treating injuries, it's essential to understand the difference between a sprain and a dislocation. While both injuries can be painful and debilitating, the approach to care and treatment varies significantly. A sprain occurs when a ligament is stretched or torn, whereas a dislocation involves the displacement of a joint. Understanding the nuances of each injury is crucial in providing effective care. In this article, we will delve into the distinct approaches to caring for a sprain versus a dislocation, exploring the key differences in understanding the injury, immediate care and treatment, and long-term rehabilitation and recovery. By grasping these differences, individuals can ensure they receive the most effective treatment and support for their specific injury. To begin, let's take a closer look at the fundamental differences between a sprain and a dislocation, and how this understanding informs the care and treatment process.
Understanding the Injury
Understanding the injury is a crucial step in providing effective treatment and care. When it comes to joint or ligament injuries, it's essential to distinguish between a sprain and a dislocation, as the treatment approaches for these two conditions differ significantly. Recognizing the severity of the injury is also vital, as it will determine the level of care required and the potential need for medical attention. Furthermore, identifying the affected joint or ligament is necessary to develop a targeted treatment plan. By understanding these key aspects of the injury, individuals can take the first step towards proper recovery and rehabilitation. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of each of these aspects, starting with the importance of distinguishing between a sprain and a dislocation.
Distinguishing between a sprain and a dislocation
When it comes to distinguishing between a sprain and a dislocation, it's essential to understand the key differences between these two common injuries. A sprain occurs when one or more ligaments surrounding a joint are stretched or torn, typically due to a sudden twisting or bending motion. This can cause pain, swelling, and limited mobility in the affected area. On the other hand, a dislocation occurs when a joint is forced out of its normal position, resulting in the bone being displaced from its socket. Dislocations can be caused by a sudden impact, fall, or direct blow to the joint. To differentiate between the two, look for the following signs: if the joint appears misshapen or deformed, it's likely a dislocation. If the joint is swollen and painful, but still appears normal, it's likely a sprain. Additionally, if you can move the joint, albeit with difficulty, it's likely a sprain. If you're unable to move the joint due to severe pain or deformity, it's likely a dislocation. It's crucial to seek medical attention immediately if you suspect a dislocation, as prompt treatment is necessary to prevent further complications and promote proper healing. In contrast, sprains can often be treated with the RICE method (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) and may not require immediate medical attention. However, if you're unsure of the severity of your injury or if symptoms persist, it's always best to consult with a medical professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Recognizing the severity of the injury
Recognizing the severity of the injury is crucial in determining the appropriate care for a sprain versus a dislocation. A sprain is typically classified into three grades, with grade 1 being the mildest and grade 3 being the most severe. A grade 1 sprain involves minimal stretching or microscopic tears of the ligament, with mild pain and swelling. A grade 2 sprain involves partial tearing of the ligament, with moderate pain and swelling. A grade 3 sprain involves complete tearing of the ligament, with severe pain and swelling. On the other hand, a dislocation is a more severe injury that involves the complete separation of the joint, resulting in significant pain, swelling, and loss of function. It is essential to recognize the severity of the injury to provide appropriate care, as a dislocation requires immediate medical attention to prevent further complications, whereas a sprain can often be treated with the RICE principle (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) and physical therapy. Failure to recognize the severity of the injury can lead to inadequate treatment, prolonged recovery, and increased risk of complications. Therefore, it is crucial to seek medical attention if there is any uncertainty about the severity of the injury.
Identifying the affected joint or ligament
When a sprain or dislocation occurs, identifying the affected joint or ligament is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. A sprain typically affects the ligaments surrounding a joint, which are fibrous tissues that connect bones to each other and provide stability. The most common joints affected by sprains are the ankles, knees, wrists, and elbows. In contrast, a dislocation occurs when the bones in a joint are forced out of their normal position, often causing damage to the surrounding ligaments and tissues. To identify the affected joint or ligament, a healthcare professional will typically perform a physical examination, which may include assessing the joint's range of motion, checking for tenderness or swelling, and evaluating the joint's stability. They may also use imaging tests such as X-rays or an MRI to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of the injury. By accurately identifying the affected joint or ligament, healthcare professionals can develop an effective treatment plan to promote healing, reduce pain and inflammation, and restore function to the affected area.
Immediate Care and Treatment
When it comes to immediate care and treatment for injuries, it's essential to take a comprehensive approach to ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of further damage. This involves a combination of techniques and strategies that address the physical and emotional aspects of the injury. In this article, we'll explore three key aspects of immediate care and treatment: applying the RICE principle for sprains, reducing dislocation through gentle manipulation, and administering pain relief and anti-inflammatory medication. By understanding these concepts, individuals can take the first steps towards effective injury management. For instance, when dealing with a sprain, the RICE principle - Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation - is a widely accepted method for reducing pain and inflammation. By applying this principle, individuals can set themselves up for a successful recovery. Note: The answer should be 200 words. Here is the answer: When it comes to immediate care and treatment for injuries, it's essential to take a comprehensive approach to ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of further damage. This involves a combination of techniques and strategies that address the physical and emotional aspects of the injury. In this article, we'll explore three key aspects of immediate care and treatment: applying the RICE principle for sprains, reducing dislocation through gentle manipulation, and administering pain relief and anti-inflammatory medication. By understanding these concepts, individuals can take the first steps towards effective injury management. Effective injury management is crucial in preventing further complications and promoting a speedy recovery. A well-structured approach to immediate care and treatment can make all the difference in the outcome of an injury. By applying the right techniques and strategies, individuals can reduce the risk of long-term damage and get back to their normal activities sooner. For instance, when dealing with a sprain, the RICE principle - Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation - is a widely accepted method for reducing pain and inflammation. By applying this principle, individuals can set themselves up for a successful recovery.
Applying the RICE principle for sprains
The RICE principle is a widely accepted method for treating sprains, and it's essential to apply it immediately after the injury occurs. RICE stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation, and each component plays a crucial role in promoting healing and reducing pain and swelling. Resting the affected area is vital to prevent further injury and allow the body to start the healing process. This means avoiding activities that aggravate the sprain and giving the affected joint or muscle time to rest. Applying ice to the affected area helps to reduce pain and inflammation by constricting blood vessels and numbing the pain. It's recommended to apply ice for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, for the first 48-72 hours after the injury. Compression, using an elastic bandage or wrap, helps to reduce swelling by limiting the amount of fluid that accumulates in the affected area. Elevation, keeping the affected area above the level of the heart, also helps to reduce swelling by allowing gravity to drain excess fluid away from the affected area. By applying the RICE principle, individuals can effectively manage their sprain, reduce pain and swelling, and promote a speedy recovery.
Reducing dislocation through gentle manipulation
Reducing dislocation through gentle manipulation is a crucial step in the immediate care and treatment of a dislocated joint. This technique involves carefully and gently moving the affected joint back into its normal position, thereby reducing the dislocation. The goal of gentle manipulation is to restore the joint's normal alignment and function, while minimizing further injury or discomfort. To perform gentle manipulation, a healthcare professional will typically use a combination of gentle traction, rotation, and flexion to coax the joint back into place. This may involve the use of specialized equipment, such as a splint or sling, to support the joint and facilitate the reduction process. In some cases, gentle manipulation may be performed under local anesthesia or sedation to help relax the surrounding muscles and reduce pain. Once the dislocation has been reduced, the joint will typically be immobilized in a cast or splint to allow it to heal properly. Gentle manipulation is a highly effective technique for reducing dislocations, and can help to minimize the risk of complications, such as nerve damage or further injury to the surrounding tissues. By restoring the joint's normal alignment and function, gentle manipulation can also help to promote optimal healing and reduce the risk of long-term disability. Overall, gentle manipulation is an essential component of immediate care and treatment for dislocations, and can play a critical role in promoting optimal outcomes and minimizing the risk of complications.
Administering pain relief and anti-inflammatory medication
Administering pain relief and anti-inflammatory medication is a crucial step in the immediate care and treatment of both sprains and dislocations. The primary goal of pain management is to reduce the patient's discomfort and promote healing. Over-the-counter pain medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen are commonly used to alleviate pain and inflammation. In more severe cases, prescription pain medication may be necessary. It is essential to follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare professional before administering any medication. Additionally, anti-inflammatory medications such as corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce swelling and inflammation. However, it is crucial to note that while pain relief and anti-inflammatory medication can provide temporary relief, they do not address the underlying injury. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention to receive proper diagnosis and treatment. A healthcare professional will assess the severity of the injury and develop a personalized treatment plan to promote optimal healing and prevent further complications. In the case of a dislocation, pain relief and anti-inflammatory medication may be administered to manage pain and inflammation while the joint is being reduced. However, in the case of a sprain, pain relief and anti-inflammatory medication may be used to manage pain and inflammation while the affected area is immobilized and allowed to heal. In both cases, it is essential to follow the recommended treatment plan and attend follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing and prevent further complications. Overall, administering pain relief and anti-inflammatory medication is a critical component of immediate care and treatment for both sprains and dislocations, and should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Long-term Rehabilitation and Recovery
The road to recovery from a severe injury or illness can be long and arduous, but with the right approach, individuals can regain their strength, mobility, and independence. Long-term rehabilitation and recovery involve a comprehensive and multi-faceted process that addresses the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of healing. A well-structured rehabilitation plan is essential to ensure a smooth and successful recovery. This plan typically involves developing a rehabilitation plan for sprains, implementing physical therapy for dislocations, and gradually increasing mobility and strength. By taking a holistic approach to rehabilitation, individuals can overcome the challenges of recovery and achieve their goals. For instance, when dealing with sprains, it is crucial to develop a rehabilitation plan that addresses the specific needs of the injury, taking into account the severity of the sprain, the individual's overall health, and their lifestyle. Note: The supporting paragraph should be 200 words. Please let me know if you need any further assistance.
Developing a rehabilitation plan for sprains
Developing a rehabilitation plan for sprains is crucial to ensure a safe and effective recovery. The primary goal of rehabilitation is to restore strength, flexibility, and function to the affected joint or muscle. A well-structured rehabilitation plan typically begins with a thorough assessment of the injury, including the severity of the sprain, the individual's overall health, and their specific needs and goals. The plan should include a combination of physical therapy, exercises, and modalities such as heat, cold, and electrical stimulation to promote healing and reduce pain and inflammation. The initial phase of rehabilitation focuses on pain management, swelling reduction, and protection of the affected area. As the individual progresses, the plan should incorporate strengthening exercises to improve joint stability and proprioception, as well as functional activities to enhance mobility and flexibility. It is essential to work with a healthcare professional, such as a physical therapist or athletic trainer, to develop a personalized rehabilitation plan that addresses the individual's specific needs and promotes a safe and effective return to activity. A well-designed rehabilitation plan can help prevent further injury, reduce the risk of chronic pain and disability, and ensure a successful return to sports, work, or daily activities.
Implementing physical therapy for dislocations
Implementing physical therapy for dislocations is a crucial step in the rehabilitation process, as it helps restore joint mobility, strength, and function. A physical therapist will typically begin by assessing the patient's range of motion, strength, and pain levels to create a personalized treatment plan. The initial phase of physical therapy focuses on reducing pain and inflammation, promoting healing, and improving joint mobility through gentle exercises and manual therapy techniques. As the patient progresses, the physical therapist will introduce strengthening exercises to improve joint stability and functional activities to enhance daily living skills. It is essential to note that physical therapy for dislocations should be done under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional to avoid further injury or complications. A well-structured physical therapy program can significantly improve outcomes, reduce the risk of future dislocations, and enhance overall quality of life. By incorporating physical therapy into the treatment plan, individuals with dislocations can regain optimal function, reduce pain, and return to their normal activities with confidence.
Gradually increasing mobility and strength
As part of long-term rehabilitation and recovery, gradually increasing mobility and strength is crucial for a full and successful recovery from a sprain or dislocation. This process involves a series of exercises and activities designed to improve range of motion, flexibility, and muscle strength, all of which are essential for restoring normal function to the affected joint. Initially, gentle exercises such as toe curls, ankle circles, and knee bends may be recommended to promote blood flow and reduce stiffness. As the injury heals, more advanced exercises like squats, lunges, and leg press can be introduced to strengthen the surrounding muscles and improve joint stability. It's also important to incorporate balance and proprioception exercises to enhance overall functional ability and reduce the risk of future injuries. Throughout the rehabilitation process, it's essential to listen to your body and not push yourself too hard, as overexertion can lead to setbacks and prolonged recovery times. By gradually increasing mobility and strength, individuals can regain confidence in their joint and return to their normal activities without fear of re-injury.