How Long Do Tulips Last
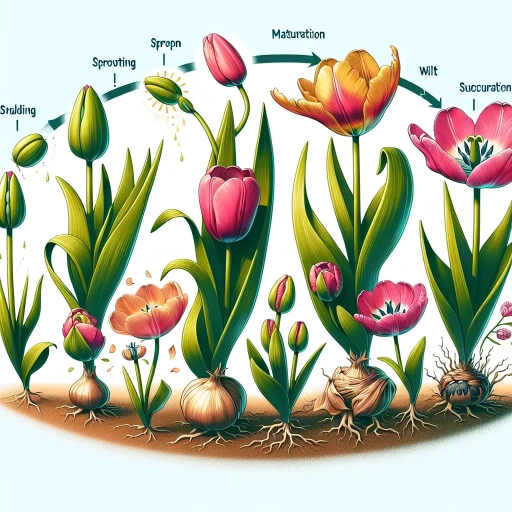 Tulips, known for their vibrant colors and simple elegance, are a favorite among garden enthusiasts and floral admirers alike. But how long do these captivating flowers last? That's exactly what we're here to explore. In the next few paragraphs, we'll delve into the life cycle of a tulip, understanding its stages from seed to bloom and everything in between. We'll also examine various external and internal factors that play pivotal roles in the lifespan of these radiant flowers. Plus, we'll share some proven tips and tricks to aid in enhancing the longevity of your tulip blooms, ensuring that they continue to add splashes of color and charm to your surroundings for longer periods. So, are you ready to journey into the intricate, fascinating life of a tulip? Join us as we first take a closer look at a tulip's life cycle, and learn its stages to appreciate the intricacies of this flower's existence.
Tulips, known for their vibrant colors and simple elegance, are a favorite among garden enthusiasts and floral admirers alike. But how long do these captivating flowers last? That's exactly what we're here to explore. In the next few paragraphs, we'll delve into the life cycle of a tulip, understanding its stages from seed to bloom and everything in between. We'll also examine various external and internal factors that play pivotal roles in the lifespan of these radiant flowers. Plus, we'll share some proven tips and tricks to aid in enhancing the longevity of your tulip blooms, ensuring that they continue to add splashes of color and charm to your surroundings for longer periods. So, are you ready to journey into the intricate, fascinating life of a tulip? Join us as we first take a closer look at a tulip's life cycle, and learn its stages to appreciate the intricacies of this flower's existence.1. Understanding the Tulip Life Cycle
The remarkable cycle of the tulip, from a humble seed to a radiant blossom, is a masterstroke of nature. This article delves deep into understanding the tulip life cycle, deciphering the intricate biological mechanisms at its core, probing the distinct stages of growth, and shedding light on its riveting stage of dormancy. Tulips are world-famous for their vibrant colors and aesthetic grace, but the underlying biology that orchestrates this phenomenal onset of beauty is just as fascinating. In the section, 'Exploring the Biology of Tulips', we unravel the detail-specific elements and mechanisms that contribute to the formation of these floral beauties. Through the 'Growth Period of Tulips', a detailed exposition of every stage of the plant's life, from germination to the bloom, is presented, offering insights into the conditions that influence tulip growth. From there, the focus shifts to 'The Dormancy Stage in Tulips', an often overlooked yet crucial period in the tulip life cycle that has profound implications for its survival and propagation. Embark on this scientific journey into the life of tulips, beginning with an in-depth examination of their fascinating biology.
A. Exploring the Biology of Tulips
Tulips, belonging to the Liliaceae family, are one of the most popular and colorful spring-blooming flowers. Their biology is as captivating as their beauty, having a life cycle that may seem complex but is fascinatingly systematic. This fact is crucial when it comes to understanding how long tulips last. The biology of a tulip begins with a bulb, tulips' primary method of propagation. Within this bulb are all the necessary nutrients and energy reserves that a tulip requires to bloom. The bulb also contains the embryo of a new plant, encapsulated to protect the future flower through cold winter months. Through a process known as vernalization, the tulip bulb develops its roots during winter, preparing for the growth spurt of spring. Experience in gardening or biological wisdom is not necessary to appreciate the beauty of a tulip. However, knowing that its vibrant color results from a complex mixture of pigments in the petals, can deepen our appreciation. For instance, anthocyanins responsible for the vibrant hues ranging from red, purple to blue. Carotenoids contribute to the yellows and oranges, and flavonols attribute to a lighter yellow or white colors. These pigments interact to create an array of tulip colors and patterns, a feat of nature that leaves us in awe each springtime. The anatomical structuring of tulips too plays a significant role in their life cycle. The tulip’s style, the tapered stalk that holds the pollen-covered stigma aloft, spite being almost microscopic, serves the significant function of assisting in pollination. The tulips’ beautifully-shaped petals not only add to their aesthetic appeal but also function as a protective covering for the reproductive parts. The tulip’s biology is intimately linked to its environment. They prefer a cool, dormant period in the fall and winter, to gear up for their vibrant bloom in the spring. When these environmental conditions are manipulated, as in a carefully regulated greenhouse environment, tulips can be tricked into blooming out of season. Knowledge of tulip biology can be incredibly useful for those aiming to extend their tulips' lifespan or manipulate their bloom time. By controlling the bulb’s access to water, light, and temperature, one can encourage early or late blooming, and extend the life of these beauties. This reveals an interesting intersection between botanical science and the art of gardening. Understanding the biology of tulips can help in predicting their longevity. Given their biological and environmental needs, tulips can last from 1 week to around a month in bloom. The ongoing cycle from bulb to flower, regeneration, and dormancy forms the basis of tulips' durability and consistent return every spring. Therefore, the life cycle and biology of tulips are key contributors to their resilience, making them a perennial favorite in gardens across the globe.
B. Growth Period of Tulips
B. Growth Period of Tulips The growth period of tulips is quite fascinating, a true testament to the miracle of nature. This stage in the tulip life cycle is characterized by a bounty of change and development. After successful planting, which typically occurs in the fall, tulips embark on a journey of transformation in the spring where they burst through the soil's surface with a captivating spectacle of color. During the growth period, tulips diligently photosynthesize, converting sunlight into energy to fuel their progression. This is a fundamental process ensuring their development from barely-there shoots to stunning blooms, commanding admiration from all who behold them. Spring's conducive climate paves the way for the tulips to grow rapidly. It is during this period that the tulips’ stems thicken and lengthen, their leaves unfurling as their buds become more pronounced. In this phase, tulips require special attention and care from gardeners. Ensuring they receive six to seven hours of sunlight daily and watering them judiciously (since they have a relatively low tolerance for excess moisture) can help optimize their growth. Conversely, overlooking these needs may hamper the tulips’ development, leading to less than optimal blooms or, in extreme cases, their premature demise. Growth periods vary among tulip types, echoing the rich biodiversity within this stunning flower species. Some tulips, like the Single Early and Double Early varieties, have shorter growth periods, with their radiant blossoms appearing earlier in spring. Others, like the late-blooming Single Late and Parrot tulips, require longer growth periods to develop their intricate and flamboyant blooms. Within this growth period dwell plentiful tales of change and metamorphosis - the manifold processes working in harmony to convert a humble bulb into an awe-inducing bloom. The cultivation journey during this phase, though labor-intensive, rewards gardeners with a vibrant display that succinctly encapsulates the cyclical beauty of life. Consequently, understanding this stage contributes significantly to mastering the tulip’s life cycle and effectively prolonging their bloom period for sustained visual pleasure. Each stage, from shoot to bloom, is essential in this intriguing cycle, the growth period, however, holds substantial weight, defining the success of the bloom and the extent of its enchanting spectacle.
C. The Dormancy Stage in Tulips
C. The Dormancy Stage in Tulips
In the multifaceted life cycle of a tulip, one of the most fascinating and crucial phases is the dormancy stage, often referred to as the bulb's "sleeping" phase. This phase, generally occurring in the late summer and fall after the growing season, plays a pivotal role in the perennial recurrence of these colourful flowers. As the foliage fades and withers, the bulb redirects its energy to its core. This transition is not a sign of an ending, but a testament to the tulip's resilience and adaptation. The journey to dormancy starts when the bloom period concludes. The initial appearance of wilting is not, in fact, indicative of a health issue or poor maintenance. Instead, it signifies the tulip's preparation for the future blooming season. The bulb enters a rest period, absorbing nutrients from the dying leaves and storing them for future growth. This process results in a stronger tulip plant that is better equipped to thrive in the subsequent year. Throughout this resting phase, the bulb undergoes several changes. It becomes dormant and dries out, building a hardened shell designed to protect it against inclement weather conditions and opportunistic pests. This hardening also helps to maintain the stored nutrients, promoting survival and future bloom. Another key facet of the dormancy stage is the division of the tulip bulb. During this period, the central bulb will often split into smaller bulblets which can be replanted to produce new flowers. This natural propagation allows for an expanding tulip dynasty, replicating the beauty of the parent plant in new locations. As autumn takes hold and winter draws near, the tulip remains in its dormancy stage, bracing for the cold months ahead. It's a period of rest and rejuvenation, a strategic and essential pause in preparation for the brilliant resurrection of colors and vibrancy in the spring. The dormancy stage in the tulip’s life cycle is a testament to the unmatched resilience of nature, a proof of the saying that sometimes, taking a step back is necessary for a greater leap forward. In understanding the life cycle of a tulip, appreciating the dormancy stage is essential. It's a quiet, yet busy time, where the tulip fortifies itself for future blossoming, proving that every moment in a tulip's life cycle, whether visibly beautiful or silently productive, bears significant importance. Welcome each stage with understanding and patience, providing optimal care and support - the rewards, in turn, are a bounty of vibrant tulip blooms when spring rolls back around.2. Factors Influencing The Lifespan of Tulips
The lifespan of tulips is not just haphazardly determined; it can be profoundly affected by various factors. Understanding these factors plays an integral role in fostering the bloom and longevity of these beautiful flowers. Three crucial elements play pivotal roles in shaping a tulip's lifespan, namely the impact of climate and weather conditions, the role of soil and nutrient management, and the influence of bulb quality and care. Climate and weather conditions are elemental to the longevity of tulips. Tulips, originally from the cool climes of the Himalayas and Eastern Turkey, have a predisposition to cold winters and long, cool springs. They long for a period of winter chill to enable healthy blooming in spring. Temperature fluctuations, precipitations, and other environmental elements can remarkably impact the tulips' growth cycle, health, and longevity. Given the direct influence of weather on tulips, gardeners must keep an eye on weather patterns and adapt their planting techniques accordingly. In the forthcoming section, we shall delve deeper into how climatic conditions influence the lifespan of tulips.
A. Impact of Climate and Weather Conditions
A. Impact of Climate and Weather Conditions on Tulips' Lifespan
The environment and weather conditions significantly influence the lifespan of tulips. Unraveling the complexity of these factors, climate and weather, it becomes clear that they hold a tremendous impact on the viability and longevity of these popular perennials. The climate in particular, holds a cardinal role in determining the growth and vitality of tulips. Ideally, these flowers flourish in areas with long, chilly winters and hot, dry summers, reminiscent of their natural home in the mountains of Turkey. This denotes the tulip's requirement for a cold resting phase, known scientifically as vernalization, where temperatures drop below 45 degrees Fahrenheit for a at least 12 weeks. It's during this period where the tulip bulbs prepare and foster the foundation of the sprouting flowers. Hence, regions with insufficiently cold winters can find their tulips struggling to bloom or even surviving, subsequently diminishing their lifespan. Turning to the intricacies of weather, a few elements stand out. Firstly, rainfall, or the lack thereof, impacts tulip vitality. While excessive moisture can lead to bulb rot, too little can result in undernourished and weakened plants. Tulips ideally require a well-draining soil that retains just enough moisture for growth but does not pool water. Secondly, sunshine plays a pivotal role. Direct, bright sunlight for at least half a day assists these photophilous flowers in synthesizing nutrients efficiently through photosynthesis, enhancing their strength and lifespan. Additionally, erratic or extreme weather conditions such as hailstorms, floods, or heatwaves can cause irreparable damage to the sensitive tulip plants, consequently affecting their durability. In conclusion, acknowledging the role that climate and weather conditions play in influencing the lifespan of tulips can provide invaluable insight for their successful cultivation. By offering a supportive environment that mimics their native conditions, one enhances their chance of having a garden teeming with vibrant, long-lived tulips. Though climate and weather are just two pieces of the puzzle, understanding their impact indeed provides a more comprehensive view of the factors influencing the lifespan of tulips. Thus, the nurturing hand of a gardener that understands this can cultivate tulips more adeptly, having the potential to extend their floral sojourn significantly.B. The Role of Soil and Nutrient Management
B. The Role of Soil and Nutrient Management The health and longevity of tulips are largely dependent on the role played by soil and nutrient management — a critical aspect that cannot be overlooked when discussing factors that influence the lifespan of tulips. The type of soil in which tulips are planted, its pH level, its nutrient content, and overall management significantly impacts how long these beautiful perennial plants can thrive and bloom. The ideal soil for tulips is a well-draining type, like sandy or loamy soil. These soils allow water to drain quickly, preventing the risk of waterlogging and root rot, two conditions that can considerably shorten the lifespan of the tulips. Moreover, a soil pH range of 6 to 7 is optimal for tulips, allowing them to absorb necessary nutrients effectively, and contributing to their overall health and longevity. Nutrient management also plays a pivotal role in the lifespan of tulips. These resplendent flowers require a healthy combination of nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium for growth and development. Nitrogen aids in creating vibrant and healthy foliage, while phosphorus helps in root and bulb formation. Potassium, on the other hand, strengthens the stems and also contributes to the color and size of the blooms. Consistently ensuring these nutrients are available in adequate amounts in the soil will markedly prolong the lifespan of the tulips. An effective soil and nutrient management strategy includes frequent soil testing to monitor pH and nutrient levels, timely application of fertilizers, and proper practices to avoid soil degradation or pest infestation. Mulching can also help in retaining moisture in the soil while simultaneously breaking down to provide additional organic matter. These practices guarantee that the soil remains healthy, which is an essential prerequisite for the long life and vibrant blossom of tulip plants. In conclusion, the role of soil and nutrient management is paramount in determining the lifespan of tulips. By understanding and implementing these key practices, one can ensure the successful growth of tulips, contributing to their longevity, and continually enjoy their burst of spring splendor.
C. Influence of Bulb Quality and Care
C. Influence of Bulb Quality and Care on the Lifespan of Tulips
Tulip bulbs' quality, and the care they receive form the nucleus of the numerous factors influencing their lifespan. Each tulip bulb carries a storehouse of the plant's genetic material, and its quality and subsequent care affect the long-term vitality, vibrancy, and longevity of tulips. The selection of higher quality, disease-free bulbs sets the trajectory for an extended lifespan. Healthier bulbs are identifiable by their firm texture, larger size, and absence of visual defects or disease spots. On the other side of the equation is bulb care, equally possessing considerable influence. Initial care begins even before planting. Correct storage, that is cool, dry, and well-ventilated conditions, maintain the bulb’s vigor until planting time. An optimal planting depth and location, with an ample balance of sunlight and shade, creates an environment conducive to the bulb’s growth and longevity. A nutrient-rich soil, with an appropriate pH level, nourishes the bulb, further prolonging its lifespan. Post-planting care is a diligent process. Regular, clockwise bulb rotation maintains balanced light exposure, promoting even growth. Consistent watering without waterlogging the soil keeps the bulb hydrated yet prevents rot. Besides, periodic bulb inspections reveal potential infections or pests, and prompt treatment helps retain the bulb’s health. Moreover, seasonal care is a deciding factor in tulip longevity. During dormancy after the bloom, the leaves photosynthesize and replenish the bulb’s nutrient store for the next growth cycle. Removing spent flowers but leaving the leaves untouched allows this essential process. An appropriate fertilization schedule fulfills the bulb’s nutritional needs, providing an additional headway toward an extended life cycle. Thus, the influence of bulb quality and care on the lifespan of tulips is multi-faceted and interconnected, encompassing selection, storage, planting conditions, regular maintenance, and systematically fulfilling the plant’s changing seasonal needs. Ensuring these aspects translates into tulips that not only last longer but also bloom with vibrant vigor year after year.3. Tips to Promote Longevity in Tulips
Tulips, with their radiant hues and expressive blooms, have long been a symbol of new beginnings and the charm of springtime. Cultivating a vibrant and resilient tulip garden involves more than just planting and hoping for the best. There are definite, evidence-backed techniques that can dramatically enhance the lifespan and vibrancy of these gorgeous flowers. This article aims to provide you with three key tips to promote longevity in tulips—namely, understanding proper watering techniques, effectively controlling pests and diseases, and mastering the art of appropriate pruning and deadheading. Fostering tulips requires a delicate balance of attention and knowledge, and mastering these three areas can significantly improve your tulip gardening journey. Our initial discussion dives into one of the most critical factors for tulip survival: Proper watering. A nuanced understanding of watering techniques can mean the difference between a garden of flourishing tulips and a disappointing wilted patch. Let's delve into these crucial components to ensure your tulips aren't just surviving, but thriving.
A. Proper Watering Techniques for Tulips
Proper watering is a critical aspect to ensure the longevity of tulips—often, people believe it's simply about watering every day, but that is not the case. Understanding the watering requirements of tulips is imperative to nurturing a vibrant and lasting bloom. Tulips, hailing from the often dry mountainous regions of Persia and Turkey, are perfectly adapted to less frequent watering. They thrive best when the soil can dry out fully in between watering, so daily watering can actually lead to detrimental effects like bulb rot and disease susceptibility. Overwatering is one of the primary errors of tulip care, but determining the right amount is not as complex as it seems. An easy rule to follow is the 'soak and dry' technique—water your tulips deeply, then allow the soil to dry out completely. The drying out period welcomes the growth of strong, healthy roots which are essential for a long-lasting bloom. Typically, tulips need to be watered once a week if there has been no rainfall. However, it's important to remember that these needs may fluctively increase in particularly dry spells or peak summers. Another important point to consider while watering is the time of day. It's advisable to water in the early morning or late evening when temperatures are cooler. This minimizes evaporation and ensures maximum hydration. Additionally, aim to water at the bases of your plants, avoiding overhead watering. This prevents your tulips from experiencing unnecessary dampness on their petals and leaves that can potentially lead to fungal diseases. In essence, promoting a long-lasting, healthy tulip garden doesn't require constantly moist soil—it requires intelligent, strategic watering. If your tulips are watered correctly with deep, planned watering, protected from harmful elements, and given the chance to dry completely, they have a significantly higher likelihood of surviving longer and more vibrantly. As is often the case with nature, more is not always better. A little can go a long way in ensuring the beauty and longevity of your tulips.
B. Effective Pests and Disease Control
Effective pests and disease control is an integral part of promoting longevity in tulips. A healthy tulip is a long-lasting tulip, and despite their renowned robustness, these perennial blooms are not immune to various pests and diseases. These threats, if not effectively managed, can greatly shorten the lifespan of tulips, transforming them from a beacon of beauty into a pitiful sight. With right knowledge and preventive measures, you can maintain the vibrancy of tulips for lengthy periods. Firstly, aphids, snails, and rodents are common pests that pose a significant threat to tulips. These pests are attracted to the bright colors and sweet nectar of tulips, making them the likely culprits in case of obvious physical damage or impaired growth of your tulips. Crucially, creating an unfavorable environment for these pests, such as fostering predatory insects and using natural repellents, provides a natural and eco-friendly method of control. Moreover, tulips are also susceptible to fungal diseases like tulip fire and gray mold, often manifested in discoloration and rotting of the bloom. The key to combat these diseases lies in a healthy and clean planting environment. As a preventive measure, invest in disease-resistant tulip bulbs, ensure adequate spacing between plants for good air circulation, and implement regular cleansing of your garden to remove plant debris that may harbor pathogens. Lastly, bacterial diseases, mostly soft rot, are not rare for tulips. In case of infection, the bulb becomes discolored and emits a foul odor as it slowly decays. The best practice here is again prevention. Always select firm, healthy bulbs for planting, avoid waterlogging, and adapt crop rotation in your garden to reduce disease build-up in the soil. In severe cases, resorting to bactericidal treatments may be necessary for disease control. In conclusion, effective pests and disease control forms the backbone of a vigorous, long-lasting tulip. It requires fervent attention, careful strategy, and proactive decision-making. By implementing these measures, not only do we promote the longevity of our beloved tulips, but also align ourselves with the broader objectives of biodiversity conservation and sustainable gardening.