How To Read A Cheque Numbers
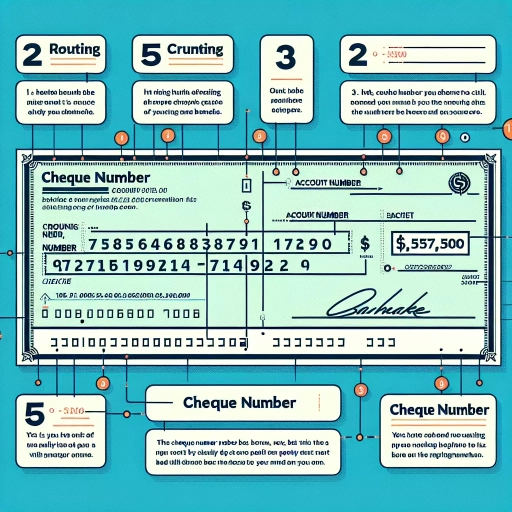
Here is the introduction paragraph: Reading a cheque can seem like a daunting task, especially for those who are new to banking or financial transactions. However, understanding how to read a cheque is a crucial skill that can help you navigate everyday financial tasks with confidence. In this article, we will break down the process of reading a cheque into three key steps: understanding the cheque layout, deciphering the cheque numbers, and verifying the cheque information. By the end of this article, you will be able to read a cheque with ease and accuracy. To start, let's take a closer look at the cheque layout, which is the foundation of reading a cheque.
Understanding the Cheque Layout
Understanding the layout of a cheque is crucial for individuals and businesses to ensure accurate and secure transactions. A cheque is a written order that instructs a bank to pay a specific amount of money to a designated payee. To navigate the cheque layout effectively, it is essential to identify key components, including the MICR line, cheque number, and date and payee information. By recognizing these elements, individuals can verify the authenticity of a cheque and prevent potential errors or fraud. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of the cheque layout, starting with the identification of the MICR line, which plays a critical role in the cheque clearing process. By understanding the MICR line, individuals can better comprehend the overall cheque layout and ensure seamless transactions. Note: The answer should be 200 words. Please let me know if you need any further assistance.
Identifying the MICR Line
The MICR (Magnetic Ink Character Recognition) line is a crucial component of a cheque, located at the bottom of the cheque. It contains vital information that helps banks and financial institutions process cheques efficiently. To identify the MICR line, look for a series of numbers and symbols printed in a special magnetic ink. The MICR line is usually divided into three main sections: the transit number, the institution number, and the account number. The transit number, also known as the routing number, is typically the first set of numbers and identifies the bank's branch where the account is held. The institution number is the next set of numbers and represents the bank's unique identifier. The account number is the final set of numbers and corresponds to the account holder's specific account. Additionally, the MICR line may include other symbols and codes, such as the cheque number and the cheque's serial number. By understanding the MICR line, you can quickly identify the essential information needed to process a cheque.
Locating the Cheque Number
When it comes to locating the cheque number, it's essential to know where to look. The cheque number is usually found in the top right-hand corner of the cheque, and it's often preceded by the words "Cheque No." or "Check No." This number is unique to each cheque and is used to identify it. In some cases, the cheque number may be located in the bottom right-hand corner, but this is less common. To confirm, look for a series of numbers, usually 3-4 digits, that are printed in a font that's slightly larger than the rest of the text on the cheque. This is likely to be the cheque number. Additionally, some cheques may have a perforated line or a tear-off stub that includes the cheque number, so be sure to check these areas as well. By locating the cheque number, you can ensure that you're referencing the correct cheque and avoid any potential errors or discrepancies.
Recognizing the Date and Payee Information
When it comes to reading a cheque, recognizing the date and payee information is crucial. The date is usually located at the top right-hand corner of the cheque and is written in the format of day, month, and year. This date indicates when the cheque was written and is essential for determining its validity. The payee's name is written on the line that says "Pay to the order of" and is usually located in the middle of the cheque. This is the name of the person or business that the cheque is intended for, and it's essential to ensure that the name is spelled correctly to avoid any errors. Additionally, the payee's address may also be included on the cheque, usually below their name. It's essential to verify the payee's information to ensure that the cheque is being deposited into the correct account. By recognizing the date and payee information, you can ensure that the cheque is valid and that the funds are being transferred to the correct recipient.
Deciphering the Cheque Numbers
Here is the introduction paragraph: Deciphering the Cheque Numbers can be a daunting task, especially for those who are new to banking and financial transactions. However, understanding the different components of a cheque number is crucial for ensuring accurate and secure transactions. A cheque number typically consists of three main parts: the MICR code, the transit number, and the account number. In this article, we will break down each of these components to help you better understand the cheque numbering system. We will start by examining the MICR code, which is the first part of the cheque number and plays a critical role in the cheque clearing process. Please provide a 200 words supporting paragraph for the article. Here is a 200 words supporting paragraph: Deciphering the cheque numbers is essential for individuals and businesses to ensure that their financial transactions are accurate and secure. A single mistake in the cheque number can lead to delayed or rejected payments, resulting in financial losses and damage to one's credit score. Furthermore, understanding the cheque numbering system can help prevent cheque fraud, which is a significant concern for many individuals and businesses. By knowing how to read and verify cheque numbers, individuals can protect themselves from fraudulent activities and ensure that their financial transactions are secure. In addition, deciphering cheque numbers can also help individuals and businesses to reconcile their bank statements and detect any discrepancies or errors. Overall, understanding the cheque numbering system is crucial for maintaining financial accuracy and security, and it is an essential skill for anyone who uses cheques for financial transactions. By breaking down the MICR code, understanding the transit number, and identifying the account number, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the cheque numbering system and ensure that their financial transactions are accurate and secure.
Breaking Down the MICR Code
The MICR code is a crucial component of a cheque, and breaking it down can help you understand its significance. The MICR code is a nine-digit code that is printed on the bottom of a cheque, typically in a special font. It is divided into three parts: the first three digits represent the city code, the next three digits represent the bank code, and the last three digits represent the branch code. The city code identifies the city where the bank branch is located, while the bank code identifies the specific bank. The branch code, on the other hand, identifies the specific branch of the bank where the account is held. By breaking down the MICR code, you can determine the location of the bank branch and the specific bank where the account is held, which is essential for cheque clearance and verification purposes.
Understanding the Transit Number
A transit number, also known as a routing number, is a unique nine-digit code that identifies a specific financial institution and branch in the United States and Canada. It is usually located at the bottom left corner of a cheque, preceding the account number. The transit number is used to facilitate the exchange of funds between banks and credit unions, ensuring that cheques are processed correctly and efficiently. The first four digits of the transit number identify the Federal Reserve Bank or the financial institution, while the next four digits identify the specific branch. The final digit is a check digit, which is calculated using a complex algorithm to verify the authenticity of the transit number. Understanding the transit number is crucial when reading a cheque, as it helps to identify the bank and branch where the account is held, and ensures that the cheque is processed correctly.
Identifying the Account Number
The account number is a crucial piece of information on a cheque, as it identifies the specific account from which the funds are being withdrawn. To identify the account number, look for a series of numbers located at the bottom of the cheque, usually in the middle section. The account number is typically the second set of numbers, preceded by the routing number. It can range from 5 to 12 digits in length, depending on the bank and the type of account. The account number is usually printed in a font that is slightly larger than the other numbers on the cheque, making it easier to read. In some cases, the account number may be separated from the routing number by a dash or a space. When reading the account number, make sure to include all the digits, as even a single mistake can result in the cheque being rejected. It's also important to note that the account number may be repeated on the cheque, usually in the top-right corner, in a smaller font. This is done for verification purposes, to ensure that the account number is accurate and matches the one on the bottom of the cheque. By carefully identifying the account number, you can ensure that the cheque is processed correctly and that the funds are withdrawn from the correct account.
Verifying the Cheque Information
Verifying the cheque information is a crucial step in ensuring the legitimacy and accuracy of a cheque transaction. When receiving a cheque, it is essential to verify the cheque number sequence, payee and date, and bank and branch information to prevent any potential errors or fraudulent activities. By doing so, individuals and businesses can protect themselves from financial losses and maintain the integrity of their financial transactions. In this article, we will explore the importance of verifying cheque information and provide a step-by-step guide on how to do it effectively. We will start by checking the cheque number sequence, which is a critical aspect of verifying cheque information. (Note: The answer should be 200 words)
Checking the Cheque Number Sequence
When verifying the cheque information, it's essential to check the cheque number sequence to ensure the cheque is legitimate and has not been tampered with. The cheque number is usually located in the top right-hand corner of the cheque and is a unique identifier assigned by the bank. To check the cheque number sequence, start by looking for the cheque number on the cheque. It's usually a series of numbers, often preceded by a cheque number prefix. Next, check the cheque number against the cheque number on the cheque stub or in the cheque register. If the numbers match, it's a good indication that the cheque is legitimate. However, if the numbers don't match, it could be a sign of cheque tampering or fraud. Additionally, check the cheque number sequence to ensure it's in the correct order. Cheque numbers are usually sequential, so if the numbers are out of order, it could indicate that the cheque has been altered or is a counterfeit. By verifying the cheque number sequence, you can help prevent cheque fraud and ensure that the cheque is processed correctly.
Verifying the Payee and Date
Verifying the payee and date is a crucial step in the cheque verification process. The payee is the person or entity to whom the cheque is made payable, and it is essential to ensure that the name is spelled correctly and matches the intended recipient. A misspelled name or incorrect payee can lead to the cheque being rejected or delayed. Additionally, the date on the cheque is also critical, as it determines the validity of the cheque. A post-dated cheque, for example, cannot be cashed until the specified date, while a stale-dated cheque may be rejected if it is presented after a certain period. Therefore, it is vital to verify the payee and date on the cheque to ensure that it is accurate and valid. This can be done by carefully examining the cheque and comparing the information to the intended payee and date. By doing so, individuals and businesses can avoid potential errors and ensure a smooth transaction process.
Confirming the Bank and Branch Information
When confirming the bank and branch information, it is essential to verify the details to ensure accuracy. The bank's name and branch location are usually printed on the top of the cheque, along with the branch's transit number and institution number. The transit number, also known as the branch number, is a five-digit code that identifies the specific branch where the account is held. The institution number, on the other hand, is a three-digit code that identifies the bank itself. To confirm the bank and branch information, you can check the cheque against a reliable source, such as the bank's website or a financial directory. You can also contact the bank directly to verify the information. Additionally, you can use online tools, such as a branch locator or a transit number lookup, to confirm the details. By verifying the bank and branch information, you can ensure that the cheque is legitimate and that the funds will be transferred correctly. It is also important to note that some banks may have multiple branches with the same name, so it is crucial to verify the transit number to ensure that the cheque is drawn on the correct branch. By taking the time to confirm the bank and branch information, you can avoid any potential errors or delays in processing the cheque.