How Does A Furnace Work
 Whether you are researching efficient home heating or simply curious about how the central heating system in your abode works, understanding the inner mechanics of a furnace is fascinating and valuable. This article will dive deep into the operational intricacies of a modern furnace, shedding light on the core elements that ensure comfort during winter's deepest freeze. We will first demystify the concept by breaking down the essential components of a furnace, enabling you to comprehend how all the parts connect and function in harmony. Following that, we will explore the complex process of heat generation; how does the furnace create heat from its fuel source and equally distribute it in your home? Lastly, we'll delve into the critical topic of furnace efficiency and the importance of regular maintenance, vital for ensuring optimal functioning. If you're ready to embark on this educative journey, our first stop is 'understanding the essential components of a furnace.'
Whether you are researching efficient home heating or simply curious about how the central heating system in your abode works, understanding the inner mechanics of a furnace is fascinating and valuable. This article will dive deep into the operational intricacies of a modern furnace, shedding light on the core elements that ensure comfort during winter's deepest freeze. We will first demystify the concept by breaking down the essential components of a furnace, enabling you to comprehend how all the parts connect and function in harmony. Following that, we will explore the complex process of heat generation; how does the furnace create heat from its fuel source and equally distribute it in your home? Lastly, we'll delve into the critical topic of furnace efficiency and the importance of regular maintenance, vital for ensuring optimal functioning. If you're ready to embark on this educative journey, our first stop is 'understanding the essential components of a furnace.'
Understanding the Essential Components of a Furnace
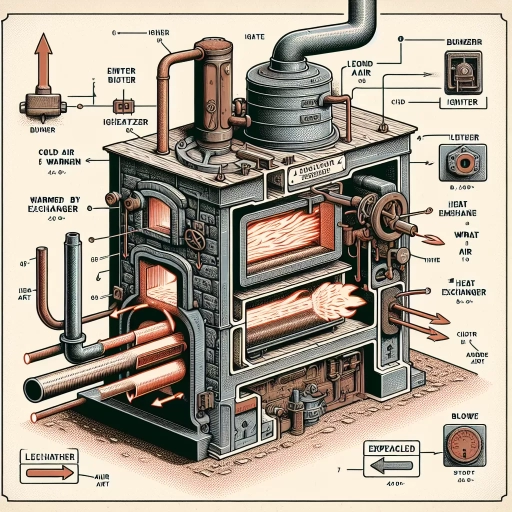
Understanding the core components of a furnace is vital to maintain its functionality and your comfort throughout the winter season. This article will dissect the integral parts, illustrating the operations of the burner and the combustion chamber, the heat exchanger and the blower, and the flue and venting system. Comprehending their roles not only adds to your technical knowledge but may also prove beneficial, especially when encountering heating issues. Firstly, let's turn up the heat by discussing the heart of the furnace - the burner and the combustion chamber. This is where the magic, or more appropriately the combustion, happens, turning cold air into comforting warmth. Arriving armed with a deeper understanding of how these components work together will aid in early trouble detection, facilitating smoother maintenance sessions and averting potential mishaps. To further keep your home toasty, the voyage continues as we delve into the unique roles of the heat exchanger and the blower, an duo where one wouldn't function optimally without the other. Lastly, our journey within the furnace concludes featuring the flue and venting system - an often-overlooked yet crucial aspect of your heating system. Now, let's embark on this enlightening expedition into the burner and the combustion chamber.
The Burner and the Combustion Chamber
The Burner and the Combustion Chamber are indispensable entities in a furnace's anatomy, integral to its overall functionality. The burner, often fueled by natural gas or propane, ignites to generate a flame - a crucial step in the process of getting your furnace to work. Once the gas valve opens, the burner combusts the gas to create this necessary heat. Essentially, think of it as the heart of a furnace, incessantly pumping out heat to keep your space warm. Following the burner is the robust combustion chamber. This pivotal compartment is where the magic really happens. It's no small feat, for within its confines, the chemical conversion of fuel into heat energy occurs. Securely connected to the burner, the combustion chamber dutifully houses the flame. It ensures the combustion process occurs safely and efficiently, away from any sensitive parts of the furnace that could be damaged by the intense heat of the flame. Together, the burner and combustion chamber form an intricate dance of heat production and control, titrating the harshest elements to keep your unit working safely. They are the furnace's workhorses - unyielding, robust, and essential to its operation, transforming cold, crisp air into a warm, cozy ambiance. This deep understanding of the essential components of a furnace, especially the role these two parts play, allows us to appreciate our heating systems more. Knowing the principle behind how a furnace works not only provides us with useful knowledge for basic troubleshooting but also allows us to make informed decisions when the time comes for maintenance or purchasing a new unit. This embodiment of thermodynamic brilliance underscores how these seemingly unfathomable appliances are designed to provide us with the basic human need for warmth. Remember, every time we enjoy our heated rooms during harsh winters, it's the diligences of the burner and the combustion chamber working in harmony that we have to thank. Their roles within the complex mechanics of a furnace are indispensable and central to its function, truly an epitome of engineering marvel.
The Heat Exchanger and the Blower
The Heat Exchanger and the Blower components of a furnace play pivotal roles in the overall function of the furnace. They are essential elements that serve in pushing the warm air and circulating it throughout your living space while ensuring safety. The heat exchanger is a critical component responsible for heating the air. Its unique, robust design consists of various tubes or coils that can withstand high temperatures. The exchanger heats the air as the furnace burns the fuel — gas or oil. After the combustion process, the created heat transfers to the metal walls of the exchanger, warming the circulating air without directly exposing it to the flame. However, the heat exchanger also serves a safety role. The burning fuel produces harmful gases, such as carbon monoxide, which can be detrimental if released into the living environment. The heat exchanger, when working correctly, acts as a barrier, keeping these harmful gases contained and safely venting them outside through an exhaust vent. Simultaneously, the blower, also known as the fan, kicks in. Once the air is sufficiently heated by the heat exchanger, the blower propels this warm air into the air ducts, which then distribute it throughout your home. It's the powerhouse of air circulation within the furnace system. This unassuming component is driven by a motor whose speed can typically be adjusted to control the amount of heated air pumped into your living space. The blower, therefore, helps in maintaining the desired room temperature with uniform heat delivery. Both the heat exchanger and the blower work hand-in-hand in ensuring that your furnace operates efficiently and safely. Regular maintenance of these components is essential to prolong the furnace's lifespan and prevent common problems that might cause inefficiency or potential risks such as gas leaks. Understanding these vital components provides a more profound comprehension of how your heating system works, and highlights the significance of choosing quality components and ensuring regular maintenance.
Flue and Venting System
Flue and Venting System An essential component of any furnace which is integral to its effective and safe operation is the flue and venting system. This system is designed to safely divert combustion byproducts, such as harmful gases and particulate matter, from your furnace to the outdoors. Its role is of paramount importance because if these toxic byproducts don't get adequately vented, it could potentially lead to lethal carbon monoxide build-up inside the house. Flues work with the assistance of the natural principle of hot air rising. As the furnace heats the air, it becomes lighter, urging it to move upwards and out through the flue. The construction of the flue allows this harmful air to exit the furnace without mingling with the clean, warmed air that's being disseminated in your home. Modern venting systems are also equipped with a draft inducer fan. This fan helps to push the exhaust gases up the flue, making the process more efficient. It also ensures that your furnace performs at its optimum level. To work well, draft inducers need to maintain a delicate balance between the air pressure inside and outside the flue to enable the safe transport of gases. The vent pipe, which is part of the venting system, is specially designed to withstand the acidic nature of flue gases, preventing leakage and damage over time. Some advanced systems use double-walled vent pipes to enhance safety and efficiency. The interior pipe carries out the flue gases, while the exterior one circulates fresh air into the furnace. This design helps in preheating the combustion air and cooling the flue gases, ensuring increased efficiency and safety. In essence, the flue and venting system is the furnace's defensive shield, protecting the home and its occupants from potential harm. It also supports the effective functioning of the furnace, enabling it to generate heat economically and efficiently. So while it's behind-the-scenes equipment, it's absolutely vital to your home's comfort and safety. Understanding this component is critical to appreciate how a furnace works and the importance of regular maintenance to ensure its longevity and effectiveness.
The Process of Generating Heat
The process of generating heat is a complex and fascinating science, inequitably embedded in our everyday lives. In an effort to fully illuminate this process, this article will break down the finer details, exploring three core elements: Igniting the Burner, Heat Exchange and Distribution, and finally, Exhaust and Emission. Initially, we will delve into the Ignition of the Burner, a fundamental crux of any heat generating system. From there, we will explore the nuanced mechanisms of Heat Exchange and Distribution, demonstrating how the power of one tiny flame can be harnessed and proliferated throughout a system. Finally, an understanding of heat's generation would be incomplete without discussing the process of Exhaust and Emission, an oft-overlooked but crucial facet of this energy transference. The wisdom lies in the detail, and as we journey from the elemental spark towards heat proliferation and its subsequent emissions, we embark on a fascinating exploration of the art and science of generating heat, starting with the critical first step of Igniting the Burner.
Igniting the Burner
In the heart of a furnace, the activity that fundamentally reignites warmth lies in igniting the burner. This integral procedure is the lifeblood of a well-functioning heating system. A furnace uses a series of operations to generate heat, with the ignition of the burner standing as a crucial stage within this intricate mechanical dance. As soon as the thermostat signals a drop beneath the preset temperature, the furnace springs to life, dutifully commencing it's vital task. This process is fundamentally fueled by the burner's ignition. However, the spark that produces the necessary heat isn't created by mere chance - there is an underlying science to it. When the thermostat calls for heat, the ignition process jumpstarts. In modern furnaces, electronic ignition systems have replaced the old method of constant pilot lights, resulting in higher efficiency and safety. These electronic systems, either in the form of intermittent pilots or hot surface igniters, only ignite the gas burner when required to heat the room. The core of the furnace, the burner, is what allows the fuel (usually natural gas or oil) to interact with the ignition source. When the burner ignites, a combustion reaction occurs that produces heat. This heat is then captured and dispersed by the furnace's heat exchanger, a series of coiled tubes designed to absorb and radiate heat. The intricacy of the burner's design ensures optimal fuel usage, creating efficient heating and maintaining stable, comfortable indoor temperatures. This delicate process is shrouded in a ruthless fidelity to efficiency, with every detail of igniting the burner optimized for safety and energy conservation - from the precision of gas release to the exact timing of the ignition spark. Improved over years of engineering research and application, current generation furnaces are a testament to seamless blending of utility, user convenience, and environmental stewardship. For those outside the HVAC industry, this complex process may seem intimidating. However, understanding how the furnace and its burner work helps consumers make better informed decisions about purchasing, operating, and maintaining their home heating systems. It exemplifies the beauty of engineering and sophistication of modern technology employed to create a comfortable living environment. In the grand scheme of generating heat within a furnace, igniting the burner is thus a crucial milestone. This step forms the foundation for successive operations in the heat generation process, propelling the furnace to fulfill its essential role in the domestic heating system.
Heat Exchange and Distribution
Heat exchange and distribution play a pivotal role in the process of generating heat within a furnace. This process is underpinned by the principles of thermodynamics, involving the transfer of thermal energy from a high to a low-temperature entity. At the heart of a furnace system, heat exchangers are remarkable devices capable of efficiently transferring heat from the combustion gases produced by burning fuel to the air blown through the furnace. This ingenious mechanism allows the furnace to consistently and effectively distribute heated air throughout a property, contributing to the overall efficiency and comfort offered by the heating system. The ingenious engineering and innovation behind heat distribution come into play once the heat exchanger has successfully absorbed the maximum amount of thermal energy from the combustion gases. It's at this juncture that a blower fan kicks into action, succinctly distributing this conditioned air throughout your home or property. This is often achieved through ductwork, effectively maintaining a warm and homely environment during those chilly months. What's particularly interesting about the heat exchange and distribution process is its cyclical nature. As the thermostat signals the need for more heat, the furnace springs into action, reheating air that is then circulated around the home. Once the desired temperature is reached, the thermostat signals the furnace to stop, until the cycle needs to be repeated. Understanding the mechanics of heat exchange and distribution isn't just beneficial from an academic standpoint. It can also empower homeowners and residents, allowing them to troubleshoot any potential heating issues or anomalies. Furthermore, this knowledge aids us in appreciating the complex nuances and intricate feats of engineering that contribute to bringing us the comfort we often take for granted. This realm truly is the unsung hero of the HVAC world, silently ensuring our environments remain at comforting temperatures. In conclusion, the process of heat exchange and distribution is a critical element of how a furnace operates. It follows a systematic and scientifically guided method which involves capturing, augmenting, and distributing heat - providing us with the warmth we need. Progress in heating technology and understanding these heating principles allows for continuous innovations and improvements, leading our quest for more energy-efficient and effective heating solutions in the future. As we span the bridge between the technical aspects of thermodynamics and the end-user experience in our homes, it's clear that the process of heat exchange and distribution is an truly integral part of how a furnace works.
Exhaust and Emission
Exhaust and Emissions in the Furnace Process A critical segment of understanding how a furnace works is grasping the concept of exhaust and emissions. The core of this process, the generator unit, works by kindling a fuel source – commonly natural gas, though propane and oil are also used – to heat a series of metal tubes or coils. A prevalent byproduct of this combustion process is exhaust gas, often comprising harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxide, and sulfur dioxide. Setting in motion the mechanics of a furnace, these gases play a significant role in generating heat. As the fuel burns, it triggers a chain of events where heat is transferred to air or water, which is then distributed throughout the respective system or space. Simultaneously, the exhaust gases are expelled from the system via a flue or exhaust vent. It is noteworthy that effective exhaust management is crucial, considering these gases are potentially harmful if not properly vented. Therefore, modern furnaces come with built-in safety mechanisms that guarantee that these gases are safely led out from the home or building. This combustion process has a crucial bearing on the furnace's efficiency and its carbon footprint. Lower quantities of these pollutants imply a cleaner and more efficient generation of heat. This is where emission control becomes pivotal. Advanced technologies in the latest models of these heating units focus on maximizing energy output while minimizing harmful pollutants helping in the production more heat per unit of fuel consumed, minimizing wastage and maximizing energy efficiency. However, it’s worth noting that excess heat generated can damage the furnace system or even elevate fire risks. Thus, an understanding of exhaust and emissions is not just about acknowledging the environmental implications but also about ensuring the safety and longevity of the system itself. Overall, the role of exhaust and emissions in the process of generating heat within a furnace interlinks several ends. In essence, it demonstrates the synchronous working of multiple parts and processes in creating and maintaining a warm and comfortable environment, all while endorsing responsible energy use and avoiding harmful emissions to the environment.
Furnace Efficiency and Regular Maintenance
The concept of Furnace Efficiency, Regular Maintenance, and their interconnected significance cannot be overemphasized for the maintenance of a warm and cozy atmosphere in your homes during bitterly cold days. Clarity on Furnace Efficiency Measurements, understanding the Importance of Regular Furnace Maintenance and gaining insights into Common Furnace-related Problems and Their Solutions can equip homeowners with valuable knowledge to effectively manage and optimize their heating unit's performance. Furnace Efficiency Measurements, the first among these topics, provide the crucial yardstick that helps ascertain the optimal functioning of your furnace. By measuring the amount of heat generated from the amount of fuel consumed, these measurements provide insightful data about your furnace's capabilities. In tandem, understanding the importance of regular furnace maintenance is key. It ensures the smooth running of the system, minimizing the potential of breakdowns, and ultimately saving cost. Lastly, having a grasp on common furnace-related problems and their solutions offers a proactive approach to avoiding major hassle or malfunction during those seemingly unbearable winter months. As we delve into this exploration, our focus will first be on the underestimated yet essential aspect, The Furnace Efficiency Measurements. This is one domain where a little knowledge can contribute to big savings and enhanced furnace functioning.
Furnace Efficiency Measurements
Furnace efficiency measurements are an essential aspect of understanding how a furnace works and ensuring its optimal functionality. The effectiveness of a furnace can be measured using a standard known as Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE). This metric determines the total efficiency of a furnace over the course of a year, taking into account the conversion of fuel into heating energy. A higher AFUE percentage indicates a more efficient furnace. Besides, furnaces with higher efficiency ratings often come with features like sealed combustion, variable speed blowers, and condensing technology, which further enhance their performance and reduce heat loss. Furnace efficiency not only impacts energy utilization but also influences environmental sustainability and household heating costs. An efficient furnace consumes less fuel, thus reducing carbon emissions and contributing to environmental conservation. Moreover, it provides effective heating solutions that bolster energy savings, resulting in lower utility bills. Relatively efficient furnaces can save homeowners hundreds or even thousands of dollars in energy costs over the furnace's lifetime. However, achieving and maintaining high furnace efficiency requires regular maintenance. A properly maintained furnace runs more efficiently, reduces energy consumption, and extends the system's lifespan. Regular furnace maintenance consists of inspecting and replacing the air filters, cleaning the blower, and ensuring the motor and blower assembly are in good working order. Furthermore, routine check-ups can identify potential problems early, allowing for cost-effective and timely repairs that prevent expensive breakdowns. Conclusively, understanding furnace efficiency measurements is crucial as it dictates the overall performance of the heating system. Higher efficiency means lower energy consumption, reduced environmental impact, and considerable savings on heating costs. However, to keep a furnace running at peak efficiency, it is crucial to perform regular system maintenance, ensuring long-lasting performance, cost savings, and a comfortable indoor environment. The relationship between furnace efficiency and regular maintenance is thus not merely a correlation, but a symbiotic relationship necessary for the sustainability of both the home and the environment.
Importance of Regular Furnace Maintenance
Regular furnace maintenance is an essential component to ensure the overall efficiency of any heating system. This practice not only extends the lifespan of the furnace but also helps in cost cutting, maintains the indoor air quality, and, most importantly, prevents unforeseen mechanical breakdowns in the biting cold. The essence of regular furnace maintenance lies in ensuring that the internal mechanisms operate at optimal levels. The furnace, like any equipment, is subject to wear and tear over time. Dust and dirt can build up in the filters, ducts, and vents, impeding air flow and forcing the unit to work harder. This extra strain invariably leads to more significant energy consumption, resulting in higher utility bills. By cleaning or replacing filthy filters and clearing out the ventilation system, routine maintenance ensures that the furnace operates at maximum efficiency, thus reducing energy costs. Another significance of maintaining your furnace regularly is that it preserves the quality of your indoor air. Poor furnace upkeep can lead to the dissemination of dust, pollen, and other airborne irritants throughout your home. Regular cleaning and changing of filters will significantly reduce the amount of these allergens, providing you and your family with healthier air to breathe. Perhaps the most crucial aspect of regular furnace maintenance is the prevention of unexpected breakdowns. Nothing can be more disastrous than having a furnace give out during a cold spell. Routine check-ups of all the furnace components, especially as the colder months approach, can help spot potential issues and fix them before they escalate into costly repairs or replacements. Finally, regular maintenance enhances the longevity of your furnace. By ensuring that every element is working as it should, these practice systematically delays the breakdown of the furnace components, prolonging the life of your heating system and thus saving significant amounts of money over time. In conclusion, the importance of regular furnace maintenance cannot be overstated. For optimal furnace efficiency, consistent upkeep procedures should be a priority for every homeowner. This routine practice is a small investment that will undoubtedly pay off in the form of lower energy bills, improved home air quality, fewer breakdowns, and an extended furnace lifespan.
Common Furnace-related Problems and Their Solutions
Keeping your furnace efficient and problem-free is often an outcome of regular maintenance, but even the most meticulously cared for system can fall prey to the occasional hiccup. Common furnace-related problems range from minor inconveniences to critical issues that demand immediate attention. A ubiquitous issue is the flame sensor malfunction. The flame sensor monitors the burner, shutting off gas supply if it senses no flame, hence preventing dangerous situations. If it acts up, professional assistance may be needed for its cleaning or replacement. Filter-related problems are equally common. Indeed, if energy bills are inexplicably rising or your furnace isn't delivering optimal heat, a jammed-up filter could be the villain. It's crucial to change furnace filters every three months, or more frequently if you have pets or residents with allergies. Ignition and pilot control issues have caused many a cold winter night. Improper function prevents the furnace from heating at all. Modern furnaces mostly use intermittent pilots or hot surface ignition – if either fails, the services of a trained technician would be a prudent choice. Another likely suspect for inefficient furnaces or ineffective heat is the thermostat malfunction. Regular check-ups help in identifying and rectifying this issue early. Then there's the dreaded blower run continuously problem, it could be due to a faulty limit switch which then necessitates replacement by a professional. The blower motor is the heart of your furnace—it circulates the warm air throughout your house. If this vital component hesitates or outright refuses to run, lubrication or a motor replacement might be necessary. Lastly, consider the age of your furnace. Even with the best maintenance routine, a furnace that’s 15-20 years old might simply not function as efficiently because of normal wear and tear. Every problem has a solution, and the prescription for most furnace-related issues is regular maintenance. Regular inspections can help catch small problems before they turn into costly repairs or major system failures. Being aware of common problems also equips homeowners to recognize signs of trouble, take proactive steps, and keep the warmth flowing unhindered, thus ensuring a cozy and comfortable living space.