How To Draw Hands
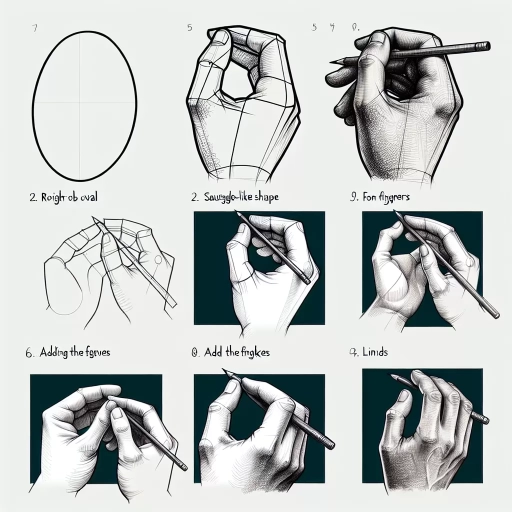
Understanding the Basics of Hand Anatomy
The Bones and Knuckles
When it comes to drawing hands, understanding the structure beneath the skin is vital. The human hand consists of twenty-seven bones, with fourteen of them being phalanges - fingers and thumbs. At the base of each digit are the knuckles, bumps of bone that can be traced and felt through the skin. The shape of these bones impacts the way light and shadow interact with the hand, creating a unique challenge when drawing. You'll want to familiarize yourself with the shapes and positions of these bones to create a skeleton upon which you'll build your hand drawing.
The Joints and Flexibility
Flexibility is a distinguishing factor of hands. Understanding the role of the joints in hand movement contributes to drawings appearing more realistic and fluid. Hands possess an astonishing range of motion, thanks to the many joints in the fingers and wrists. Studying the way these joints interact and how they limit or extend flexibility can give your hand drawings a more authentic feel. This involves observing real hands in various positions and angles, noting how fingers curl, the hand bends, the skin folds, and the tendons shift.
The Skin and Texture
One of the commonly overlooked aspects of hand drawing is replicating the texture of skin. The hand's skin is not uniform; its texture changes depending on the area – rougher on the palm, smoother on the back, and wrinkled around knuckles and joints. Understanding these textures can add another level of realism to your hand drawings. Using different shading techniques, you can mimic the appearance of different skin textures. Experimenting with cross-hatching or stippling, for example, could help achieve a skin-like appearance.
Practical Steps to drawing a Hand
Starting with Basic Shapes
When drawing a hand, it's recommended to start with simple shapes and lines before adding details. The palm can be represented as a square or rectangle, while each finger can be simplified into cylinders. These basic shapes provide a framework which can be refined to create the unique characteristics of the hand. Constant practice using this method can increase your speed and accuracy, ultimately improving the quality of your hand drawings.
Adding Details and Shading
Once the basic structure is on paper, it's time to add details. This includes refining the shape of the fingers, adding knuckles and wrinkles, and portraying fingernails. Shading plays an essential role in bringing the hand to life. It adds depth and dimension, provides texture, and can help denote the hand's position and movement.
Maintaining Proportions and Perspective
Proportion and perspective are crucial in achieving a realistic representation of hands. The size and length of each finger, the thickness of the palm, and the relative size of the hand to the body are all elements that must be considered. An understanding of basic human anatomy can help maintain proportion, while observing hands from various angles can aid in capturing perspective.
Refining Skills through Practice and Analysis
Continuous Practice
Hand drawing is a skill that improves over time. With continuous practice, the ability to capture the nuances of hands will become more intuitive. It's advised to often draw hands in different positions, scenarios, and lighting conditions to further refine your abilities.
Studying Master Works
Analyzing the work of master artists can be incredibly beneficial. Looking at how these artists manage light and shadow, line work, and detail can offer new insights and techniques. Try to replicate their hand drawings, focusing particularly on the elements that stand out to you the most.
Seeking Critiques and Feedback
Finally, seeking critiques and feedback is a crucial part of improving your hand drawing skills. Other people can provide a fresh perspective on your work and point out areas that might need improvement. Constructive feedback can better equip you to tackle challenging aspects of hand drawing, ultimately improving the quality of your future drawings.