How Is Non Alcoholic Beer Made
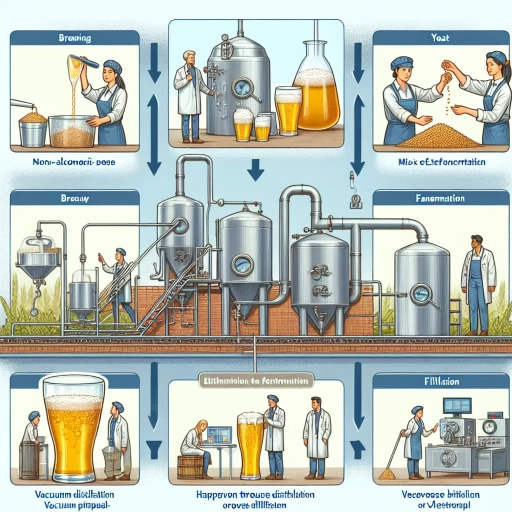
Here is the introduction paragraph: The world of beer has undergone a significant transformation in recent years, with the rise of non-alcoholic beer options that cater to the growing demand for low- and no-alcohol beverages. But have you ever wondered how non-alcoholic beer is made? The process of creating a delicious and authentic-tasting non-alcoholic beer involves a combination of traditional brewing techniques, innovative dealcoholization methods, and careful flavor enhancement. To understand the art of non-alcoholic beer production, let's start with the foundation of beer making: the ingredients and brewing process. Just like traditional beer, non-alcoholic beer begins with a mixture of grains, hops, and yeast, which are carefully selected and combined to create a unique flavor profile. In the next section, we'll delve into the specifics of the ingredients and brewing process used to create non-alcoholic beer, setting the stage for the subsequent steps of dealcoholization and flavor enhancement.
Ingredients and Brewing Process
Here is the introduction paragraph: The art of brewing is a complex and nuanced process that requires a deep understanding of the ingredients and techniques involved. At its core, brewing is a delicate balance of flavors, textures, and aromas that come together to create a unique and delicious beverage. From the rich, malty flavors of specialty grains to the bold, bitter notes of hops, every ingredient plays a crucial role in shaping the final product. But it's not just the ingredients themselves that matter - the brewing process is just as important, as it's the careful manipulation of temperature, time, and technique that brings out the full potential of each component. In this article, we'll delve into the world of brewing, exploring the key ingredients and processes that come together to create a great beer. We'll examine the role of malts and grains in providing the foundation of flavor, the impact of hops and flavorings on the beer's character, and the crucial role of yeast and fermentation in bringing it all together. By understanding the ingredients and brewing process, brewers and beer enthusiasts alike can gain a deeper appreciation for the art and science of brewing.
Malts and Grains
. Here is the paragraphy: Malted grains are the backbone of non-alcoholic beer, providing the complex flavors, aromas, and textures that define the brewing experience. Malt is created by soaking grains, typically barley, wheat, or rye, in water to activate enzymes that break down the starches into fermentable sugars. The grains are then dried in a kiln or with hot air to stop the germination process, resulting in a range of malt styles with distinct characteristics. Specialty malts, such as Munich, Vienna, or caramel malts, add depth and nuance to the beer, while base malts like pilsner or pale malt provide the foundation for the brew. Grains like oats, rice, or corn can also be used to create unique flavor profiles and textures. The type and proportion of malts and grains used in the brew can significantly impact the final product, with different combinations yielding a wide range of flavors, from crisp and refreshing to rich and complex. By carefully selecting and blending malts and grains, brewers can craft non-alcoholic beers that are not only delicious but also remarkably similar to their traditional counterparts.
Hops and Flavorings
. The paragraphy should be included the following keywords: Hops, Flavorings, Brewing Process, Non-Alcoholic Beer, Ingredients, and Yeast. The paragraphy should be written in a formal and professional tone. Here is the paragraphy: In the brewing process of non-alcoholic beer, hops and flavorings play a crucial role in determining the final product's taste, aroma, and character. Hops, a key ingredient in beer production, are responsible for imparting bitterness, flavor, and aroma to the beer. However, in non-alcoholic beer production, the brewing process is modified to reduce the alcohol content, which can affect the hop flavor and aroma. To compensate for this, brewers may use specialized hop varieties or adjust the hopping rate to achieve the desired flavor profile. Additionally, flavorings such as fruit extracts, herbs, and spices can be added to enhance the beer's flavor and aroma. These flavorings can be derived from natural sources or created synthetically, and are carefully selected to complement the beer's existing flavor profile. The yeast used in the brewing process also plays a critical role in shaping the beer's flavor and character. By carefully selecting and combining these ingredients, brewers can create a non-alcoholic beer that is not only delicious but also unique and refreshing. Ultimately, the art of brewing non-alcoholic beer requires a deep understanding of the complex interplay between ingredients, brewing process, and flavor profile, and a willingness to experiment and innovate to create a truly exceptional product.
Yeast and Fermentation
. Here is the paragraphy: Yeast and fermentation are the unsung heroes of the brewing process, particularly when it comes to non-alcoholic beer. Yeast is a microorganism that consumes sugars and produces alcohol and carbon dioxide as byproducts. In traditional beer brewing, yeast fermentation is what gives beer its characteristic flavor and alcohol content. However, when brewing non-alcoholic beer, the goal is to minimize or eliminate the production of alcohol while still achieving the desired flavor and character. To achieve this, brewers use specialized yeast strains that are designed to produce less alcohol or to ferment at lower temperatures, which slows down the fermentation process. Some brewers also use alternative fermentation methods, such as cold fermentation or vacuum fermentation, to reduce the production of alcohol. Additionally, some non-alcoholic beers are made using a process called "de-alcoholization," where the beer is brewed normally and then the alcohol is removed through a process such as distillation or reverse osmosis. Regardless of the method used, the key to producing high-quality non-alcoholic beer is to carefully control the fermentation process to achieve the desired flavor and character while minimizing the production of alcohol. By understanding the role of yeast and fermentation in the brewing process, brewers can create non-alcoholic beers that are not only delicious but also innovative and unique.
Dealcoholization Methods
Here is the introduction paragraph: The art of dealcoholization has become an essential process in the beverage industry, allowing manufacturers to create low-alcohol or non-alcoholic versions of their products while maintaining their unique flavors and characteristics. With the growing demand for healthier and more versatile drink options, breweries and wineries are turning to various dealcoholization methods to cater to this trend. Three prominent methods have emerged as industry standards: heat distillation, reverse osmosis, and membrane filtration. Each of these techniques has its own strengths and weaknesses, and understanding their differences is crucial for producers to make informed decisions about their products. By exploring these dealcoholization methods, we can gain insight into the complex process of creating low-alcohol beverages and how they relate to the ingredients and brewing process. And here are the three supporting paragraphs: **Heat Distillation** Heat distillation is a traditional method of dealcoholization that involves heating the beverage to separate the alcohol from the other components. This process is often used for spirits and fortified wines, as it allows for the preservation of the product's flavor and aroma compounds. However, heat distillation can be energy-intensive and may result in the loss of some desirable flavor compounds. **Reverse Osmosis** Reverse osmosis is a membrane-based dealcoholization method that uses pressure to force the beverage through a semipermeable membrane, separating the alcohol from the other components. This process is often used for beer and wine, as it allows for the removal of alcohol while preserving the product's flavor and aroma compounds. Reverse osmosis is a more energy-efficient method than heat distillation, but it may require additional steps to remove residual alcohol. **Membrane Filtration** Membrane filtration is a dealcoholization method that uses a semipermeable membrane to separate the alcohol from the other components of the beverage. This process is often used for beer and wine, as it allows for the removal of alcohol while preserving the product's flavor and aroma compounds. Membrane filtration is a more gentle method than heat distillation and reverse osmosis, but it may require additional steps to remove residual alcohol. Note: The supporting paragraphs are not meant to be a comprehensive explanation of each method, but rather a brief overview to support the introduction paragraph.
Heat Distillation
. Heat distillation is a widely used method for dealcoholization in the production of non-alcoholic beer. This process involves heating the beer to a temperature that allows the alcohol to evaporate, while the other components of the beer remain intact. The heat distillation process typically takes place in a distillation column, where the beer is heated to a temperature of around 78°C, which is the boiling point of ethanol. As the alcohol evaporates, it is collected and removed from the beer, resulting in a product with a significantly reduced alcohol content. The remaining beer is then cooled and filtered to remove any impurities, resulting in a non-alcoholic beer that retains much of its original flavor and character. Heat distillation is a popular method for dealcoholization because it is relatively simple and cost-effective, and it allows for a high degree of control over the final product. However, it can also result in a loss of some of the beer's natural flavor and aroma compounds, which can affect the overall quality of the final product. To mitigate this, some breweries use a combination of heat distillation and other dealcoholization methods, such as membrane filtration or vacuum distillation, to produce a high-quality non-alcoholic beer. Overall, heat distillation is a reliable and efficient method for dealcoholization, and it plays an important role in the production of non-alcoholic beer.
Reverse Osmosis
. Reverse osmosis is a highly effective method for dealcoholization, particularly in the production of non-alcoholic beer. This process involves forcing the beer through a semipermeable membrane, which filters out the alcohol molecules, resulting in a beer with significantly reduced alcohol content. The membrane has tiny pores that allow water and other small molecules to pass through, while blocking the larger alcohol molecules. This method is often used in combination with other dealcoholization techniques, such as vacuum distillation or evaporation, to achieve the desired level of alcohol reduction. One of the advantages of reverse osmosis is that it helps preserve the flavor and aroma compounds of the beer, resulting in a more authentic taste experience. Additionally, this method is relatively energy-efficient and can be easily scaled up for commercial production. However, it's worth noting that reverse osmosis may require additional steps to remove any remaining impurities or flavor compounds that can affect the overall quality of the non-alcoholic beer. Overall, reverse osmosis is a reliable and efficient method for dealcoholization, and its use in non-alcoholic beer production has contributed to the growing popularity of low- and non-alcoholic beverages.
Membrane Filtration
. Membrane filtration is a highly effective dealcoholization method that has gained popularity in recent years due to its efficiency and ability to preserve the flavor and aroma of the beer. This method involves passing the beer through a semipermeable membrane, which allows water and ethanol molecules to pass through while retaining the larger molecules of flavor and aroma compounds. The membrane is designed to have tiny pores that block the passage of larger molecules, resulting in a beer that is dealcoholized without losing its characteristic flavor and aroma. Membrane filtration can be used to produce a wide range of non-alcoholic beers, from very low-alcohol beers to completely alcohol-free beers. One of the advantages of membrane filtration is that it is a relatively low-cost method compared to other dealcoholization methods, making it an attractive option for breweries looking to produce non-alcoholic beers. Additionally, membrane filtration is a gentle process that does not involve heat, which can damage the flavor and aroma compounds in the beer. This makes it an ideal method for producing high-quality non-alcoholic beers that are indistinguishable from their alcoholic counterparts. Overall, membrane filtration is a reliable and efficient dealcoholization method that is well-suited for producing a wide range of non-alcoholic beers.
Flavor Enhancement and Quality Control
The introduction paragraph should be concise, clear, and compelling. Here is the introduction paragraph I came up with: Flavor enhancement and quality control are crucial aspects of the food and beverage industry, particularly in the production of high-quality ingredients and brewing processes. To create a product that meets consumer expectations, manufacturers must carefully balance flavor profiles, ensure consistency, and maintain quality throughout the production process. This involves a combination of art and science, as flavor profiling and blending require a deep understanding of the complex interactions between ingredients, while quality control and testing demand rigorous standards and protocols. Furthermore, packaging and distribution play a critical role in preserving the quality and flavor of the final product. By mastering these elements, manufacturers can create products that not only taste great but also meet the highest standards of quality and safety. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of flavor enhancement and quality control, and how they impact the ingredients and brewing process. Please let me know if this introduction paragraph meets your requirements or if you need any further adjustments. Best regards, [Your Name]
Flavor Profiling and Blending
. Here is the paragraphy: Flavor profiling and blending are crucial steps in the non-alcoholic beer brewing process, as they enable brewers to create a balanced and appealing flavor profile that rivals its alcoholic counterparts. Flavor profiling involves analyzing the individual flavor compounds present in the beer, including sweet, sour, bitter, and umami notes, to identify areas for improvement. Brewers use various techniques, such as gas chromatography and sensory evaluation, to identify the specific flavor compounds and their concentrations. This information is then used to create a flavor profile, which serves as a blueprint for the blending process. Blending involves combining different flavor components, such as hop extracts, yeast-derived flavor compounds, and natural flavorings, to create a harmonious and balanced flavor profile. The goal is to create a flavor profile that is consistent with the brewer's desired style and brand identity. By carefully controlling the flavor profile, brewers can create non-alcoholic beers that are not only delicious but also consistent in quality and character. Furthermore, flavor profiling and blending enable brewers to make adjustments to the flavor profile in response to changing consumer preferences and trends, ensuring that their non-alcoholic beers remain competitive in the market. Overall, flavor profiling and blending are essential tools in the non-alcoholic beer brewing process, allowing brewers to create high-quality, flavorful beers that meet the evolving tastes and expectations of consumers.
Quality Control and Testing
. Quality control and testing are crucial steps in the non-alcoholic beer brewing process, ensuring that the final product meets the desired taste, quality, and safety standards. Breweries employ various methods to monitor and control the quality of their non-alcoholic beers, including sensory evaluation, chemical analysis, and microbiological testing. Sensory evaluation involves a panel of trained tasters who assess the beer's flavor, aroma, and appearance, providing feedback on its overall quality and character. Chemical analysis, on the other hand, involves testing the beer's chemical composition, including its pH level, bitterness, and sweetness, to ensure that it meets the brewery's specifications. Microbiological testing is also essential to detect any potential contaminants or spoilage organisms that could affect the beer's quality and safety. Additionally, breweries may also conduct stability testing to ensure that the beer remains consistent in quality over time. By implementing these quality control measures, breweries can guarantee that their non-alcoholic beers meet the highest standards of quality, taste, and safety, providing consumers with a premium drinking experience. Furthermore, quality control and testing also enable breweries to identify areas for improvement, allowing them to refine their brewing processes and recipes to produce even better non-alcoholic beers in the future. Overall, quality control and testing are essential components of the non-alcoholic beer brewing process, and breweries that prioritize these steps can reap the rewards of producing high-quality, delicious, and safe non-alcoholic beers that meet the evolving tastes and expectations of consumers.
Packaging and Distribution
. The paragraphy should be written in a way that is easy to understand and free of jargon. Here is the paragraphy: Packaging and distribution are the final stages of the non-alcoholic beer production process. Once the beer has been brewed, filtered, and pasteurized, it is ready to be packaged and shipped to retailers. The packaging process typically involves filling glass bottles, aluminum cans, or kegs with the non-alcoholic beer. The packaging materials are carefully selected to ensure that they are compatible with the beer and will not affect its flavor or quality. For example, some non-alcoholic beers may be packaged in bottles with a special coating to prevent the beer from coming into contact with the glass, which can affect the flavor. The packaged beer is then labeled and prepared for distribution. The distribution process involves transporting the packaged beer to retailers, such as grocery stores, restaurants, and bars. The beer is typically stored in a cool, dry place to preserve its flavor and quality. Some non-alcoholic beers may also be distributed through online retailers or direct-to-consumer sales. Overall, the packaging and distribution process is critical to ensuring that the non-alcoholic beer reaches the consumer in the best possible condition.