How Long Does It Take To Grow A Pineapple
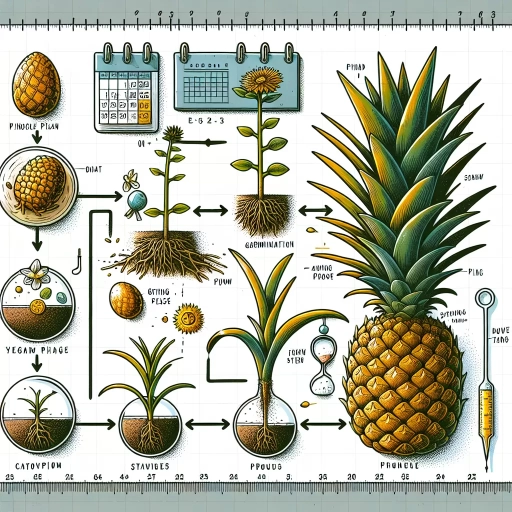
Understanding the Growth Cycle of a Pineapple
The Propagation Stage
The initial stage of growing a pineapple is known as propagation. This process involves planting the top portion of the fruit, also known as the "crown," into the soil. In contrast to most other fruits, pineapples cannot be grown from seeds. The vitality of a pineapple plant entirely depends on how it is propagated. This task should be performed carefully, as a poorly propagated pineapple plant may not bear fruit, or in worst scenarios, it may wilt and die.
One effective method of propagation is to soak the crown in water until roots begin to form. This is normally observed after about two to three weeks of soaking. Once roots have developed, the plant can be transferred to well-drained soil. The proper execution of these early-life steps is critical for a healthy pineapple plant.
A key point to note is that the propagation phase may be significantly influenced by environmental factors. For instance, the rate at which roots form may be quicker in warm, tropical climates compared to cooler climates. Additionally, the type of soil used for planting and the watering schedule can also substantially affect the progress of the plant at this stage.
The Maturing Stage
The maturing phase is the next stage in the growth cycle of a pineapple. This is the period during which the pineapple plant develops and becomes more robust in order to withstand various environmental threats. During this stage, the plant focuses on leaf and root development as it aims at accumulating sufficient resources to fruit.
This phase usually takes about 12 to 18 months, depending on the climatic conditions. Suitable temperatures for growth range from 20-30 degrees Celsius. Additionally, the plant requires a significant amount of sunlight for photosynthesis. The quality of the soil also plays a major role in the development of the pineapple plant. Highly fertile soils rich in organic matter tend to support rapid growth.
One essential aspect to monitor during this stage is the health of the plant. Any signs of diseases or pests should be starkly addressed to prevent detrimental effects on fruiting. Common pests that affect the pineapple plant include mealybugs and scales. In case of an infestation, proper pest control measures should be swiftly implemented.
The Fruiting Stage
The final stage of the pineapple plant’s growth cycle is the fruiting stage. This is when the plant bears fruit - a mature pineapple. Given the right conditions and care, a pineapple plant will typically initiate fruiting around 20 months after planting. It then takes around 6 months for the fruit to ripen once the plant begins to flower.
During this stage, it is imperative to provide the plant with the necessary nutrients it needs to develop a healthy fruit. Regular fertilization with a balanced nutrient mix can help meet this goal. Also, ensuring the plant gets enough sunlight is essential as lack of it can lead to a smaller fruit or delay the fruiting process.
In regards to harvesting the fruit, it should be noted that a pineapple will not continue to ripe after being picked. So growers should consider factors like firmness and color to make sure the pineapple is at peak ripeness before harvesting. Hence, growers need to wait patiently and perform their due diligence in monitoring the evolution of the pineapple through the fruiting stage.