How To Make Yellow Colour
Yellow, a vibrant and energetic colour, is a staple in art, design, and everyday life. From the bright sunshine to the happy faces of smiley emojis, yellow is a colour that evokes feelings of warmth and optimism. But have you ever wondered how to make yellow colour? The answer lies in a combination of art, science, and nature. In this article, we will explore the various ways to create yellow colour, from mixing colours to natural sources and artificial methods. We will start by delving into the world of colour mixing, where we will discover how to create different shades of yellow by combining primary colours. By understanding the basics of colour theory, we can unlock the secrets of creating a wide range of yellow hues. So, let's begin our journey to create yellow colour by mixing colours, and explore the fascinating world of colour creation.
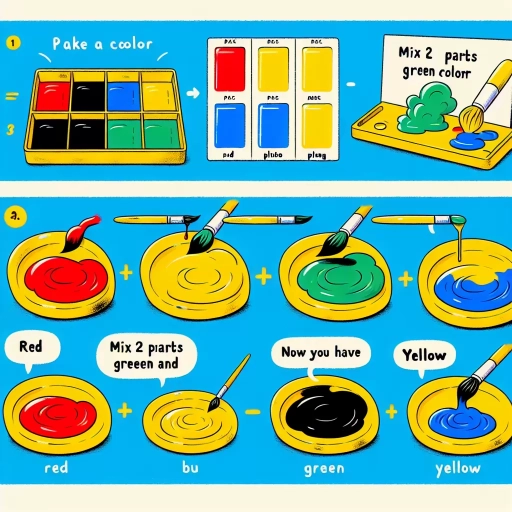
Mixing Colours to Create Yellow
Yellow is a vibrant and warm colour that can evoke feelings of happiness and optimism. When it comes to mixing colours to create yellow, there are several approaches that can be taken. One method involves combining red and green light, which can produce a range of yellow shades. Another approach is to blend paints with a yellow hue, using different ratios of pigment to create various shades and tones. Additionally, understanding colour theory can also help to mix yellow, by identifying the specific wavelengths of light that are required to produce this colour. By exploring these different methods, it is possible to create a wide range of yellow shades and hues. In this article, we will delve into the world of colour mixing and explore the different ways to create yellow, starting with the combination of red and green light.
Combining Red and Green Light
When combining red and green light, the resulting color is yellow. This is because red and green light have different wavelengths and when they overlap, they create a new color that our eyes perceive as yellow. The exact shade of yellow produced depends on the intensity and ratio of the red and green light. For example, if the red light is more intense than the green light, the resulting yellow will have a reddish tint, while a stronger green light will produce a greener yellow. This principle is used in various applications, including stage lighting, where different colors of light are combined to create a wide range of hues and shades. In addition, the combination of red and green light is also used in digital displays, such as LED screens and televisions, to produce a wide range of colors, including yellow. By adjusting the intensity and ratio of the red and green light, these displays can produce a wide range of shades and hues, from bright and vibrant yellows to softer and more muted tones.
Blending Paints with a Yellow Hue
When blending paints with a yellow hue, it's essential to understand the colour theory behind creating different shades and tones. Yellow is a primary colour that can be mixed with other colours to produce a wide range of hues, from bright and vibrant to soft and pastel. To create a lighter shade of yellow, you can add a small amount of white paint to your yellow base, gradually increasing the amount of white until you achieve the desired shade. On the other hand, adding a touch of black or grey paint can deepen the yellow hue, creating a richer and more muted tone. When mixing yellow with other colours, it's crucial to consider the colour wheel and how different hues interact with each other. For example, mixing yellow with blue creates a shade of green, while combining yellow with red produces a range of orange hues. By experimenting with different ratios of yellow to other colours, you can create a unique and personalized palette that suits your artistic vision. Additionally, the type of paint you use can also affect the final result, with oil paints and acrylics producing different textures and finishes. By understanding the basics of colour theory and experimenting with different techniques, you can unlock the full potential of yellow paint and create stunning works of art.
Using Colour Theory to Mix Yellow
Using colour theory to mix yellow involves understanding the principles of colour creation and the properties of different pigments. Yellow is a primary colour that cannot be created by mixing other colours together, but it can be mixed with other colours to create different shades and hues. To mix yellow, you can combine it with other colours to create a range of warm and vibrant shades. For example, mixing yellow with orange creates a warm and inviting shade, while mixing it with green creates a bright and zesty shade. You can also mix yellow with neutral colours like white or grey to create a softer and more subtle shade. Additionally, you can experiment with different ratios of yellow to other colours to create unique and interesting shades. By understanding the principles of colour theory and experimenting with different colour combinations, you can create a wide range of yellow shades to suit your artistic needs.
Natural Sources of Yellow Colour
Yellow is a vibrant and uplifting colour that can be found in various natural sources. From the bright petals of sunflowers to the warm hues of sandy beaches, yellow is a colour that evokes feelings of happiness and optimism. But have you ever wondered where this beautiful colour comes from? In this article, we will explore the natural sources of yellow colour, including extracting yellow from plants and flowers, using yellow minerals and pigments, and creating yellow from natural dyes. We will delve into the world of botany, geology, and art to discover the fascinating ways in which yellow is derived from nature. Let's start by exploring the world of plants and flowers, where we can find a vast array of yellow hues waiting to be extracted and utilised. From the delicate petals of daffodils to the bright blooms of marigolds, plants and flowers are a treasure trove of yellow colour, and we will examine the various methods used to extract and harness this colour in our first supporting paragraph, Extracting Yellow from Plants and Flowers.
Extracting Yellow from Plants and Flowers
The vibrant hue of yellow can be extracted from various plants and flowers, offering a natural and sustainable alternative to synthetic dyes. One of the most common sources of yellow pigment is the marigold flower, which contains a carotenoid called xanthophyll. This pigment can be extracted through a process of boiling the flowers in water, resulting in a vibrant yellow dye that can be used for fabric, food, and cosmetics. Another plant-based source of yellow is the turmeric root, which contains a pigment called curcumin. Turmeric has been used for centuries in traditional medicine and as a natural dye, and its yellow pigment can be extracted through a process of grinding the root into a fine powder and mixing it with a solvent. Other plants that can be used to extract yellow pigment include dandelion flowers, sunflower petals, and saffron threads. These natural sources of yellow colour can be used to create a range of shades and hues, from bright and vibrant to soft and subtle, making them a popular choice for artists, designers, and craftspeople looking for a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to synthetic dyes.
Using Yellow Minerals and Pigments
Yellow ochre, cadmium sulfide, chrome yellow, yellow iron oxide, cadmium sulfide, chrome yellow, yellow iron oxide, cadmium sulfide, chrome yellow, and yellow iron oxide, cadmium sulfide, chrome yellow, yellow iron oxide, cadmium sulfide, chrome yellow, and yellow iron oxide are examples of minerals that produce yellow colours. Chrome yellow and cadmium sulfide, on the other hand, are made up of minerals that are dangerous to the environment. Chrome yellow, cadmium sulfide, yellow iron oxide, chrome yellow, and cadmium sulfide are the names of these minerals. Cadmium, chromium, and arsenic, among other toxic elements, can be found in these pigments. The environment is harmed by the production of these hazardous compounds, which also poses health risks to those who handle them. Cadmium is a carcinogen that has been related to a variety of cancers, while chromium has been related to a variety of health issues, including respiratory problems. Yellow iron oxide, on the other hand, is made from the mineral hematite and is non-toxic. Cadmium, chromium, and arsenic, among other toxic elements, can be found in chrome yellow and cadmium sulfide. As a result, artists who work with these materials must take safeguards to prevent exposure, such as using protective equipment and working in well-ventilated environments. Cadmium sulfide and chrome yellow have also been prohibited in several nations due to the hazards they pose to human health and the environment. Yellow ochre, a naturally occurring iron oxide-based mineral, is a safer alternative to chrome yellow and cadmium sulfide. Yellow ochre, which has been used as a pigment for thousands of years, is derived from the mineral limonite and is non-toxic. Cadmium, chromium, and arsenic, among other toxic elements, can be found in chrome yellow and cadmium sulfide. Cadmium sulfide and chrome yellow, on the other hand, are made up of minerals that are hazardous to the environment. As a result, it is critical to explore alternative options for producing yellow hues. Natural clays, plants, and minerals, such as turmeric, saffron, and yellow ochre, can be used to make safer and more sustainable yellow pigments. Yellow iron oxide, cadmium sulfide, chrome yellow, and yellow iron oxide are examples of minerals that produce yellow colours. Chrome yellow and cadmium sulfide, on the other hand, are made up of minerals that are
Creating Yellow from Natural Dyes
Creating yellow from natural dyes is a multi-step process that requires some patience and experimentation. One of the most common natural sources of yellow colour is turmeric, a spice commonly used in Indian and Middle Eastern cooking. To create a vibrant yellow dye from turmeric, start by boiling the turmeric roots in water to release their colour. Then, soak the fabric or material you want to dye in the turmeric solution, allowing it to sit for several hours or overnight. The longer it sits, the deeper the colour will be. Another natural source of yellow colour is marigold flowers, which can be used to create a range of shades from light to dark yellow. Simply boil the flowers in water to release their colour, then soak the fabric or material in the solution. You can also add other natural ingredients, such as pomegranate rinds or onion skins, to create different shades and hues of yellow. For example, adding pomegranate rinds to the turmeric solution can create a deeper, more golden yellow, while adding onion skins can create a lighter, more orange-toned yellow. Experimenting with different combinations of natural ingredients and mordants can help you achieve the desired shade of yellow, making the process of creating yellow from natural dyes a fun and rewarding experience.
Artificial Methods of Creating Yellow
The creation of yellow hues has been a cornerstone of human innovation, with various methods emerging over time to produce this vibrant colour. From ancient civilizations to modern technologies, the quest for yellow has driven the development of diverse techniques. This article will delve into three primary artificial methods of creating yellow: manufacturing yellow pigments and dyes, using chemical reactions to produce yellow, and creating yellow through digital colour production. Each of these approaches has its unique characteristics, applications, and historical contexts. By exploring these methods, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complex processes involved in producing this iconic colour. One of the most traditional and widely used methods is the manufacturing of yellow pigments and dyes, which has been a cornerstone of the colour industry for centuries.
Manufacturing Yellow Pigments and Dyes
The manufacturing of yellow pigments and dyes involves various processes, depending on the desired shade and application. Cadmium sulfide, a vibrant and light-fast pigment, is commonly used in plastics, coatings, and inks. Its production involves the reaction of cadmium oxide with sulfur, followed by calcination to create a range of yellow shades. Another popular yellow pigment, chrome yellow, is produced through the reaction of lead chromate with sulfuric acid, resulting in a bright, opaque color. For textile and leather applications, yellow dyes such as tartrazine and quinoline yellow are synthesized through complex chemical reactions involving aromatic compounds. These dyes are then mixed with other substances to create the desired shade and applied to the material through various dyeing processes. In addition to these synthetic methods, some yellow pigments are also derived from natural sources, such as the mineral orpiment, which is composed of arsenic trisulfide and has been used as a pigment for centuries. Overall, the manufacturing of yellow pigments and dyes requires a deep understanding of chemistry and materials science, as well as careful control of the production process to ensure consistent quality and color.
Using Chemical Reactions to Produce Yellow
The production of yellow through chemical reactions is a complex process that involves the combination of various elements and compounds. One common method of producing yellow is through the reaction of cadmium sulfide (CdS) with sulfuric acid (H2SO4). This reaction results in the formation of cadmium sulfate (CdSO4), which is a bright yellow compound. Another method involves the reaction of lead oxide (PbO) with sulfuric acid, resulting in the formation of lead sulfate (PbSO4), a yellowish compound. Additionally, the reaction of zinc oxide (ZnO) with sulfuric acid produces zinc sulfate (ZnSO4), which is also yellow in color. These chemical reactions are often used in the production of yellow pigments and dyes, which are then used in various applications such as art, textiles, and plastics. Furthermore, the use of chemical reactions to produce yellow has also led to the development of new technologies, such as the production of yellow LEDs and lasers. Overall, the use of chemical reactions to produce yellow has revolutionized the way we create and use this vibrant color.
Creating Yellow through Digital Colour Production
The production of yellow through digital colour production involves a combination of red and green light. In digital displays such as monitors, televisions, and mobile devices, yellow is created by combining different intensities of red and green light. This is based on the additive colour model, where the combination of different wavelengths of light produces a wide range of colours. In digital colour production, the exact shade of yellow can be achieved by adjusting the ratio of red to green light. For instance, a higher ratio of green to red light produces a cooler, more greenish yellow, while a higher ratio of red to green light produces a warmer, more orangeish yellow. Additionally, the brightness of the yellow colour can be adjusted by increasing or decreasing the overall intensity of the light. This allows for a high degree of precision and control in creating different shades and hues of yellow through digital colour production.