How To Throw A Curveball
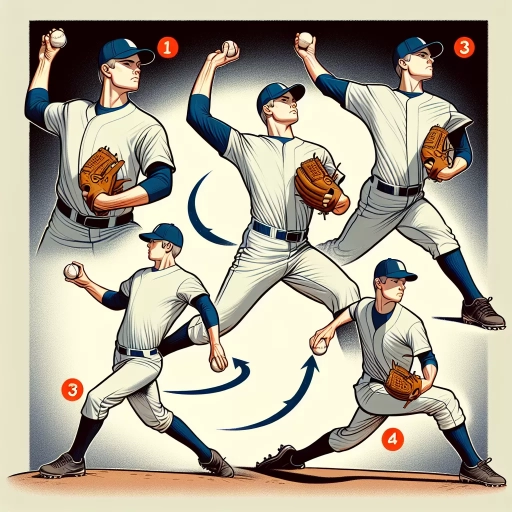
Basics of Throwing a Curveball
Understanding the Concept of a Curveball
Before we delve into the intricacies of throwing a curveball, it's crucial to grasp what a curveball is. In simple terms, a curveball is a type of pitch in baseball thrown with a distinctive grip and hand movement that causes the ball to move down and to the left when thrown by a right-handed pitcher and down and to the right when thrown by a left-handed pitcher. Many find the curveball difficult to hit due to its unique motion and the sharp change in direction it can create. Understanding its principles provides a window into the physics of baseball, embellishing how pitchers manipulate the ball's seams to make it move in unpredictable manners.
Significance of Grip
One of the rudimentary aspects of throwing a curveball lies in how the ball is gripped. The traditional curveball grip requires the pitcher to put the middle and index fingers together and place them on the ball's seam where the seam is narrowest, forming a "C" shape. The thumb is positioned underneath, ensuring balance. The remaining two fingers stay aside, not touching the ball. The grip element is vital as it directly impacts the initial direction and movement of the pitch. A solid grip allows for effective control and precision, two major components for a successful curveball.
Importance of Arm Motion and Wrist Snap
Moving beyond the grip, mastering the arm motion and wrist snap is fundamental. Arm motion should replicate a fastball's arm motion to disguise the pitch type. The curveball’s distinguishing feature is the downward wrist snap upon release. This snap imparts a spin that results in the ball’s final drop and curve. The right execution, coupled with a strategic grip, provides the perfect foundation for throwing a successful curveball.
Common Mistakes and Corrections
Avoiding “Hanging” Curveballs
“Hanging” curveballs are mistakes that primarily result from improper release or insufficient wrist snap. These pitches end up floating in the strike zone, becoming easy targets for batters. With adequate practice in maintaining a proper grip and honing wrist snap, one can avoid the mistake of “hanging” curveballs resulting in more effective pitches.
Circumventing Early Rotation
Another common problem is the early rotation, which usually happens when the pitcher opens the shoulders too early, leading to a pitch that doesn't break. Understanding the correct sequence of motion helps to address this. By concentrating on maintaining the shoulder's closed position until the arm comes over, pitchers can ensure that the ball breaks as expected.
Preventing Arm-side Misses
A common occurrence with curveballs is missing to the arm side. This typically occurs when the pitcher's hand moves under or around the side of the ball rather than staying behind. Persistent practice with an attention to maintaining direction can help correct these misses, rendering the pitches more accurate and more challenging to hit.
Mastering the Curveball
Practice is Key
The best route to mastery of any craft, including throwing a curveball, is substantial and consistent practice. Part of this involves teaching your muscles the unique and specific movements required for the pitch. Repeated and meaningful engagement ensures these actions become ingrained, leading to improved accuracy and effectiveness on the mound.
Physical Conditioning
In addition to practice, physical condition plays a significant role. Proper upper body strength, specifically in the arm and wrist, allows for better control and reduces the risk of injury. Therefore, exercises targeting these areas should be incorporated into a routine regimen.
Consulting with Coaches and Pros
Seeking guidance from experienced individuals can prove invaluable in mastering a curveball. Coaches and professional players offer insights into techniques, strategies, and ways to work through common mistakes that can significantly aid in advancement. This, together with personal practice and physical conditioning, paves the way for successful curveball mastery.