How Long Do Onions Take To Grow
Onions are a staple ingredient in many cuisines around the world, and growing them can be a rewarding experience for gardeners of all levels. But have you ever wondered how long it takes for onions to grow? The answer lies in understanding the different stages of onion growth, as well as the factors that can affect their growth rate. In this article, we'll delve into the world of onion cultivation and explore the various stages of onion growth, from seed germination to harvest. We'll also examine the factors that can impact onion growth, such as weather, soil quality, and pest management. Additionally, we'll provide tips on how to optimize onion growth for a faster harvest. By the end of this article, you'll have a better understanding of how to grow onions successfully and be able to enjoy a bountiful harvest. So, let's start by understanding the different stages of onion growth.
Understanding Onion Growth Stages
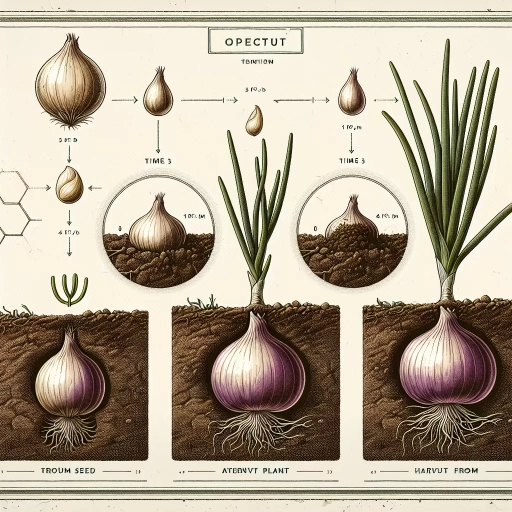
Onions are one of the most widely cultivated and consumed vegetables globally, and understanding their growth stages is crucial for successful cultivation. The growth of onions can be divided into three main stages: germination period, thinning and transplanting, and bulb formation. During the germination period, onions develop their root system and first set of leaves, laying the foundation for future growth. Thinning and transplanting is a critical stage where seedlings are given adequate space to grow, and weak seedlings are removed to promote healthy growth. Finally, bulb formation is the stage where onions develop their characteristic bulb shape and size. In this article, we will delve into each of these stages in detail, starting with the germination period, where it all begins.
Germination Period
The germination period of onions is a critical stage in their growth cycle, typically lasting between 7 to 14 days, depending on factors such as temperature, moisture, and seed quality. During this time, the seed absorbs water, and the embryo inside begins to sprout, developing its first set of leaves, known as the cotyledon or seed leaf. The ideal temperature for onion germination is between 65°F to 75°F (18°C to 24°C), with consistent moisture levels. It's essential to maintain a humid environment, as dry conditions can slow down or prevent germination. Onions can be started indoors 4-6 weeks before the last frost date, and then transplanted outside when the weather warms up. In regions with mild winters, onions can be directly sown in the fall or early spring, allowing them to germinate and grow during the cooler months. Proper care during the germination period sets the stage for healthy seedling development and ultimately, a bountiful onion harvest.
Thinning and Transplanting
Onions are typically thinned and transplanted when they are between 1-2 inches tall, and have 2-3 sets of leaves. This process involves carefully removing weaker seedlings, leaving about 1 inch of space between each remaining plant. Thinning allows the remaining onions to receive adequate sunlight, water, and nutrients, promoting healthy growth and development. Transplanting, on the other hand, involves moving the seedlings to a new location, usually with more space, to accommodate their growing needs. This process is usually done when the onions are around 4-6 inches tall, and have 4-5 sets of leaves. Transplanting helps to prevent overcrowding, reduces competition for resources, and allows the onions to grow to their full potential. By thinning and transplanting onions at the right time, gardeners can encourage healthy growth, prevent disease, and ultimately, harvest a bountiful crop of delicious and flavorful onions.
Bulb Formation
Onion bulb formation is a critical stage in the onion growth cycle, typically occurring 60 to 90 days after planting. During this phase, the onion plant's energy is redirected from leaf growth to bulb development. The process begins when the day length increases, triggering a hormonal response that signals the plant to start forming a bulb. As the bulb grows, the leaves begin to yellow and fall over, a process known as "lodging." This is a natural part of the growth cycle, and it helps to direct the plant's energy towards the bulb. The bulb will continue to grow and mature, eventually forming a protective skin that helps to preserve the onion for storage. Proper care during this stage, including adequate moisture and nutrient supply, is essential for promoting healthy bulb formation and maximizing yields. By understanding the onion bulb formation process, gardeners can optimize their growing conditions and techniques to produce high-quality, flavorful onions.
Factors Affecting Onion Growth Rate
Onions are one of the most widely cultivated and consumed vegetables globally, and their growth rate is influenced by a combination of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for farmers and gardeners to optimize onion production and achieve high yields. Three key factors that significantly impact onion growth rate are weather and climate conditions, soil quality and fertilization, and watering and irrigation. Weather and climate conditions, in particular, play a critical role in determining the growth rate of onions, as they require specific temperature and moisture levels to thrive. For instance, onions grow best in cool, dry weather with average temperatures ranging from 15°C to 20°C. Extreme temperatures, either too high or too low, can significantly slow down onion growth. Therefore, it is essential to consider the weather and climate conditions when planting and cultivating onions.
Weather and Climate Conditions
Weather and climate conditions play a significant role in determining the growth rate of onions. Onions are a cool-season crop, which means they thrive in temperate climates with moderate temperatures and adequate moisture. Ideal weather conditions for onion growth include daytime temperatures between 60°F and 80°F (15°C and 27°C) and nighttime temperatures around 50°F to 60°F (10°C and 15°C). Onions also require a certain amount of chill hours, which is the amount of time the bulbs spend in temperatures below 40°F (4°C), to form properly. In areas with mild winters, onions may not receive enough chill hours, resulting in poor bulb formation. Onions are also sensitive to extreme weather conditions such as heavy rainfall, drought, and high winds, which can cause damage to the plants and reduce yields. In regions with high temperatures and low humidity, onions may bolt, or go to seed, prematurely, reducing their quality and flavor. Overall, onions are adapted to grow in a wide range of climates, but optimal weather conditions are essential for achieving high yields and quality bulbs.
Soil Quality and Fertilization
Soil quality and fertilization play a crucial role in determining the growth rate of onions. Onions require a well-draining, fertile soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0 to grow optimally. Soil with poor drainage can lead to waterlogged soil conditions, causing the onions to rot. On the other hand, soil with inadequate nutrients can result in stunted growth and reduced yields. Fertilization is essential to provide onions with the necessary nutrients for healthy growth. A balanced fertilizer with a ratio of 10-10-10 (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium) is recommended for onions. Nitrogen promotes leaf growth, phosphorus supports root development, and potassium helps with overall plant health. Additionally, onions benefit from the application of sulfur, which helps to reduce disease susceptibility and improve flavor. It is essential to follow a fertilization schedule, applying fertilizer at planting time and again at the bulb formation stage. Over-fertilization can be detrimental to onion growth, leading to excessive vegetative growth at the expense of bulb formation. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor soil quality and adjust fertilization accordingly to ensure optimal onion growth. By maintaining good soil quality and providing adequate fertilization, growers can promote healthy onion growth, leading to higher yields and better quality bulbs.
Watering and Irrigation
Watering and irrigation play a crucial role in onion growth, as onions require consistent moisture, especially during the germination and bulb formation stages. Onions need about 1-2 inches of water per week, either from rainfall or irrigation. It's essential to maintain a moist but not waterlogged soil, as excessive water can lead to rot and other diseases. Drip irrigation or soaker hoses are recommended, as they deliver water directly to the roots, reducing evaporation and runoff. Mulching around the plants also helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Onions are sensitive to overwatering, so it's crucial to monitor soil moisture and adjust irrigation schedules accordingly. In areas with low rainfall, supplemental irrigation may be necessary to ensure optimal growth. Proper watering and irrigation techniques can significantly impact onion growth rate, yield, and quality.
Optimizing Onion Growth for Faster Harvest
Onions are one of the most widely used vegetables in cooking, and growing them can be a rewarding experience for gardeners. However, optimizing onion growth for a faster harvest requires careful consideration of several key factors. To achieve a bountiful and speedy onion harvest, it's essential to choose the right onion variety, provide adequate sunlight and space, and prune and train the plants effectively. By selecting a variety that is well-suited to your climate and growing conditions, you can set your onions up for success from the start. With the right variety in place, you can then focus on providing the necessary sunlight and space for optimal growth, and finally, prune and train the plants to promote healthy development and maximize yields. In this article, we'll explore each of these critical factors in more detail, starting with the importance of choosing the right onion variety.
Choosing the Right Onion Variety
Choosing the right onion variety is crucial for optimizing onion growth and achieving a faster harvest. With over 700 varieties of onions to choose from, selecting the right one can be overwhelming. However, by considering factors such as climate, soil type, and desired harvest period, you can narrow down your options. For example, if you live in a cooler climate, you may want to choose a variety that matures quickly, such as 'Ebenezer' or 'Redwing', which can be harvested in as little as 60 days. On the other hand, if you live in a warmer climate, you may want to choose a variety that is more heat-tolerant, such as 'Texas Grano' or 'Yellow Granex', which can take up to 120 days to mature. Additionally, if you want to grow onions for storage, you may want to choose a variety that is known for its long storage life, such as 'Stuttgarter' or 'Copra', which can be stored for up to 6 months. By choosing the right onion variety for your specific needs, you can optimize onion growth and achieve a faster harvest.
Providing Adequate Sunlight and Space
Onions require adequate sunlight and space to grow optimally. Providing sufficient sunlight is crucial for onion growth, as it promotes healthy development and bulb formation. Onions need at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day, but 8-10 hours is ideal. If you're growing onions indoors, ensure they receive sufficient supplemental lighting, such as LED grow lights. In addition to sunlight, onions also require adequate space to grow. Planting onions too close together can lead to reduced growth, increased disease susceptibility, and lower yields. The ideal spacing for onions depends on the variety, but a general rule of thumb is to plant them 4-6 inches apart. This allows for good air circulation, which helps prevent disease and promotes healthy growth. Furthermore, providing adequate space also enables onions to receive sufficient nutrients and water, leading to a faster harvest. By providing your onions with the right amount of sunlight and space, you'll be rewarded with a bountiful and healthy harvest.
Pruning and Training
Pruning and training are essential techniques for optimizing onion growth and promoting a faster harvest. Pruning involves removing select leaves or stems to direct the plant's energy towards bulb formation, while training involves manipulating the plant's growth habit to maximize space and sunlight exposure. By pruning the onion plant, you can encourage it to focus its energy on producing a larger, healthier bulb, rather than expending energy on leaf growth. This can be done by removing any weak or damaged leaves, as well as trimming back the plant to about half its height. Training the onion plant involves providing support for the stems and leaves, which can help to prevent lodging and promote upright growth. This can be achieved by using stakes or a trellis to keep the plant upright, or by gently twining the stems around a central support. By pruning and training your onion plants, you can promote healthy growth, increase yields, and enjoy a faster harvest. Regular pruning and training can also help to prevent pests and diseases, by removing any infected or damaged areas and promoting good air circulation. Overall, pruning and training are simple yet effective techniques for optimizing onion growth and promoting a faster harvest.