How To Eat Persimmon
Understanding the Health Benefits of Persimmons
The Nutritional Profile of Persimmons
Persimmons are defined by their rich vitamin content, fiber, and beneficial plant compounds. They are low in calories but high in fiber, making them a good option for weight management. This orange-colored fruit is also loaded with Vitamins A, C, E, and K; potassium, manganese, copper, and dietary fiber. These vitamins play vital roles in the body; for instance, Vitamin A plays an essential role in vision and immune function, while Vitamin C is necessary for tissue repair and iron absorption.
The Antioxidant Power of Persimmons
Persimmons contain several potent antioxidants, including carotenoids and flavonoids which help fight oxidative damage in the body. Oxidative damage is linked to several chronic diseases like heart conditions, cancer, and type 2 diabetes. Eating foods rich in antioxidants, such as persimmons, is one way of fortifying your body against these ailments.
Persimmons and Heart Health
Persimmons contain nutrients that are heart-friendly. The fiber, potassium, and antioxidants in persimmons all contribute to heart health. Fiber helps to lower LDL cholesterol, often referred to as the "bad" cholesterol, while potassium helps to regulate blood pressure.
Choosing, Preparing, and Eating Persimmons
How to Choose the Perfect Persimmon
There are many varieties of persimmons, but the two most widely available types in the market are Fuyu and Hachiya. To pick the perfect persimmon, pay attention to its color and feel. A ripe Fuyu persimmon should be firm, with a reddish-orange skin, while a ripe Hachiya should be fully softened. Unripe persimmons can be bitter, so taking the time to choose a ripe fruit is important.
Preparing Your Persimmon for Eating
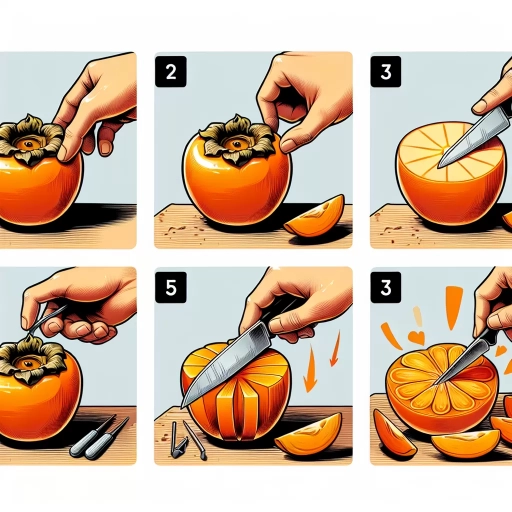
To prepare a persimmon for eating, you first rinse the fruit thoroughly in clean water. Then, remove the leaf-like portion at the top, slice it into quarters or thin slices, and remove its central core. Following the preparation, you can eat it fresh, dehydrated, as a snack, or incorporate it into meals and desserts.
Recipes: Incorporating Persimmons into Your Diet
Persimmons are versatile and can be incorporated into various dishes. Here are some ways to enjoy them:
- Persimmon Salad: You can add thinly sliced Fuyu persimmons to your favorite salad recipe. Their sweet, mild taste pairs well with mixed greens, cheeses, and tangy dressings.
- Persimmon Smoothie: Add a ripe persimmon into your smoothie. You may also combine it with oranges, bananas, and ginger for a refreshing nutritious drink.
- Persimmon Cookies: For a sweet treat, you can try making persimmon cookies. Add pureed ripe Hachiya persimmon to your cookie batter, and flavor it with spices like cinnamon and nutmeg.
The Role of Persimmons in Dietary Management
Eating Persimmons for Weight Management
Persimmons' high fiber content helps to promote feelings of fullness. This can reduce the urge to snack between meals, therefore aiding in weight management. Furthermore, they are relatively low in calories, making them a good addition to a calorie-controlled diet.
Controlling Blood Sugar Levels with Persimmons
Persimmons have a low Glycemic Index (GI) score which means eating them does not lead to a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. This makes them an ideal fruit for those with diabetes or those aiming to manage their blood sugar levels.
Persimmons in Digestive Health
The high fiber content in persimmons plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. It aids in regular bowel movement and can help prevent constipation. Plus, studies suggest that dietary fiber may help in preventing certain digestive conditions, such as diverticulosis and hemorrhoids.