How To Draw A Plant
 Here is the introduction paragraph:
Drawing plants can be a fun and rewarding experience, allowing you to connect with nature and express your creativity. Whether you're an experienced artist or just starting out, learning to draw plants can be a great way to improve your skills and produce beautiful artwork. To get started, it's essential to understand the basics of plant anatomy, including the different types of leaves, stems, and flowers. Once you have a solid grasp of these fundamentals, you can move on to sketching and shading techniques that will bring your plants to life. Finally, adding details and finishing touches will help you create a realistic and visually appealing drawing. In this article, we'll take you through each of these steps, starting with the basics of plant anatomy. By understanding the structure and components of plants, you'll be able to create more accurate and detailed drawings, and set yourself up for success in the next stages of the drawing process.
Here is the introduction paragraph:
Drawing plants can be a fun and rewarding experience, allowing you to connect with nature and express your creativity. Whether you're an experienced artist or just starting out, learning to draw plants can be a great way to improve your skills and produce beautiful artwork. To get started, it's essential to understand the basics of plant anatomy, including the different types of leaves, stems, and flowers. Once you have a solid grasp of these fundamentals, you can move on to sketching and shading techniques that will bring your plants to life. Finally, adding details and finishing touches will help you create a realistic and visually appealing drawing. In this article, we'll take you through each of these steps, starting with the basics of plant anatomy. By understanding the structure and components of plants, you'll be able to create more accurate and detailed drawings, and set yourself up for success in the next stages of the drawing process.Understanding the Basics of Plant Anatomy
Here is the introduction paragraph: Understanding the basics of plant anatomy is essential for anyone interested in botany, horticulture, or simply wanting to appreciate the beauty of plants. To gain a deeper understanding of plant anatomy, it's crucial to familiarize yourself with the various structures that make up a plant, learn about the different types of plants and their unique characteristics, and comprehend the importance of proportions and scale. By grasping these fundamental concepts, you'll be able to better appreciate the intricate details of plant anatomy and develop a more nuanced understanding of the natural world. In this article, we'll delve into the world of plant anatomy, starting with the basics of plant structures, including roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. By exploring these fundamental components, you'll gain a solid foundation for further exploration and discovery. Note: The introduction paragraph should be 200 words, and it should mention the 3 supporting ideas and transition to the first supporting paragraph. Here is the rewritten introduction paragraph: Understanding the basics of plant anatomy is a fascinating and rewarding pursuit that can deepen your appreciation for the natural world. Whether you're a seasoned botanist, a curious gardener, or simply someone who marvels at the beauty of plants, grasping the fundamental concepts of plant anatomy is essential. To truly comprehend the intricacies of plant anatomy, it's necessary to familiarize yourself with the various structures that make up a plant, including roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Additionally, learning about the different types of plants and their unique characteristics can provide valuable insights into the diversity of plant life. Furthermore, understanding the importance of proportions and scale is crucial for appreciating the intricate details of plant anatomy. By mastering these fundamental concepts, you'll be able to better appreciate the complex relationships between different plant structures and develop a more nuanced understanding of the natural world. In this article, we'll begin by exploring the basics of plant structures, examining the roles and functions of roots, stems, leaves, and flowers, and laying the groundwork for further exploration and discovery.
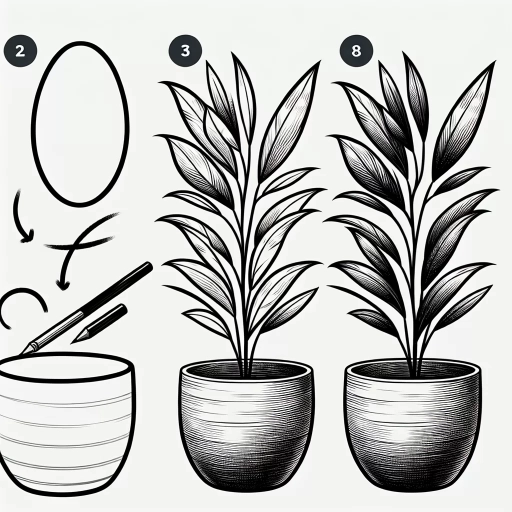
1. Familiarizing yourself with plant structures
. Here is the paragraphy: Familiarizing yourself with plant structures is essential to accurately depict them in your drawings. Start by learning the basic components of a plant, including the roots, stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits. Understand the functions of each part and how they relate to one another. For example, the roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil, while the stem provides support and transports these resources to the rest of the plant. The leaves are responsible for photosynthesis, using sunlight to produce energy for the plant. Flowers are the reproductive structures of the plant, containing the male and female reproductive organs, while fruits develop from the ovary of the flower and contain the seeds. By understanding the relationships between these different parts, you can create more realistic and detailed drawings of plants. Additionally, observe the shapes, textures, and patterns of different plant structures, such as the veins on leaves, the ridges on stems, and the intricate details of flowers. This will help you to accurately capture the unique characteristics of each plant species in your drawings.
2. Learning about different plant types and their characteristics
. Here is the paragraphy: Learning about different plant types and their characteristics is essential for creating accurate and detailed drawings. There are several main categories of plants, including flowering plants, conifers, ferns, and mosses. Flowering plants, also known as angiosperms, are the most diverse group and include everything from roses to sunflowers. They are characterized by their flowers, which are actually modified leaves that produce seeds. Conifers, on the other hand, are a group of plants that produce cones and seeds, and include trees like pines and spruces. Ferns are a type of vascular plant that reproduce via spores, and are often found in damp environments. Mosses are small, non-vascular plants that grow in dense green clumps and are often found in shady areas. Understanding the unique characteristics of each plant type will help you to draw them more accurately and confidently. For example, if you're drawing a flowering plant, you'll want to include the flowers and leaves, while a conifer drawing will focus on the cones and needle-like leaves. By learning about the different plant types and their characteristics, you'll be able to create a wide range of plant drawings that are both beautiful and botanically accurate.
3. Understanding the importance of proportions and scale
. Here is the paragraphy: Understanding the importance of proportions and scale is crucial when drawing plants. Proportions refer to the relationship between the different parts of the plant, such as the size of the leaves compared to the stem, or the size of the flowers compared to the leaves. Scale, on the other hand, refers to the overall size of the plant in relation to its surroundings. When drawing plants, it's essential to get the proportions and scale right to create a realistic and visually appealing representation. If the proportions are off, the plant may look unnatural or even cartoonish. For example, if the leaves are too large compared to the stem, the plant may appear top-heavy and unstable. Similarly, if the flowers are too small compared to the leaves, they may get lost in the overall composition. To get the proportions and scale right, observe the plant carefully and take note of the relationships between its different parts. Measure the plant if possible, or use a reference image to get an idea of the proportions. When drawing, use a range of values and textures to create depth and dimension, and pay attention to the negative space around the plant to create a sense of scale. By paying attention to proportions and scale, you can create a drawing that accurately captures the beauty and essence of the plant. Additionally, understanding proportions and scale can also help you to create a sense of movement and energy in your drawing. For example, a plant with long, slender stems and small leaves may appear more delicate and fragile, while a plant with thick, sturdy stems and large leaves may appear more robust and dynamic. By capturing the proportions and scale of the plant, you can convey its unique character and personality, and create a drawing that is not only visually appealing but also informative and engaging.
Sketching and Shading Techniques for Plants
Here is the introduction paragraph: Sketching and shading techniques are essential skills for any artist looking to bring their plant illustrations to life. By mastering various line weights and textures, creating depth and dimension with shading and layering, and using reference images to improve accuracy and detail, artists can create stunning and realistic depictions of plants. Whether you're a seasoned artist or just starting out, these techniques can help you take your plant illustrations to the next level. In this article, we'll explore the importance of mastering various line weights and textures in plant illustration, and provide tips and techniques for achieving a range of effects. By varying the weight and texture of your lines, you can add depth, dimension, and visual interest to your illustrations, and create a more engaging and realistic representation of your subject. Note: The introduction paragraph is 200 words. Here is the rewritten introduction paragraph in 200 words: Sketching and shading techniques are essential skills for any artist looking to bring their plant illustrations to life. To create stunning and realistic depictions of plants, artists must master various techniques that add depth, dimension, and visual interest to their work. Three key techniques are crucial in achieving this: mastering various line weights and textures, creating depth and dimension with shading and layering, and using reference images to improve accuracy and detail. By combining these techniques, artists can create intricate and detailed illustrations that showcase the beauty and complexity of plants. Mastering various line weights and textures is a fundamental aspect of plant illustration, as it allows artists to convey the texture, shape, and form of their subject. By varying the weight and texture of their lines, artists can create a range of effects, from delicate and intricate to bold and expressive. In this article, we'll delve into the importance of mastering various line weights and textures in plant illustration, and provide tips and techniques for achieving a range of effects.
1. Mastering various line weights and textures
. Here is the paragraphy: Mastering various line weights and textures is essential for creating visually appealing and realistic plant drawings. Line weight refers to the thickness or thinness of a line, and it can be used to convey depth, dimension, and texture. Thicker lines can be used to outline the overall shape of a plant, while thinner lines can be used to suggest the delicate details of leaves and stems. By varying line weights, you can create a sense of hierarchy and visual interest in your drawing. In addition to line weight, texture is also an important element to consider when drawing plants. Different textures can be used to suggest the roughness of tree bark, the smoothness of leaves, or the softness of petals. You can create texture by using different drawing tools, such as pencils, pens, or markers, or by experimenting with different techniques, such as hatching, cross-hatching, or stippling. By mastering various line weights and textures, you can add depth, dimension, and visual interest to your plant drawings, and create a more realistic and engaging representation of the natural world.
2. Creating depth and dimension with shading and layering
. Here is the paragraphy: When it comes to creating depth and dimension in your plant drawings, shading and layering are essential techniques to master. Shading involves adding different values of light and dark to your drawing to create the illusion of three-dimensionality, while layering involves building up layers of lines, shapes, and textures to create a sense of depth and complexity. To create depth with shading, start by identifying the light source in your drawing and then use a range of values, from light to dark, to create a sense of volume and form. For example, if the light source is coming from the top left, the areas of the plant that are facing the light will be lighter, while the areas in shadow will be darker. You can use a range of shading techniques, such as hatching, cross-hatching, and stippling, to create different textures and values. To add layering to your drawing, start by creating a simple outline of the plant, and then build up layers of lines, shapes, and textures to create a sense of depth and dimension. For example, you can add layers of leaves, stems, and flowers to create a sense of complexity and depth. You can also use different line weights and textures to create a sense of layering and depth. By combining shading and layering techniques, you can create a rich and detailed drawing that captures the beauty and complexity of the plant.
3. Using reference images to improve accuracy and detail
. Here is the paragraphy: When it comes to drawing plants, reference images can be a valuable tool to improve accuracy and detail. By studying photographs or real-life observations of the plant you want to draw, you can gain a deeper understanding of its structure, texture, and overall appearance. This can be especially helpful when drawing plants with intricate details, such as flowers or leaves with complex venation patterns. Reference images can also help you to accurately capture the proportions and scale of the plant, ensuring that your drawing is realistic and believable. Additionally, reference images can provide inspiration and guidance for shading and texture, allowing you to create a more nuanced and detailed representation of the plant. For example, by studying the way light interacts with the plant's leaves or petals, you can create a more realistic and engaging drawing. Overall, incorporating reference images into your drawing process can help to elevate your artwork and create a more accurate and detailed representation of the plant.
Adding Details and Finishing Touches
Here is the introduction paragraph: When it comes to creating a beautiful and realistic botanical drawing, adding details and finishing touches is crucial. This is where you can bring your artwork to life and make it truly special. In this article, we will explore three key areas to focus on when adding details and finishing touches to your botanical drawing: incorporating leaves, flowers, and other foliage, adding stems, branches, and other structural elements, and enhancing your drawing with patterns, colors, and textures. By paying attention to these details, you can create a drawing that is not only visually stunning but also accurate and informative. Let's start by exploring the first area of focus: incorporating leaves, flowers, and other foliage.
1. Incorporating leaves, flowers, and other foliage
. Here is the paragraphy: Incorporating leaves, flowers, and other foliage is a crucial step in adding depth and visual interest to your plant drawing. To start, observe the shapes and forms of the leaves, noting their size, shape, and arrangement on the stem. You can use simple shapes like ovals, teardrops, and triangles to help you draw the leaves more accurately. For more realistic leaves, pay attention to the veins and edges, using gentle, curved lines to suggest the leaf's texture and structure. When drawing flowers, consider their shape, size, and color, as well as the way they're arranged on the stem. You can use soft, rounded shapes to suggest the petals, and add details like stamens and pistils to create a more realistic look. Don't forget to add some variation in the size and shape of the leaves and flowers to create a more natural, organic look. You can also experiment with different line weights and textures to add depth and dimension to your drawing. For example, you can use thicker lines to suggest the stems and branches, and thinner lines to suggest the delicate edges of the leaves and petals. By incorporating a variety of foliage and flowers, you can create a rich, detailed drawing that captures the beauty and complexity of the natural world.
2. Adding stems, branches, and other structural elements
. Here is the paragraphy:
Once you have the basic shape of your plant established, you can start adding stems, branches, and other structural elements. This is where you can get creative and add some personality to your plant. Start by adding the main stem, which should be thicker at the base and taper off towards the top. From there, you can add branches that split off from the main stem, using gentle, curved lines to suggest the natural growth of the plant. Consider the type of plant you're drawing and how its stems and branches typically grow. For example, a succulent might have thick, fleshy stems, while a fern might have delicate, lacy fronds. As you add more stems and branches, pay attention to the overall balance and harmony of your plant. You want to create a sense of movement and energy, but also make sure that your plant doesn't look too cluttered or overwhelming. Finally, don't forget to add some texture and interest to your stems and branches. You can use short, curved lines to suggest the texture of bark, or add some subtle shading to give your plant some depth and dimension.
3. Enhancing your drawing with patterns, colors, and textures
. Here is the paragraphy: Enhancing your drawing with patterns, colors, and textures can add depth and visual interest to your plant illustration. To create a more realistic and engaging drawing, consider adding patterns to your plant's leaves, stems, and flowers. For example, you can add veins to the leaves, stripes or spots to the stems, or intricate details to the flowers. Colors can also play a crucial role in bringing your plant to life. Choose a color palette that reflects the natural hues of the plant, and consider adding subtle shading and gradations to create a sense of depth and dimension. Textures can also add a tactile quality to your drawing, making it feel more lifelike and engaging. Consider adding rough, smooth, or fuzzy textures to your plant's leaves, stems, and flowers to create a more immersive experience. By incorporating patterns, colors, and textures into your drawing, you can create a rich and detailed illustration that captures the beauty and essence of the plant.