How Do Dogs Mate
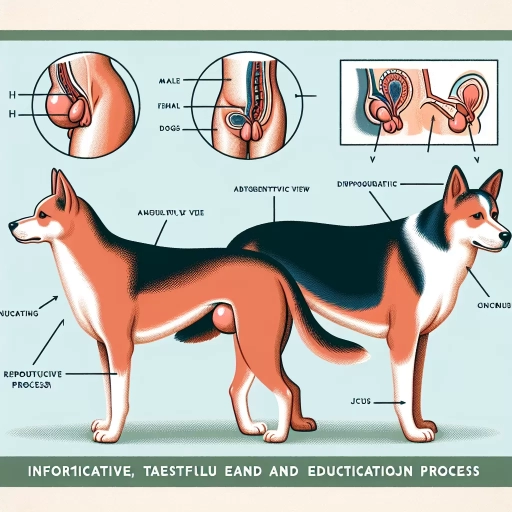
Dogs, like all living beings, have an innate desire to reproduce and continue their genetic lineage. The process of dog mating is a complex and fascinating phenomenon that involves a series of physiological, behavioral, and hormonal changes. For dog breeders and owners, understanding the intricacies of canine reproduction is crucial for ensuring successful breeding and whelping. In this article, we will delve into the world of dog mating, exploring the underlying biology of canine reproduction, the mating process itself, and the essential factors that contribute to successful breeding and whelping. To begin, it is essential to understand the fundamental principles of canine reproduction, including the reproductive anatomy, hormonal cycles, and breeding seasons. By grasping these concepts, we can better appreciate the intricacies of the mating process and the critical factors that influence successful breeding and whelping. Let's start by Understanding Canine Reproduction.
Understanding Canine Reproduction
Canine reproduction is a complex and fascinating process that is crucial for the continuation of a breed or bloodline. Understanding canine reproduction is essential for breeders, veterinarians, and dog owners who want to ensure the health and well-being of their dogs. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of canine reproduction, covering the reproductive anatomy of dogs, the canine reproductive cycle, and the factors that affect fertility. By understanding these key concepts, individuals can make informed decisions about breeding, whelping, and caring for their dogs. Let's start by exploring the reproductive anatomy of dogs, which lays the foundation for understanding the entire reproductive process.
Reproductive Anatomy of Dogs
The reproductive anatomy of dogs is a complex system that plays a crucial role in the mating process. In males, the reproductive system consists of the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, prostate gland, and penis. The testes produce sperm, which are then stored in the epididymis before being transported through the vas deferens to the penis during ejaculation. The prostate gland produces fluids that make up a significant portion of the semen. In females, the reproductive system includes the ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix, and vagina. The ovaries produce eggs, which are released into the oviducts during ovulation. The oviducts then transport the eggs to the uterus, where fertilization occurs. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina, and the vagina is the muscular canal that connects the cervix to the outside of the body. Understanding the reproductive anatomy of dogs is essential for breeders and pet owners to appreciate the complexities of canine reproduction and to make informed decisions about breeding and reproductive health.
Canine Reproductive Cycle
Here is the paragraphy: The canine reproductive cycle, also known as the estrous cycle, is a complex process that involves various physiological and hormonal changes in a female dog's body. The cycle typically lasts around 2-3 weeks and is divided into four stages: proestrus, estrus, diestrus, and anestrus. During proestrus, which lasts around 4-9 days, the female dog's body prepares for breeding by increasing estrogen levels, causing the vulva to swell and discharge a bloody fluid. As the cycle progresses to estrus, the female dog becomes receptive to breeding and is usually fertile for 5-14 days. This is the optimal time for mating, as the sperm can survive inside the female's reproductive tract for up to 10 days. After estrus, the cycle enters diestrus, a period of 60-90 days during which the female dog's body prepares for pregnancy or returns to anestrus, a state of reproductive dormancy. Understanding the canine reproductive cycle is crucial for responsible dog breeding and can help prevent unwanted litters. By recognizing the physical and behavioral changes that occur during each stage, dog owners and breeders can make informed decisions about breeding and ensure the health and well-being of their dogs.
Factors Affecting Fertility
Fertility in dogs is influenced by a variety of factors, including age, breed, health, nutrition, and lifestyle. Age is a critical factor, as a dog's fertility peaks between one and five years of age, after which it gradually declines. Certain breeds, such as Bulldogs and Pugs, are known to have lower fertility rates due to their brachycephalic (flat-faced) skull structure, which can lead to reproductive issues. A dog's overall health also plays a significant role in its fertility, with conditions such as hypothyroidism, Cushing's disease, and certain infections affecting the reproductive system. Nutrition is also essential, as a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals is necessary to support reproductive health. Lifestyle factors, such as stress, exercise, and exposure to toxins, can also impact a dog's fertility. For example, excessive exercise or stress can disrupt hormone production, while exposure to toxins such as pesticides and heavy metals can damage reproductive cells. Furthermore, certain medical procedures, such as spaying or neutering, can also affect a dog's fertility. Understanding these factors is crucial for dog owners and breeders to optimize their dog's reproductive health and increase the chances of successful breeding.
The Mating Process in Dogs
The mating process in dogs is a complex and highly regulated process that involves a series of physical and behavioral changes. For a successful mating, it is essential to understand the pre-mating behavior and preparation, the act of mating itself, and the post-mating care and considerations. Pre-mating behavior and preparation are crucial in ensuring that both the male and female dogs are physically and emotionally ready for mating. This includes understanding the female's heat cycle, preparing the breeding environment, and ensuring the health and fertility of both dogs. Once the dogs are ready, the act of mating can take place, which involves a series of specific steps that must be followed to ensure successful fertilization. After mating, post-mating care and considerations are vital in ensuring the health and well-being of the female dog and the developing puppies. By understanding these three critical components of the mating process, dog breeders and owners can increase the chances of a successful breeding and a healthy litter of puppies. Pre-mating behavior and preparation are the first steps in this process, and it is essential to get them right to set the stage for a successful mating.
Pre-Mating Behavior and Preparation
Pre-mating behavior and preparation are crucial steps that occur before the actual mating process in dogs. This stage is characterized by a series of physical and behavioral changes that prepare the male and female dogs for successful breeding. In males, pre-mating behavior is marked by increased restlessness, roaming, and sniffing, as they search for a receptive female. They may also exhibit dominance behaviors such as mounting and posturing to establish their dominance over other males. In females, pre-mating behavior is characterized by changes in their reproductive cycle, including the onset of estrus, which is marked by a bloody discharge and a swollen vulva. They may also exhibit restlessness, pacing, and vocalization, indicating their receptiveness to mating. Before mating, both males and females undergo physical changes, including the enlargement of the reproductive organs and the preparation of the reproductive tract. The male's penis becomes engorged and erect, while the female's vulva becomes swollen and receptive. The pre-mating behavior and preparation stage is essential for successful breeding, as it ensures that both dogs are physically and behaviorally ready for mating, increasing the chances of successful conception and a healthy litter.
The Act of Mating: A Step-by-Step Guide
The act of mating, also known as coitus or copulation, is a natural process that occurs between two dogs when they are in heat. The mating process typically begins with the male dog, also known as the stud, approaching the female dog, also known as the dam, and engaging in a series of courtship behaviors. These behaviors may include sniffing, licking, and mounting, and are designed to stimulate the female and prepare her for mating. Once the female is receptive, the male will mount her from behind and insert his penis into her vagina. The male will then begin to thrust, and the female will typically stand still and allow the mating to occur. The entire process usually takes around 10-30 minutes, although it can vary depending on the individual dogs and the circumstances. After mating, the male and female will often remain tied together for a short period of time, a phenomenon known as a "tie," which is caused by the male's penis becoming swollen and the female's vagina contracting. This tie can last anywhere from a few minutes to an hour, and is a natural part of the mating process. During this time, the male and female will often stand still and remain calm, allowing the sperm to fertilize the egg. After the tie is broken, the male and female will separate, and the mating process will be complete. It's worth noting that mating can occur naturally, or it can be facilitated by a breeder or veterinarian in a controlled environment. In either case, it's essential to ensure that the dogs are healthy, well-cared for, and of suitable breeding age to minimize the risk of complications and ensure a successful outcome.
Post-Mating Care and Considerations
Here is the paragraphy: After mating, it's essential to provide proper post-mating care and considerations to ensure the health and well-being of both the male and female dogs. The female dog should be monitored closely for any signs of stress, discomfort, or complications, such as vaginal discharge, swelling, or bleeding. The male dog should also be checked for any signs of injury or stress. It's crucial to keep the female dog calm and relaxed, as excessive stress can lead to complications during pregnancy. A nutritious diet and regular exercise can help support the female dog's reproductive health. Additionally, it's recommended to schedule a follow-up veterinary check-up to confirm pregnancy and monitor the female dog's health. The veterinarian may perform an ultrasound or X-ray to confirm the pregnancy and detect any potential complications. It's also essential to consider the female dog's age, health, and breeding history when planning for whelping and raising a litter. Proper post-mating care and considerations can help ensure a healthy pregnancy and successful whelping.
Ensuring Successful Breeding and Whelping
Ensuring successful breeding and whelping requires careful planning, attention to detail, and a commitment to the health and well-being of the breeding stock and their offspring. To achieve this goal, breeders must focus on three key areas: selecting healthy breeding stock, managing the breeding process for success, and caring for the pregnant bitch and newborn puppies. By prioritizing these aspects, breeders can minimize the risks associated with breeding and whelping, and maximize the chances of producing healthy, thriving puppies. One of the most critical steps in this process is selecting healthy breeding stock, as this lays the foundation for a successful breeding program. By choosing breeding stock with good conformation, temperament, and genetic diversity, breeders can reduce the risk of inherited health problems and increase the chances of producing puppies that are robust and resilient. Therefore, it is essential to carefully evaluate potential breeding stock and make informed decisions about which dogs to breed.
Selecting Healthy Breeding Stock
Here is the paragraph: Selecting healthy breeding stock is crucial for the success of any dog breeding program. Breeders should prioritize dogs with excellent physical and mental health, good temperament, and a strong genetic foundation. When evaluating potential breeding dogs, look for individuals with a well-balanced conformation, proper movement, and a healthy coat. It's also essential to consider the dog's genetic diversity, as a lack of diversity can increase the risk of inherited health problems. Additionally, breeders should research the dog's ancestry and look for any red flags, such as a history of hereditary diseases or temperament issues. Furthermore, health testing should be a top priority, and breeders should ensure that their breeding dogs have been tested for relevant genetic disorders and have received a clean bill of health. By selecting healthy breeding stock, breeders can reduce the risk of inherited health problems and increase the chances of producing healthy, well-tempered puppies. Ultimately, the goal of responsible breeding is to improve the breed and produce dogs that are healthy, happy, and thriving, and selecting healthy breeding stock is the first step in achieving this goal.
Managing the Breeding Process for Success
Managing the breeding process for success requires careful planning, attention to detail, and a thorough understanding of canine reproduction. To begin, breeders should select healthy, genetically sound breeding stock with desirable traits, and ensure they are of optimal breeding age. A thorough veterinary examination, including reproductive health checks and genetic testing, should be conducted to identify any potential issues. Next, breeders should determine the optimal breeding time, taking into account the female's heat cycle and the male's fertility. Artificial insemination (AI) or natural breeding can be used, depending on the breeder's preference and the dogs' temperament. Once breeding has taken place, the female should be monitored closely for signs of pregnancy, and regular veterinary check-ups should be scheduled to ensure a healthy pregnancy and whelping. Throughout the breeding process, accurate record-keeping is essential to track the female's reproductive history, breeding dates, and whelping outcomes. By carefully managing the breeding process, breeders can increase the chances of a successful whelping and healthy puppies.
Caring for the Pregnant Bitch and Newborn Puppies
Caring for the pregnant bitch and newborn puppies requires attention to detail and a commitment to providing a safe and nurturing environment. As the pregnancy progresses, the bitch's nutritional needs will increase, and she will require a high-quality, nutrient-rich diet to support the growth and development of her puppies. It is essential to monitor her weight and adjust her food intake accordingly to prevent excessive weight gain, which can lead to complications during whelping. Regular veterinary check-ups are also crucial to monitor the health of the bitch and her puppies, and to detect any potential issues early on. Once the puppies are born, it is vital to provide a warm, safe, and clean environment for them to grow and develop. The bitch should be provided with a comfortable and quiet whelping box, lined with clean towels or blankets, and the puppies should be monitored closely for any signs of distress or illness. The bitch should also be encouraged to nurse her puppies, as this is essential for their growth and development. In the first few weeks, the puppies will rely solely on their mother's milk for nutrition, and it is essential to monitor their weight and overall health to ensure they are receiving adequate nutrition. As the puppies grow and develop, they will begin to transition to solid food, and it is essential to introduce them to a high-quality, nutrient-rich puppy food to support their continued growth and development. Regular veterinary check-ups are also crucial during this period to monitor the health of the puppies and detect any potential issues early on. Overall, caring for the pregnant bitch and newborn puppies requires a commitment to providing a safe and nurturing environment, and attention to detail to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and her puppies.