How Long Do Strawberries Take To Grow
Strawberries are one of the most popular fruits globally, cherished for their sweet taste, nutritional value, and versatility in culinary uses. For those interested in growing their own strawberries, understanding the growth period is crucial for planning and managing their garden effectively. The time it takes for strawberries to grow can vary significantly based on several factors, including the development stages of the plant, environmental conditions, and the specific variety of strawberry. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of strawberry growth, exploring the development stages of strawberry plants, the factors that affect their growth rate, and how different strawberry varieties have distinct growth periods. By understanding these aspects, gardeners can better anticipate and prepare for the growth cycle of their strawberry plants. Let's start by examining the development stages of strawberry plants, which set the foundation for their growth and productivity.
Strawberry Plant Development Stages
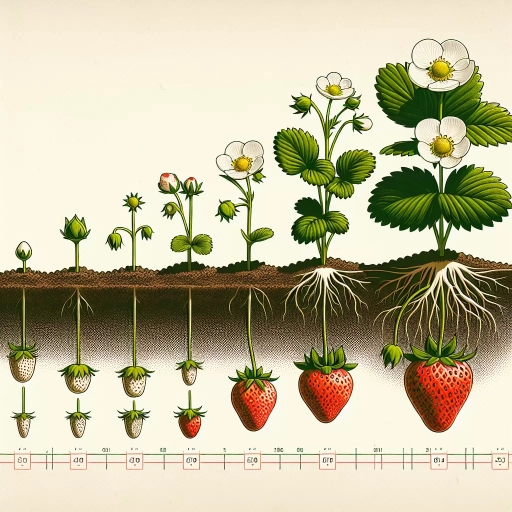
Strawberry plants undergo a series of developmental stages, from germination to maturation, to produce delicious and nutritious fruits. The journey of a strawberry plant from a tiny seed to a mature plant is fascinating and involves several critical stages. The first stage is the germination stage, where the seed begins to sprout and develop its root system. Following germination, the seedling stage is crucial for the plant's growth and development, during which it produces its first set of leaves and begins to photosynthesize. Finally, the maturation stage is where the plant reaches its full potential, producing flowers, fruits, and seeds. In this article, we will delve into each of these stages, starting with the germination stage, where it all begins.
Germination Stage
The germination stage is the initial phase of strawberry plant development, marking the beginning of a new life cycle. This critical stage typically lasts around 1-3 weeks, depending on factors such as temperature, moisture, and seed quality. During germination, the seed absorbs water, and the embryo inside begins to break down its stored food reserves. The seed coat cracks open, and a small white root called a radicle emerges, followed by a tiny green leaf called a cotyledon. As the radicle grows downward, it anchors the seedling in the soil, while the cotyledon reaches for light, starting the process of photosynthesis. Proper conditions, such as adequate moisture, warmth, and light, are essential for successful germination. Strawberry seeds typically require a period of cold stratification to break dormancy, which can be achieved by storing them in the refrigerator for 1-2 months before sowing. Once germinated, the seedling is vulnerable to disease and pests, making it crucial to provide optimal care, including sufficient light, water, and nutrients, to support its growth and development. By understanding the germination stage, strawberry growers can take the necessary steps to ensure a strong start for their plants, setting them up for success in the subsequent stages of growth.
Seedling Stage
The seedling stage of strawberry plant development is a critical period that lasts around 1-3 weeks after germination. During this stage, the seedling develops its first set of leaves, known as cotyledons or seed leaves, which are usually small, rounded, and pale green in color. These leaves are responsible for photosynthesis and provide the seedling with the necessary energy to grow. As the seedling grows, it begins to develop its true leaves, which are larger, more oval-shaped, and have a deeper green color. The true leaves are also responsible for photosynthesis and help the seedling to produce the energy it needs to grow and develop. During the seedling stage, the strawberry plant also develops its root system, which is essential for absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. The roots grow downward, anchoring the plant in the soil, while the stem grows upward, supporting the leaves and preparing the plant for the next stage of development. Overall, the seedling stage is a crucial period in the development of a strawberry plant, laying the foundation for the plant's future growth and productivity.
Maturation Stage
The maturation stage of strawberry plant development is a critical period where the fruits ripen and become ready for harvest. This stage typically occurs 60 days after flowering and can last anywhere from 7 to 14 days, depending on the variety and growing conditions. During this stage, the strawberries undergo a series of physical and biochemical changes that transform them from green, hard, and sour to sweet, juicy, and flavorful. The production of ethylene gas, a natural plant hormone, triggers a series of ripening processes, including the breakdown of cell walls, the accumulation of sugars, and the degradation of chlorophyll. As the strawberries ripen, they turn from green to white, and eventually to their characteristic red, yellow, or pink color, depending on the variety. The maturation stage is also marked by a significant increase in the production of anthocyanins, powerful antioxidants responsible for the fruit's color and nutritional value. Farmers and gardeners closely monitor the maturation stage, as strawberries are highly perishable and must be harvested at the optimal time to ensure maximum flavor, texture, and shelf life. Proper handling and storage techniques are also crucial during this stage to prevent spoilage and maintain the fruit's quality. Overall, the maturation stage is a critical phase in strawberry plant development, and careful management is essential to produce high-quality, delicious strawberries.
Factors Affecting Strawberry Growth Rate
Strawberries are one of the most widely cultivated fruits globally, and their growth rate is influenced by a combination of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for strawberry farmers and gardeners to optimize their crop yields and ensure a bountiful harvest. Three key factors that significantly impact strawberry growth rate are climate and weather conditions, soil quality and nutrient availability, and watering and irrigation practices. Among these, climate and weather conditions play a vital role in determining the growth rate of strawberries. Temperature, sunlight, and precipitation all have a direct impact on strawberry growth, and even slight variations in these conditions can significantly affect the overall yield. For instance, strawberries require a certain amount of chill hours to break dormancy, and extreme temperatures can damage the plants. Therefore, it is essential to understand how climate and weather conditions influence strawberry growth rate to ensure optimal growing conditions.
Climate and Weather Conditions
Climate and weather conditions play a significant role in determining the growth rate of strawberries. Strawberries are typically grown in temperate climates with moderate temperatures, ranging from 40°F to 70°F (4°C to 21°C). Ideal weather conditions for strawberry growth include full sun, well-drained soil, and adequate moisture. Strawberries require a certain amount of chill hours, which is the amount of time the plant spends in temperatures between 32°F and 45°F (0°C and 7°C), to break dormancy and produce flowers. In areas with mild winters, strawberries may not receive enough chill hours, resulting in reduced yields or poor fruit quality. On the other hand, extreme temperatures, either hot or cold, can damage or kill the plants. Prolonged periods of drought or excessive rainfall can also impact strawberry growth, as the plants require consistent moisture levels to produce well. In regions with high humidity, strawberries are more susceptible to fungal diseases, which can further reduce yields. Overall, strawberries are sensitive to climate and weather conditions, and optimal growth requires a delicate balance of temperature, moisture, and sunlight.
Soil Quality and Nutrient Availability
Soil quality and nutrient availability play a crucial role in determining the growth rate of strawberries. Strawberries require a well-draining, fertile soil with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5 to thrive. The ideal soil should have a mix of sand, silt, and clay, with a high organic matter content to retain moisture and nutrients. Nutrient availability is also essential, with strawberries requiring adequate amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to promote healthy growth and fruit production. Nitrogen is particularly important for leaf growth and development, while phosphorus is necessary for root development and fruiting. Potassium helps with overall plant health and resistance to disease. Additionally, strawberries also require micronutrients like calcium, magnesium, and sulfur to maintain optimal growth. Soil testing can help determine the nutrient levels in the soil, and amendments can be made to adjust the pH and nutrient availability to create an optimal growing environment for strawberries. By ensuring good soil quality and nutrient availability, strawberry growers can promote healthy plant growth, increase fruit production, and reduce the risk of disease and pests.
Watering and Irrigation Practices
Watering and irrigation practices play a crucial role in strawberry growth and development. Strawberries require consistent moisture, especially during the first few weeks after planting. It's essential to water them deeply once or twice a week, depending on weather conditions. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other diseases, while underwatering can cause stress, reducing fruit production. Drip irrigation or soaker hoses are recommended as they deliver water directly to the roots, reducing evaporation and runoff. Mulching around the plants also helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. In areas with high rainfall, strawberries may require less frequent watering, but it's still important to ensure the soil isn't waterlogged. In regions with low rainfall, supplemental irrigation may be necessary to support healthy growth. By adopting efficient watering and irrigation practices, strawberry growers can promote healthy plant development, maximize fruit production, and reduce the risk of disease.
Strawberry Varieties and Their Growth Periods
Strawberries are one of the most popular fruits in the world, and their sweet flavor and versatility have made them a favorite among fruit lovers. With over 600 varieties of strawberries, each with its unique characteristics and growth periods, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one for your garden or table. In this article, we will explore the different types of strawberry varieties and their growth periods, including June-bearing, ever-bearing, and day-neutral varieties. June-bearing varieties are known for their high yields and large fruit size, but they only produce one crop per year. Ever-bearing varieties, on the other hand, produce multiple crops throughout the growing season, but the fruit size is generally smaller. Day-neutral varieties are a hybrid of the two and offer a consistent yield throughout the growing season. By understanding the different growth periods of these varieties, you can choose the best one for your needs and enjoy a bountiful strawberry harvest. June-bearing varieties are a popular choice among strawberry enthusiasts, and for good reason.
June-Bearing Varieties
June-bearing varieties are the most common type of strawberry and are known for their high yields and large fruit size. These varieties typically take around 60 days to mature from planting and produce one large crop in the spring, usually in June, hence the name. They are often preferred by commercial growers due to their high productivity and ease of maintenance. June-bearing strawberries are also popular among home gardeners, as they are relatively easy to care for and produce a bountiful harvest. Some popular June-bearing varieties include 'Earliglow', 'Allstar', and 'Camarosa', which are known for their sweet flavor and firm texture. These varieties are typically planted in the early spring or late summer/early fall, and require full sun and well-draining soil to thrive. With proper care, June-bearing strawberries can produce fruit for several years, making them a great choice for gardeners looking for a long-term strawberry patch.
Ever-Bearing Varieties
Ever-bearing strawberry varieties are a popular choice among gardeners and strawberry enthusiasts due to their unique growth habit. Unlike June-bearing and day-neutral varieties, ever-bearing strawberries produce multiple crops throughout the growing season, typically from spring to fall. These varieties are often referred to as "remontant" or "repeat-bearing" strawberries, as they have the ability to produce flowers and fruit continuously. Ever-bearing strawberries are ideal for gardeners who want a steady supply of fresh strawberries throughout the growing season, rather than a single large harvest. Some popular ever-bearing strawberry varieties include 'Everbearing Supreme', 'Ogallala', and 'Tribute'. These varieties are known for their high yields, disease resistance, and excellent flavor. When growing ever-bearing strawberries, it's essential to provide them with full sun, well-draining soil, and regular watering to promote healthy growth and fruit production. With proper care, ever-bearing strawberries can produce multiple crops per year, making them a great choice for gardeners who want a continuous supply of fresh strawberries.
Day-Neutral Varieties
Day-neutral varieties are a type of strawberry variety that produces flowers and fruits continuously, regardless of the daylight hours. These varieties are not sensitive to the length of daylight and can produce multiple harvests throughout the growing season. Day-neutral strawberries typically take around 60 days to mature from planting to harvest, and they can produce multiple crops in a single growing season. They are ideal for gardeners who want to have a continuous supply of fresh strawberries throughout the summer months. Some popular day-neutral strawberry varieties include 'Albion', 'Camarosa', and 'Seascape'. These varieties are known for their high yields, disease resistance, and excellent flavor. Day-neutral strawberries are also a good choice for container gardening, as they can thrive in small spaces and produce a high yield. Overall, day-neutral varieties are a great option for gardeners who want to enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious strawberries throughout the growing season.