How Long Do Mosquitoes Live
Understanding The Mosquito lifespan
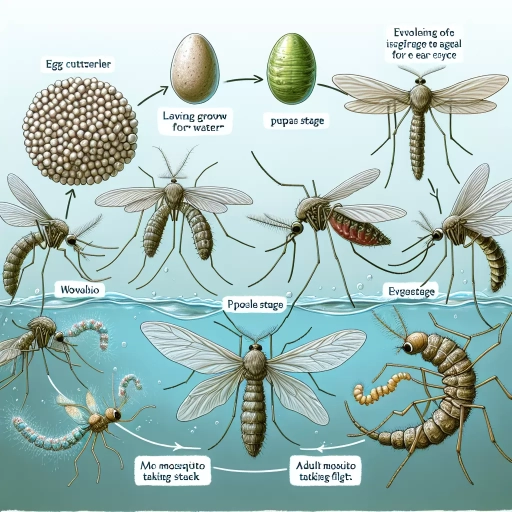
The Life Cycle of a Mosquito
Mosquitoes undergo metamorphosis in four distinct stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The time it takes for a mosquito to develop from egg to adult changes depending on the species and environmental factors. The mosquito's life begins when an adult female lays her eggs on the surface of stagnant water. Larvae emerge from the eggs, spending their days eating algae, bacteria, and other microorganisms in the water. Within 7 to 10 days, the larvae have grown enough to change into pupae. While the pupal stage is a resting phase, significant development still occurs. Within a few days, a fully developed mosquito emerges from the pupa and leaves the water. The newly emerged females are ready to take a blood meal and continue the life cycle.
Factors Influencing Mosquito Lifespan
Multiple factors influence how long a mosquito can live. Temperature significantly affects all insects, including mosquitoes. Mosquitoes, as cold-blooded creatures, are highly dependent on their surroundings. High temperatures can dramatically accelerate their life cycle, while low temperatures could inhibit their growth and development. Moreover, availability of breeding places and food sources also plays a role. Mosquitoes thrive in areas with stagnant water, where they lay their eggs. Furthermore, mosquitoes feed primarily on plant nectar; females, however, need blood for egg production.
Species Diversity and Lifespan
The lifespan of mosquitoes can also differ between species. For instance, the common house mosquito (Culex pipiens) might live two to three weeks, while the Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) has an average lifespan of one to two weeks. Male mosquitoes generally live less than female mosquitoes. In ideal conditions without any predators or diseases, female mosquitoes can live up to a month and a half. But in most cases, their lifespan tends to be much shorter due to environmental hazards and other threats such as pesticide exposure.
Mitigating Mosquito Threats
Preventing Mosquito Breeding
Given the vast impact of a mosquito's lifespan on human health, mitigating their threats becomes crucial. One of the most effective ways of mosquito control is preventing their breeding. This generally involves eliminating stagnant water sources, which serve as ideal breeding grounds for mosquitoes. Simple measures such as covering water tanks, replacing water in flower pots, and maintaining cleanliness in bird baths can go a long way in preventing mosquito breeding.
Personal Protection Measures
Personal protection measures can also play an essential role in mitigating mosquito-borne diseases. Such measures include the use of mosquito repellents, wearing long-sleeved clothing during peak mosquito activities (at dawn and dusk), and using bed nets for sleeping, especially in areas where mosquito-borne diseases are widespread. Behaviour changes to avoid peak mosquito activity hours can significantly reduce the chances of mosquito bites.
Community-Led Initiatives
Community-led initiatives form another important component of mosquito control. This includes municipal-level efforts to spray adulticides and larvicides, to maintain the cleanliness of public spaces and to raise awareness about the importance of preventing mosquito breeding. Involving the community in such endeavours ensures that these efforts have a more substantial and lasting impact in reducing mosquito population.
The Role of Science and Technology in Mosquito Control
Genetic Modification
Recent years have seen the emergence of new scientific approaches in human's fight against mosquitoes. One such approach is that of genetic modification. Through this method, scientists can manipulate mosquito genes to reduce their lifespan or to make them incapable of carrying diseases. Though these methods are promising, they also pose potential ecological and ethical issues that must be addressed.
Insecticide-impregnated Bed Nets and Traps
The use of insecticide-impregnated bed nets and traps has already proven to be effective but new advancements are continuously being made. For instance, the development of new, safer insecticides that are harmful to mosquitoes but safe for humans and implementation of new trap designs that can capture more mosquitoes.
Novel Surveillance Methods
With the help of new technology, surveillance methods for tracking mosquito populations have also improved. Innovative tools and techniques, such as drone technology and spatial data for mosquito mapping, are now being used to understand mosquito habits better and predict their growth patterns. Such data can then inform future mosquito control strategies.