How Many Rows Can Excel Handle
Microsoft Excel is a powerful spreadsheet software that has been widely used for data analysis and management. One of the most common questions asked by Excel users is how many rows the software can handle. The answer to this question is not straightforward, as it depends on various factors such as the version of Excel, the type of data being stored, and the system's hardware capabilities. In this article, we will explore the row limitations of Excel, the factors that affect its row handling, and provide tips on optimizing Excel for large datasets. We will start by examining Excel's row limitations, including the maximum number of rows that can be stored in a single worksheet and the limitations of different Excel versions.
Excel's Row Limitations
Here is the introduction paragraph: Microsoft Excel is a powerful spreadsheet software that has been widely used for data analysis and management. However, like any other software, Excel has its limitations. One of the most significant limitations of Excel is its row capacity. In this article, we will explore Excel's row limitations, including its maximum row capacity, how row limitations vary across different Excel versions, and the implications of hitting the row limit. We will start by examining Excel's maximum row capacity, which is a crucial aspect of understanding the software's limitations. Here is the supporting paragraph: Excel's row limitations can have significant implications for users who work with large datasets. When a user hits the row limit, they may experience errors, data loss, or even crashes. This can be particularly problematic for businesses or organizations that rely on Excel for critical data analysis and management. Furthermore, hitting the row limit can also limit the user's ability to perform complex data analysis, which can hinder their ability to make informed decisions. As a result, it is essential for users to understand Excel's row limitations and plan accordingly to avoid these issues. By understanding the maximum row capacity, users can take steps to optimize their data management and analysis workflows, ensuring that they can work efficiently and effectively with large datasets. This understanding begins with knowing Excel's maximum row capacity.
Excel's Maximum Row Capacity
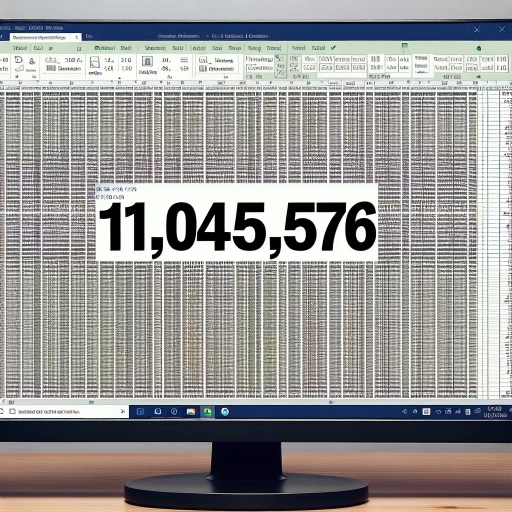
Excel's maximum row capacity is a crucial aspect to consider when working with large datasets. As of the latest versions of Excel, including Excel 2013, Excel 2016, Excel 2019, and Excel for Office 365, the maximum number of rows that can be handled is 1,048,576. This is a significant increase from the earlier versions of Excel, which had a maximum row limit of 65,536. The increased row capacity allows users to work with larger datasets and perform more complex data analysis. However, it's essential to note that the maximum row capacity can be affected by the available system resources, such as RAM and disk space. If the system resources are limited, the actual maximum row capacity may be lower than the theoretical limit. Additionally, the maximum row capacity can also be affected by the complexity of the data, such as the number of formulas, formatting, and conditional formatting rules. Therefore, it's crucial to monitor the system resources and data complexity to ensure that the maximum row capacity is not exceeded, which can lead to performance issues and errors.
Row Limitations in Different Excel Versions
In different versions of Excel, the row limitations vary significantly. In Excel 2003 and earlier versions, the maximum number of rows is limited to 65,536. This limitation was a major constraint for users who needed to work with large datasets. However, with the release of Excel 2007, Microsoft increased the row limit to 1,048,576, providing users with more flexibility and capacity to handle bigger datasets. This increased row limit has been retained in all subsequent versions of Excel, including Excel 2010, Excel 2013, Excel 2016, and Excel 2019. In addition, Excel 365, which is a cloud-based version of Excel, also has the same row limit of 1,048,576. It's worth noting that while the row limit has increased significantly over the years, the column limit has remained the same, with a maximum of 256 columns (A to IV) in all versions of Excel. Understanding these row limitations is essential for users who work with large datasets and need to plan their spreadsheet design accordingly.
Implications of Hitting the Row Limit
Hitting the row limit in Excel can have significant implications for data analysis and management. When a worksheet reaches its maximum row capacity of 1,048,576 rows, it can no longer accommodate additional data, leading to data loss or corruption. This can be particularly problematic for businesses or organizations that rely on Excel for data-driven decision-making, as incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to flawed insights and poor decision-making. Furthermore, hitting the row limit can also impact data visualization and reporting, as charts and graphs may not be able to display the full range of data, leading to incomplete or misleading representations of trends and patterns. In addition, exceeding the row limit can also cause performance issues, such as slow loading times and crashes, making it difficult to work with large datasets. To mitigate these implications, users can consider splitting large datasets into smaller worksheets or using alternative data management tools, such as databases or data analytics software, that can handle larger datasets. Ultimately, understanding the implications of hitting the row limit is crucial for effective data management and analysis in Excel.
Factors Affecting Excel's Row Handling
When working with large datasets in Excel, it's essential to understand the factors that affect row handling. Row handling refers to the process of managing and manipulating rows in a worksheet, including inserting, deleting, and formatting rows. There are several factors that can impact row handling in Excel, including system resources, worksheet complexity, and data type. System resources, such as RAM and CPU power, play a crucial role in determining how efficiently Excel can handle rows. Worksheet complexity, including the number of formulas, conditional formatting, and pivot tables, can also slow down row handling. Additionally, the data type of the cells in a row can affect how quickly Excel can process and manipulate the data. In this article, we'll explore each of these factors in more detail, starting with the impact of system resources on row handling.
System Resources and Row Handling
Excel's row handling capabilities are significantly influenced by the system resources available on the computer. The amount of RAM, processing power, and storage space can all impact how efficiently Excel can handle large datasets. When working with massive spreadsheets, it's essential to have a robust system that can provide the necessary resources to support Excel's operations. A minimum of 8 GB of RAM is recommended, but 16 GB or more is ideal for handling large datasets. Additionally, a fast processor, such as a multi-core Intel Core i5 or i7, can significantly improve Excel's performance. Adequate storage space is also crucial, as Excel files can quickly grow in size, especially when working with large datasets. A solid-state drive (SSD) can provide faster loading and saving times, reducing the overall processing time. Furthermore, having a 64-bit version of Excel and Windows can also improve performance, as it allows Excel to access more memory and handle larger datasets. By ensuring that the system resources are sufficient, users can optimize Excel's row handling capabilities and work efficiently with large datasets.
Worksheet Complexity and Row Handling
Excel's row handling capabilities are significantly influenced by worksheet complexity, which encompasses various factors that impact the application's performance. A complex worksheet is characterized by a large number of formulas, conditional formatting rules, and data validation constraints, all of which contribute to increased computational overhead. As the complexity of a worksheet grows, Excel's ability to handle rows efficiently is compromised, leading to slower performance and potential errors. For instance, a worksheet with numerous nested IF statements, VLOOKUPs, and INDEX/MATCH functions can slow down Excel's row handling, making it more challenging to manage large datasets. Furthermore, the presence of multiple pivot tables, charts, and other data visualization tools can also add to the complexity of a worksheet, thereby affecting Excel's row handling capabilities. To mitigate these issues, users can employ strategies such as simplifying formulas, reducing the number of conditional formatting rules, and optimizing data validation constraints to improve Excel's performance and row handling efficiency. By understanding the impact of worksheet complexity on row handling, users can take proactive steps to optimize their worksheets and ensure seamless data management.
Data Type and Row Handling
When it comes to data types and row handling in Excel, it's essential to understand how different data types can impact the program's ability to handle large datasets. Excel supports various data types, including numbers, text, dates, times, and logical values. However, the way Excel stores and handles these data types can significantly affect its row handling capabilities. For instance, numbers are stored as 64-bit floating-point numbers, which allows for a high degree of precision but also consumes more memory. On the other hand, text strings are stored as Unicode characters, which can be more memory-efficient but may lead to slower performance when dealing with large datasets. Dates and times are stored as serial numbers, which enables efficient calculations and sorting but can also lead to issues with date and time formatting. Logical values, such as TRUE and FALSE, are stored as binary values, which are highly memory-efficient but may not be as intuitive to work with. Understanding how these data types are stored and handled can help users optimize their datasets and improve Excel's row handling performance. For example, using numbers instead of text strings for numerical data can significantly improve calculation speed and reduce memory usage. Similarly, using dates and times in a consistent format can enable efficient sorting and filtering. By being mindful of data types and their impact on row handling, users can unlock Excel's full potential and work with large datasets more efficiently.
Optimizing Excel for Large Datasets
When working with large datasets in Excel, it's essential to optimize the application to ensure smooth performance and efficient data analysis. A well-optimized Excel setup can significantly reduce processing time, minimize errors, and enhance overall productivity. To achieve this, there are several strategies that can be employed. Firstly, implementing best practices for large dataset management is crucial, as it lays the foundation for efficient data handling. This includes techniques such as data cleaning, data normalization, and data compression. Additionally, utilizing Excel's built-in tools for optimization can also greatly improve performance. Features like data validation, conditional formatting, and pivot tables can help streamline data analysis and reduce computational overhead. Furthermore, leveraging third-party add-ins can provide enhanced performance and functionality, allowing users to tackle complex data analysis tasks with ease. By implementing these strategies, users can unlock the full potential of Excel and take their data analysis to the next level. By starting with best practices for large dataset management, users can set themselves up for success and create a solid foundation for optimized Excel performance.
Best Practices for Large Dataset Management
When dealing with large datasets in Excel, it's essential to follow best practices to ensure efficient data management, minimize errors, and optimize performance. One of the most critical best practices is to plan and design your dataset structure carefully, considering the data types, relationships, and potential growth. This involves creating a data model that is scalable, flexible, and easy to maintain. Another crucial aspect is data organization, where you should use clear and descriptive column headers, avoid duplicate data, and use data validation to ensure data consistency. Additionally, it's vital to use data compression techniques, such as removing unnecessary characters, using shorter data formats, and leveraging Excel's built-in data compression features. Regular data backups and version control are also essential to prevent data loss and ensure that changes can be tracked and reverted if needed. Furthermore, using Excel's built-in data analysis and visualization tools, such as pivot tables, charts, and conditional formatting, can help to identify trends, patterns, and insights, making it easier to make informed decisions. By following these best practices, you can ensure that your large dataset is well-managed, efficient, and provides valuable insights to drive business success.
Using Excel's Built-in Tools for Optimization
When working with large datasets in Excel, optimization is key to ensuring smooth performance and efficient data analysis. One of the most effective ways to optimize your Excel workflow is by leveraging the application's built-in tools. Excel offers a range of features and functions that can help streamline your data management and analysis processes, from data validation and formatting to data analysis and visualization. For instance, Excel's data validation tool allows you to restrict input data to specific formats, such as dates or numbers, which can help prevent errors and inconsistencies in your dataset. Additionally, Excel's formatting tools enable you to quickly and easily format large datasets, making it easier to identify trends and patterns. Excel's data analysis tools, such as pivot tables and charts, can also help you to summarize and visualize large datasets, making it easier to extract insights and make informed decisions. Furthermore, Excel's built-in functions, such as VLOOKUP and INDEX/MATCH, can help you to quickly and efficiently perform complex data analysis tasks, such as data lookup and data manipulation. By taking advantage of these built-in tools, you can optimize your Excel workflow, reduce errors, and improve your overall productivity when working with large datasets.
Third-Party Add-ins for Enhanced Performance
When dealing with large datasets in Excel, one of the most effective ways to enhance performance is by leveraging third-party add-ins. These add-ins are designed to optimize Excel's capabilities, providing users with advanced tools and features that can significantly improve data processing speed, accuracy, and overall productivity. By installing third-party add-ins, users can access a wide range of functionalities, such as data visualization, data mining, and data analysis, which can help to streamline workflows and reduce the time spent on data manipulation. For instance, add-ins like Power BI, Power Query, and Power Pivot can help users to create interactive dashboards, perform advanced data modeling, and analyze large datasets with ease. Additionally, add-ins like ASAP Utilities and Excel-Tool can provide users with a range of productivity tools, such as data cleaning, data formatting, and data validation, which can help to improve data quality and reduce errors. By leveraging these third-party add-ins, users can unlock Excel's full potential, enabling them to work more efficiently and effectively with large datasets.