What Is Tufting
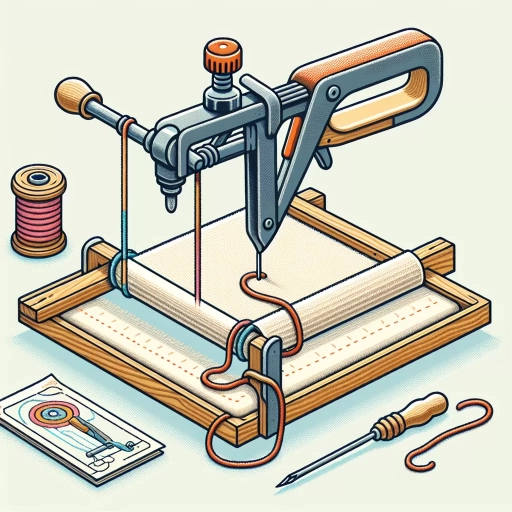
Tufting, a versatile and creative textile technique, has been gaining popularity across various industries and hobbies. At its core, tufting involves pushing yarn or thread through a primary fabric to create a dense, plush pile. This method is not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly functional. In this article, we will delve into the world of tufting, starting with a detailed explanation of **What is Tufting?**, where we explore the process and materials involved. We will then examine the diverse **Applications of Tufting**, highlighting its use in furniture, art, and other fields. Finally, we will discuss the **Benefits and Challenges of Tufting**, addressing both the advantages and the potential drawbacks of this technique. By understanding these aspects, readers will gain a comprehensive insight into the art and science of tufting. Let's begin by exploring the fundamental question: **What is Tufting?**
What is Tufting?
Tufting is a versatile and creative textile technique that has gained significant attention in recent years for its unique aesthetic and functional applications. At its core, tufting involves pushing yarn or thread through a primary fabric to create a dense, plush pile on the other side. This process can be used to create a wide range of items, from decorative wall hangings and furniture to functional items like rugs and carpets. To fully understand tufting, it is essential to delve into its **Definition and Origins**, which trace back to ancient civilizations and have evolved over time. Additionally, mastering **Basic Techniques and Tools** is crucial for anyone looking to engage in tufting, as it requires specific skills and equipment. Finally, exploring the various **Types of Tufting** reveals the diverse possibilities this craft offers, from hand tufting to machine tufting, each with its own set of challenges and benefits. By examining these aspects, one can gain a comprehensive understanding of what tufting entails and how it can be applied in various contexts. Let's begin by exploring the **Definition and Origins** of tufting.
Definition and Origins
**Definition and Origins** Tufting is a textile production method that involves pushing yarn through a primary fabric, known as the backing fabric, to create a secondary fabric with a tufted surface. This technique is widely used in various industries, including upholstery, carpet manufacturing, and even fashion. The origins of tufting date back to the early 20th century when it was first developed in the United States. Initially, tufting was used primarily for making carpets and rugs, leveraging its ability to produce dense, plush piles efficiently. The process involves using a tufting gun or needle to push the yarn through the backing material, which can be made from materials like cotton, polyester, or a blend. Each tuft is secured by a primary or secondary backing, ensuring stability and durability. The evolution of tufting has seen significant advancements over the years. From its humble beginnings in carpet manufacturing, tufting has expanded into other areas such as furniture upholstery and even artistic applications. In modern times, tufting is not only a practical method for creating functional textiles but also a popular medium for artists and craftspeople who value its versatility and creative potential. The rise of DIY tufting kits and online tutorials has democratized access to this craft, allowing enthusiasts to explore tufting from the comfort of their homes. Historically, tufting was labor-intensive and required specialized machinery. However, with technological advancements, the process has become more streamlined and accessible. Today, both manual and automated tufting machines are available, catering to different scales of production and skill levels. This adaptability has contributed to the widespread adoption of tufting across various sectors. In summary, tufting is a versatile textile technique with roots in early 20th-century carpet manufacturing. Its definition revolves around the creation of tufted surfaces by pushing yarn through a backing fabric. Over time, tufting has evolved from an industrial process to a multifaceted craft that spans from commercial production to artistic expression. Its origins highlight its practical beginnings, while its modern applications underscore its enduring relevance and creative potential.
Basic Techniques and Tools
**Basic Techniques and Tools** Tufting, a versatile and creative textile art form, relies on several fundamental techniques and tools to produce its distinctive, plush surfaces. At the core of tufting is the tufting gun, which is essentially a handheld device that pushes yarn through a primary fabric (usually a sturdy canvas or monk's cloth) to create the tufts. There are two main types of tufting guns: the electric gun and the manual gun. The electric gun is faster and more efficient, ideal for large-scale projects, while the manual gun offers greater control and precision, making it perfect for intricate designs. Another crucial tool is the primary fabric itself. This fabric serves as the base onto which the yarn tufts are attached. Monk's cloth and canvas are popular choices due to their tight weave and durability. The yarn used in tufting can vary widely in terms of material, color, and texture, allowing for immense creativity and customization. The basic technique involves loading the tufting gun with yarn, then pushing it through the primary fabric to create tufts. The depth and density of these tufts can be adjusted by changing the tension on the gun or by using different types of yarn. For more complex designs, tufters often use stencils or patterns to guide their work. Additional tools include scissors for cutting the yarn, a measuring tape for ensuring even spacing, and a comb or rake for adjusting and smoothing out the tufts. Some tufters also use a frame or hoop to keep their work taut and organized. In terms of techniques, there are several key methods. The most common is the "push-through" method where the yarn is pushed through from the back of the fabric to the front. This method allows for quick coverage but may lack precision. For more detailed work, tufters might use a "pull-through" method where the yarn is pulled through from the front to the back, offering greater control over each tuft. Understanding these basic techniques and tools is essential for mastering the art of tufting. Whether you're creating wall hangings, rugs, or furniture upholstery, these fundamentals provide the foundation upon which all tufting projects are built. By mastering these basics, tufters can unlock a world of creative possibilities and produce high-quality, visually appealing pieces that showcase their skill and artistry.
Types of Tufting
Tufting, a versatile and creative textile technique, encompasses several distinct types that cater to various applications and artistic expressions. **Hand Tufting** is one of the most common methods, where yarn or thread is pushed through a primary fabric using a tufting gun or needle. This technique allows for high customization and is often used in rug-making, upholstery, and wall hangings. **Machine Tufting**, on the other hand, employs automated machinery to speed up the process, making it more suitable for large-scale production. This method is frequently used in the manufacturing of carpets and other floor coverings. **Cut Pile Tufting** involves cutting the yarn after it has been tufted, creating a soft, plush surface. This type is commonly seen in residential carpets and rugs where comfort and durability are key. **Loop Pile Tufting** leaves the yarn uncut, forming loops on the surface of the fabric. This style is often used in commercial settings due to its resistance to wear and tear. **Cut-Loop Pile Tufting** combines both techniques, offering a mix of cut and uncut yarns for a varied texture. **Needle Punch Tufting** uses barbed needles to push fibers through a backing material without the need for yarn or thread. This method is particularly useful for creating dense, thick fabrics like those used in geotextiles and industrial applications. **Hooked Tufting**, similar to traditional rug hooking, involves using a hook to pull loops of yarn through a backing fabric. This technique is popular among crafters and artisans for its simplicity and creative freedom. Each type of tufting offers unique advantages and is suited to different purposes, from decorative arts to industrial uses. Understanding these variations can help individuals choose the most appropriate method for their specific needs, whether they are looking to create a piece of art, furnish a home, or manufacture textiles on a large scale. By selecting the right type of tufting, one can achieve the desired texture, durability, and aesthetic appeal in their final product.
Applications of Tufting
Tufting, a versatile and creative technique, has found its way into various applications across different industries. This method of inserting yarn or thread through a primary fabric to create a textured surface has been embraced for its aesthetic appeal, durability, and functionality. In the realm of **Furniture and Upholstery**, tufting is used to create luxurious and comfortable seating, adding a touch of elegance to home decor. Beyond furniture, **Textile Art and Design** leverage tufting to produce intricate and visually stunning pieces that are both artistic expressions and functional items. Additionally, **Industrial Uses** of tufting include the production of high-quality carpets, rugs, and other textile products that require robust construction. Each of these applications highlights the adaptability and value of tufting in modern design. As we delve deeper into the world of tufting, we will first explore how it revolutionizes the field of **Furniture and Upholstery**.
Furniture and Upholstery
Furniture and upholstery are integral components of interior design, enhancing both the aesthetic and functional aspects of a space. Tufting, a technique that involves pushing yarn or thread through fabric to create a series of small, evenly spaced knots, plays a significant role in this domain. In the context of furniture and upholstery, tufting is particularly notable for its ability to add texture, depth, and visual interest to various pieces. For instance, tufted headboards and ottomans are popular choices for bedrooms and living rooms because they introduce a touch of luxury and sophistication. The tufting process allows for the creation of intricate patterns and designs, making each piece unique and customizable according to individual tastes. Tufted furniture also offers practical benefits. The tufts can help distribute the filling material evenly, ensuring that cushions and mattresses maintain their shape over time. This is especially important for high-traffic areas or pieces that are subject to frequent use. Additionally, tufting can enhance the durability of upholstery by preventing the filling from shifting or clumping, thereby extending the lifespan of the furniture. From a design perspective, tufting allows for a wide range of creative possibilities. It can be used to create geometric patterns, floral motifs, or even abstract designs, making it versatile enough to fit into various decor styles. For example, a tufted Chesterfield sofa can add a classic touch to a traditional setting, while a tufted pouf can bring a modern twist to a contemporary space. The technique also enables designers to experiment with different materials and colors, further expanding the creative potential of tufted furniture. Moreover, tufting has seen a resurgence in popularity due to its artisanal appeal. Hand-tufted pieces are often valued for their craftsmanship and uniqueness, making them sought after by those who appreciate bespoke furniture. This artisanal aspect not only adds to the aesthetic value but also underscores the quality and attention to detail that goes into each piece. In summary, tufting in furniture and upholstery is a multifaceted technique that combines aesthetic appeal with practical benefits. It enhances the visual and tactile experience of a room, offers durability and longevity, and provides endless opportunities for creative expression. Whether used in traditional or modern designs, tufted furniture stands out as a testament to craftsmanship and style, making it an invaluable application of the tufting technique.
Textile Art and Design
Textile art and design encompass a wide range of creative expressions that utilize fabric as the primary medium. This field combines traditional craftsmanship with modern techniques, resulting in diverse applications across various industries. In the context of tufting, textile art and design play a crucial role in transforming raw materials into aesthetically pleasing and functional pieces. Tufting, a process involving the insertion of yarn or thread through a primary fabric to create a secondary fabric, is particularly significant in textile art due to its versatility and creative potential. Textile artists and designers who specialize in tufting can produce intricate patterns, textures, and designs that are both visually striking and tactilely engaging. These creations can range from wall hangings and tapestries to furniture upholstery and even wearable art. The ability to control the density, color, and texture of the tufted fabric allows artists to achieve a high level of detail and expressiveness, making each piece unique and often narrative-driven. In contemporary art, tufting has become a popular medium for artists looking to push the boundaries of traditional textile practices. It allows for experimentation with scale, from small, delicate pieces to large-scale installations that can transform entire spaces. Additionally, the tactile nature of tufted works invites viewer interaction, making it an engaging medium for public art projects and exhibitions. From a design perspective, tufting is also highly valued in interior design and fashion. In interior spaces, tufted textiles can add depth and warmth, creating cozy environments that are both stylish and inviting. For instance, tufted rugs can define different areas within a room while adding a touch of handmade craftsmanship. In fashion, tufted elements can be incorporated into clothing and accessories, providing a unique textural element that enhances the overall aesthetic of a garment. Moreover, the sustainability aspect of textile art and design through tufting is noteworthy. Many artists and designers are now focusing on using recycled materials or repurposing old textiles to create new tufted pieces. This approach not only reduces waste but also adds an ethical dimension to the creative process, aligning with the growing interest in eco-friendly practices within the art and design communities. In summary, textile art and design through tufting offer a rich canvas for creative expression, innovation, and practical application. Whether in fine art, interior design, fashion, or sustainable practices, tufting continues to evolve as a dynamic and versatile medium that celebrates both tradition and modernity. Its ability to blend functionality with aesthetic appeal makes it an invaluable tool for artists and designers seeking to push the boundaries of what is possible with fabric.
Industrial Uses
Industrial uses of tufting are diverse and widespread, leveraging the versatility and efficiency of this textile manufacturing process. In the automotive industry, tufted carpets and floor mats are commonly used due to their durability and resistance to wear and tear. These products are designed to withstand heavy foot traffic and harsh environmental conditions, making them ideal for vehicles. Additionally, tufted materials are used in soundproofing and insulation within car interiors, enhancing overall comfort and reducing noise levels. In the construction sector, tufted carpets and underlayment materials play a crucial role in flooring solutions. They provide thermal insulation, reduce noise levels, and offer a comfortable walking surface. Tufted products are also used in commercial settings such as offices, hotels, and public spaces where high traffic demands durable flooring solutions. The aerospace industry also benefits from tufting technology. Tufted materials are used in aircraft interiors for seating, flooring, and wall coverings due to their lightweight yet robust nature. These materials must meet stringent safety standards while providing comfort and aesthetic appeal. In healthcare facilities, tufted carpets are preferred for their ease of maintenance and hygiene. They are resistant to bacteria and other microorganisms, making them suitable for environments where cleanliness is paramount. Furthermore, tufted products are used in medical equipment such as hospital beds and wheelchairs for their comfort and durability. The sports industry utilizes tufted surfaces extensively in artificial turf fields. These fields offer a consistent playing surface year-round, regardless of weather conditions, and require minimal maintenance compared to natural grass. Tufted turf is also used in indoor sports facilities like gymnasiums and training centers. Moreover, tufting is applied in various industrial applications such as filtration systems where tufted fibers are used to capture particles and contaminants from air or water streams. This technology ensures high efficiency in purification processes across different industries. In summary, the industrial applications of tufting span multiple sectors including automotive, construction, aerospace, healthcare, sports, and filtration systems. The process offers a range of benefits including durability, ease of maintenance, comfort, and cost-effectiveness, making it an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing.
Benefits and Challenges of Tufting
Tufting, a traditional textile technique, has seen a resurgence in popularity due to its unique benefits and inherent challenges. This article delves into the multifaceted world of tufting, exploring its advantages in craftsmanship, common challenges and their solutions, as well as crucial health and safety considerations. On one hand, tufting offers unparalleled opportunities for creative expression and precision in craftsmanship, allowing artisans to produce intricate and bespoke pieces that stand out in both functionality and aesthetics. However, this craft is not without its obstacles; common challenges such as maintaining consistency, managing material costs, and ensuring durability require careful consideration and innovative solutions. Additionally, health and safety concerns, including exposure to chemicals and physical strain, must be addressed to ensure a safe working environment. By understanding these aspects, tufting enthusiasts can better navigate the complexities of this craft. Let's begin by examining the advantages in craftsmanship that make tufting such a rewarding and sought-after skill.
Advantages in Craftsmanship
Craftsmanship in tufting offers several distinct advantages that elevate the quality and appeal of the final product. **Precision and Detail**: Skilled craftsmen can achieve intricate designs and patterns with high precision, ensuring that each tuft is perfectly aligned and evenly spaced. This level of detail enhances the aesthetic appeal of the tufted piece, making it more visually appealing and sophisticated. **Customization**: Craftsmanship allows for a high degree of customization, enabling artisans to create unique pieces tailored to specific tastes or requirements. This flexibility is particularly valuable in bespoke projects where individuality is paramount. **Durability**: Well-crafted tufted items are more durable and long-lasting. Experienced craftsmen use high-quality materials and techniques that ensure the tufts remain securely in place, reducing the likelihood of wear and tear over time. **Artistic Expression**: Tufting as a craft form allows artisans to express their creativity freely. Skilled craftsmen can experiment with various colors, textures, and patterns, turning each piece into a work of art that reflects their vision and skill. **Value Appreciation**: Handcrafted tufted items often appreciate in value over time due to their uniqueness and the skill involved in their creation. This makes them not only functional but also valuable investments for collectors and enthusiasts. **Sustainability**: Craftsmanship in tufting can be more sustainable than mass-produced alternatives. Artisans often use eco-friendly materials and traditional methods that minimize waste and environmental impact. Additionally, the longevity of handcrafted pieces reduces the need for frequent replacements, contributing to a more sustainable lifestyle. **Economic Benefits**: Supporting skilled craftsmen can have positive economic impacts by preserving traditional skills and contributing to local economies. By valuing craftsmanship, consumers help ensure that these skills are passed down through generations, maintaining cultural heritage and community vitality. Overall, the advantages of craftsmanship in tufting lie in its ability to combine precision, customization, durability, artistic expression, value appreciation, sustainability, and economic benefits, making each tufted piece a testament to human skill and creativity.
Common Challenges and Solutions
When exploring the benefits and challenges of tufting, it is crucial to address the common hurdles that tufters often encounter. One of the primary challenges is **material selection and quality**. Tufters must choose the right yarns, threads, and backing materials to ensure durability and aesthetic appeal. High-quality materials can be expensive, but they are essential for creating long-lasting and visually appealing tufted pieces. Another significant challenge is **tool maintenance**; tufting guns and other tools require regular cleaning and maintenance to prevent clogging and ensure consistent performance. **Workplace ergonomics** also pose a challenge, as tufting can be physically demanding and may lead to repetitive strain injuries if proper ergonomic practices are not followed. Tufters should invest in comfortable seating, ergonomic workstations, and take regular breaks to mitigate these risks. Additionally, **learning the technique** can be daunting for beginners. It is advisable for new tufters to start with simple projects and gradually move to more complex ones as their skills improve. **Time management** is another critical aspect, as tufting projects can be time-consuming. Effective time management involves setting realistic goals, breaking down larger projects into smaller tasks, and maintaining a consistent workflow. Furthermore, **space constraints** can be a challenge, especially for those working in small studios or home environments. Efficient use of space through organized storage and a well-planned workspace can help alleviate this issue. To overcome these challenges, several solutions can be implemented. **Investing in high-quality tools** and materials from the outset can save time and money in the long run by reducing the need for frequent replacements. **Online tutorials and workshops** are invaluable resources for learning new techniques and improving existing skills. Many experienced tufters share their knowledge through online platforms, providing accessible learning opportunities. **Joining tufting communities** or forums can also be beneficial, as these networks offer support, advice, and inspiration from fellow tufters. These communities often share tips on tool maintenance, material selection, and ergonomic practices. Additionally, **setting up a dedicated workspace** with proper lighting, ventilation, and ergonomic furniture can significantly enhance productivity and comfort. In conclusion, while tufting presents several challenges, these can be effectively managed through careful planning, investment in quality tools and materials, continuous learning, and community support. By understanding and addressing these common challenges, tufters can maximize their creative potential and enjoy the numerous benefits that this craft offers.
Health and Safety Considerations
Health and safety considerations are paramount when engaging in tufting, a craft that involves using a tufting gun or needle to push yarn through a primary fabric, creating a textured surface. Several key factors must be addressed to ensure a safe and healthy working environment. **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):** Wearing appropriate PPE is crucial. This includes safety glasses or goggles to protect eyes from flying yarn or debris, gloves to prevent hand injuries from the tufting gun or needles, and a dust mask to avoid inhaling fibers and dust particles. **Work Environment:** The workspace should be well-ventilated to reduce exposure to airborne fibers and dust. A clean and organized workspace helps prevent tripping hazards and ensures easy access to tools and materials. Proper lighting is also essential to avoid eye strain and improve visibility. **Tool Safety:** The tufting gun, being the primary tool, requires careful handling. Users should follow the manufacturer's instructions for operation, maintenance, and storage. Regularly cleaning and lubricating the gun can prevent malfunctions that could lead to accidents. **Physical Health:** Tufting can be physically demanding due to prolonged sitting, repetitive motions, and potential strain on the hands and wrists. Taking regular breaks to stretch and move around can help mitigate these risks. Ergonomic seating and proper posture are also important for long-term health. **Mental Health:** The repetitive nature of tufting can sometimes lead to mental fatigue or stress. It is important to maintain a balanced work schedule and engage in activities that promote mental well-being. **Chemical Safety:** Some tufting materials, such as certain dyes or treatments applied to the yarn, may contain chemicals that are hazardous if not handled properly. Always follow safety guidelines provided by the material suppliers and ensure good ventilation when working with these materials. **Emergency Preparedness:** Having a first aid kit nearby and knowing basic first aid procedures can help in case of minor accidents. It is also wise to have emergency contact numbers readily available. By adhering to these health and safety considerations, tufters can significantly reduce the risks associated with this craft, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience while creating their artwork. This attention to detail not only protects the individual but also enhances the overall quality of the tufted piece by maintaining focus and well-being throughout the process.