What Can Go Wrong Epoxy Coating Over Wood
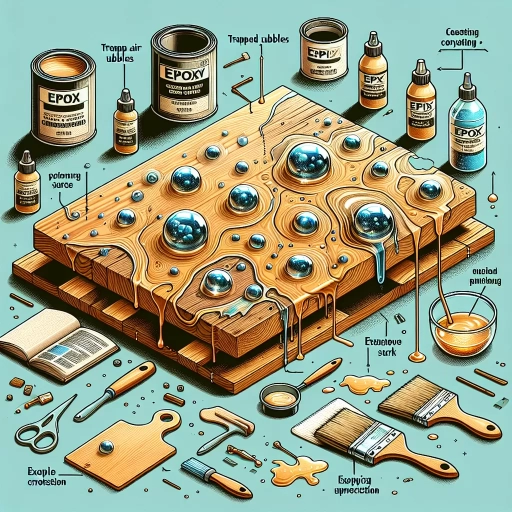
Epoxy coating over wood can be a highly effective and aesthetically pleasing way to protect and enhance wooden surfaces, but it is not without its potential pitfalls. Despite its many benefits, epoxy coating can go wrong in several critical areas. First, issues during the preparation and application process can lead to subpar results, including uneven finishes and poor adhesion. Second, material compatibility and durability concerns must be addressed to ensure the epoxy does not degrade prematurely or react adversely with the wood. Finally, environmental and maintenance factors play a significant role in the long-term performance of the epoxy coating, as exposure to certain conditions and lack of proper care can compromise its integrity. Understanding these potential issues is crucial for achieving a successful epoxy coating. Let's start by examining the preparation and application issues that can set the stage for a flawed finish.
Preparation and Application Issues
When it comes to ensuring the success of any project involving materials or coatings, preparation and application are crucial steps that cannot be overlooked. However, several common issues can significantly impact the outcome. Insufficient surface preparation, incorrect mixing ratios, and improper application techniques are among the most prevalent problems that can lead to subpar results. Each of these issues can have severe consequences, from compromised durability and performance to aesthetic flaws and safety hazards. For instance, insufficient surface preparation can lead to poor adhesion and premature failure of the material, while incorrect mixing ratios can result in inconsistent properties and reduced effectiveness. Similarly, improper application techniques can cause uneven distribution and inadequate coverage. Understanding and addressing these issues is essential for achieving high-quality outcomes. Let's start by examining one of the most critical aspects: insufficient surface preparation. --- **Insufficient Surface Preparation** --- Proper surface preparation is the foundation upon which successful applications are built. Without it, even the best materials and techniques can fail to deliver desired results. This includes cleaning the surface to remove dirt, oils, and other contaminants that could interfere with adhesion. Additionally, surfaces may need to be sanded or roughened to create a better bond between the material and the substrate. Neglecting these steps can lead to poor adhesion, which in turn can cause the material to peel off prematurely or fail under stress. Ensuring that the surface is adequately prepared is a critical first step in any application process. --- **Incorrect Mixing Ratios** --- The mixing ratio of materials is another critical factor that must be adhered to strictly. Incorrect ratios can alter the chemical composition of the material, leading to changes in its physical properties such as strength, flexibility, or durability. For example, if a coating is mixed with too much solvent, it may dry too quickly and become brittle; conversely, too little solvent could result in a coating that never fully hardens. Following the manufacturer's guidelines for mixing ratios is essential to ensure that the material performs as intended. --- **Improper Application Techniques** --- Finally, improper application techniques can also significantly impact the success of a project. This includes using the wrong tools or applying the material under adverse conditions such as extreme temperatures or humidity levels. For instance, applying a coating in direct sunlight or during high winds can lead to uneven drying and poor finish quality. Similarly, using rollers instead of brushes for certain types of coatings might result in inadequate coverage and texture issues. Understanding and adhering to best practices for application ensures that materials are applied efficiently and effectively. By addressing these preparation and application issues head-on, individuals can avoid common pitfalls and achieve superior results in their projects.
Insufficient Surface Preparation
Insufficient surface preparation is a critical issue that can significantly compromise the performance and longevity of epoxy coatings over wood. When the surface is not adequately prepared, it can lead to poor adhesion, uneven finishes, and increased susceptibility to wear and tear. Here are the key aspects to consider: 1. **Cleaning**: Failing to thoroughly clean the wood surface can leave behind dirt, oils, and other contaminants that interfere with the epoxy's ability to bond properly. This can result in blistering or peeling of the coating over time. 2. **Sanding**: Inadequate sanding does not provide a sufficient mechanical bond between the wood and the epoxy. This lack of texture prevents the epoxy from adhering securely, leading to potential delamination. 3. **Moisture Content**: Wood with high moisture content can cause the epoxy to lift or bubble as it dries. Ensuring that the wood is within the recommended moisture range is crucial for a successful application. 4. **Old Coatings**: Not removing old coatings or finishes can create a weak bond between layers. The new epoxy coating may adhere to the old finish rather than the wood itself, which can lead to premature failure. 5. **Wood Condition**: Ignoring cracks, splits, or other defects in the wood can allow moisture to penetrate beneath the epoxy coating, causing damage from within. These defects should be filled and sanded before applying any coating. 6. **Chemical Contamination**: Chemicals such as oils, waxes, or preservatives on the wood surface can inhibit adhesion. These substances must be completely removed before applying an epoxy coating. 7. **Temperature and Humidity**: Applying epoxy in conditions outside its recommended temperature and humidity range can affect its curing process and final bond strength. By neglecting these critical steps in surface preparation, you risk undermining the integrity of your epoxy coating, leading to costly repairs down the line. Proper surface preparation ensures a strong bond between the wood and epoxy, enhancing durability and aesthetic appeal. Always follow manufacturer guidelines and best practices for surface preparation to achieve optimal results with your epoxy coating project.
Incorrect Mixing Ratios
Incorrect mixing ratios are a critical issue that can significantly compromise the integrity and performance of epoxy coatings over wood. When the ratio of resin to hardener is not adhered to as specified by the manufacturer, it can lead to a range of problems. For instance, if too much resin is used relative to the hardener, the epoxy may not cure properly, resulting in a soft or tacky finish. Conversely, using too much hardener can cause the epoxy to cure too quickly, leading to brittleness and potential cracking. Both scenarios can undermine the adhesive strength and durability of the coating, making it more susceptible to peeling, flaking, or delamination from the wood surface. Moreover, incorrect mixing ratios can affect the chemical properties of the epoxy, altering its viscosity, flow characteristics, and even its color consistency. This can make application more challenging, as uneven or thickened mixtures may be difficult to spread evenly across the wood surface. Additionally, improper ratios can impact the epoxy's resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, UV light, and temperature fluctuations, which are crucial for maintaining the coating's protective qualities over time. To avoid these issues, it is essential to follow the manufacturer's instructions meticulously. This includes using accurate measuring tools and ensuring that both components are mixed thoroughly according to the recommended ratio. It is also advisable to perform small-scale tests before applying the epoxy coating on a larger scale to ensure that the mixed ratio yields the desired results. By adhering strictly to the correct mixing ratios, users can ensure a strong bond between the epoxy and wood, achieving a durable and long-lasting finish that meets their expectations.
Improper Application Techniques
Improper application techniques are a common pitfall when applying epoxy coating over wood, leading to subpar results and potential failures. One of the most critical mistakes is inadequate surface preparation. Failing to properly clean and sand the wood surface can result in poor adhesion, causing the epoxy to peel off prematurely. Additionally, not ensuring the wood is dry and free of oils or waxes can interfere with the epoxy's bonding process. Another issue is incorrect mixing of the epoxy components. If the resin and hardener are not mixed in the correct ratio or for the appropriate amount of time, it can affect the curing process, leading to a weak or brittle finish. Applying too thick a layer of epoxy at once can also cause it to drip or sag, creating uneven surfaces and bubbles. Furthermore, insufficient coverage or uneven application can leave areas unprotected, making them vulnerable to damage from moisture or wear. Environmental factors such as high humidity or extreme temperatures during application can also disrupt the curing process, resulting in a finish that lacks durability and gloss. Finally, neglecting to apply a primer or sealant before the epoxy coating can expose the wood to moisture and other elements, compromising both the wood and the epoxy layer. By understanding these common pitfalls, users can take steps to ensure a smooth, durable, and long-lasting epoxy coating over wood.
Material Compatibility and Durability Concerns
When considering material compatibility and durability, several critical factors must be taken into account to ensure the longevity and performance of the chosen materials. One of the primary concerns is the incompatibility with specific wood types, which can lead to structural weaknesses and premature degradation. Additionally, materials that lack UV resistance are susceptible to damage from sunlight, resulting in discoloration, cracking, and reduced lifespan. Furthermore, poor chemical resistance can expose materials to corrosion and degradation when exposed to various substances, compromising their integrity. Understanding these potential pitfalls is essential for making informed decisions about material selection. By addressing these issues, we can better design and construct durable and reliable structures. Let's start by examining the incompatibility with wood type, a common challenge that can significantly impact the overall durability of a project.
Incompatibility with Wood Type
When considering epoxy coating over wood, one critical aspect to address is the incompatibility with certain types of wood. Not all wood species react equally well to epoxy, and some may even cause the coating to fail prematurely. For instance, woods with high oil content, such as teak and cedar, can inhibit the adhesion of epoxy due to their natural oils and resins. These oils can migrate to the surface, creating a barrier that prevents the epoxy from bonding properly, leading to peeling or flaking over time. Similarly, woods with high moisture content or those prone to warping and shrinking, like pine or fir, can also pose significant challenges. As these woods expand and contract with changes in humidity, they can cause the epoxy to crack or delaminate. This is particularly problematic because epoxy is a rigid material that does not flex well with the natural movements of wood. Additionally, some woods may contain tannins or other chemicals that can react with the epoxy, causing discoloration or weakening the bond between the wood and the coating. For example, woods like oak and walnut contain tannins that can leach into the epoxy, resulting in an uneven color or a weakened structural integrity. To mitigate these issues, it is essential to select wood species that are known to be compatible with epoxy coatings. Hardwoods like maple and birch are generally good choices because they have lower oil content and are less prone to warping. Preparing the wood surface properly is also crucial; this includes sanding to create a smooth finish, ensuring the wood is completely dry, and applying a suitable primer if necessary. In summary, the compatibility of wood type with epoxy coating is a critical factor in ensuring the durability and longevity of the finish. Choosing the right wood species and preparing the surface correctly can significantly reduce the risk of incompatibility issues, thereby enhancing the overall performance and appearance of the epoxy-coated wood.
Lack of UV Resistance
When considering epoxy coating over wood, one critical concern is the lack of UV resistance. Ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun can significantly degrade epoxy coatings, leading to a range of issues that compromise both the aesthetic and functional integrity of the material. Here’s why UV resistance is a key factor: 1. **Color Change and Discoloration**: Exposure to UV light can cause epoxy to darken or become yellowish, which is particularly problematic if the original color was intended to be clear or light. This discoloration not only affects the appearance but also indicates underlying chemical changes that may weaken the epoxy. 2. **Cracking and Brittle Behavior**: UV radiation can break down the molecular structure of epoxy, leading to brittleness and cracking. As the epoxy becomes more brittle, it loses its flexibility and becomes prone to cracking under stress or impact, which can expose the underlying wood to moisture and other environmental factors. 3. **Loss of Adhesion**: The degradation caused by UV exposure can also weaken the bond between the epoxy and the wood surface. This loss of adhesion can result in peeling or flaking of the epoxy coating, rendering it ineffective as a protective barrier. 4. **Surface Deterioration**: Over time, UV exposure can lead to surface roughening or chalking of the epoxy, which not only detracts from its appearance but also creates a surface that is more susceptible to dirt and moisture accumulation. 5. **Chemical Breakdown**: The chemical bonds within the epoxy resin can be broken down by UV light, leading to a reduction in its mechanical properties such as tensile strength and impact resistance. This chemical breakdown accelerates the overall deterioration process. To mitigate these issues, it is essential to use UV-resistant additives or topcoats specifically designed to protect against ultraviolet radiation. Additionally, applying a UV-stable clear coat over the epoxy can provide an extra layer of protection. However, even with these precautions, it is crucial to monitor the condition of the epoxy coating regularly and address any signs of degradation promptly to ensure long-term durability and material compatibility with the wood substrate.
Poor Chemical Resistance
Poor chemical resistance is a significant concern when applying epoxy coating over wood, as it can compromise the durability and integrity of the material. Epoxy coatings, while offering excellent mechanical properties and aesthetic appeal, may not be inherently resistant to all types of chemicals. When exposed to substances such as solvents, acids, or bases, the epoxy can degrade, leading to cracking, discoloration, or even delamination from the wood substrate. This vulnerability is particularly problematic in environments where the coated surface may come into contact with cleaning agents, industrial chemicals, or other corrosive substances. For instance, in a workshop or manufacturing setting, accidental spills of solvents like acetone or methylene chloride can rapidly damage the epoxy coating, necessitating costly repairs or reapplication. Similarly, in marine applications where epoxy-coated wood is exposed to seawater or bilge chemicals, the coating's poor chemical resistance can lead to premature failure. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to select epoxy formulations specifically designed for chemical resistance and to follow strict application guidelines to ensure a robust bond between the epoxy and the wood. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspection are essential to detect any signs of chemical damage early on, thereby extending the lifespan of the epoxy-coated wood and maintaining its structural integrity. By understanding and addressing these material compatibility and durability concerns, users can better protect their investments and ensure the long-term performance of epoxy-coated wood surfaces.
Environmental and Maintenance Factors
Environmental and maintenance factors play a crucial role in the longevity and performance of various systems, structures, and materials. Understanding these factors is essential for ensuring optimal functioning and preventing premature degradation. This article delves into three key areas that significantly impact environmental and maintenance considerations: Temperature and Humidity Fluctuations, Exposure to Water or Moisture, and Inadequate Maintenance Practices. Temperature and humidity fluctuations can cause expansion and contraction, leading to structural stress and potential failure. Exposure to water or moisture can result in corrosion, mold growth, and other forms of deterioration. Meanwhile, inadequate maintenance practices can exacerbate these issues by neglecting necessary repairs and inspections. By examining these factors, we can better understand how to mitigate their negative effects. Let's begin by exploring the critical impact of Temperature and Humidity Fluctuations on our environment and maintenance routines.
Temperature and Humidity Fluctuations
Temperature and humidity fluctuations are critical environmental factors that can significantly impact the integrity and performance of epoxy coatings over wood. When temperatures rise or fall beyond the optimal range, the epoxy coating can undergo thermal expansion and contraction, leading to potential cracks and delamination from the wood substrate. High temperatures can accelerate the curing process, but if the epoxy is not fully cured, it may lead to soft spots or uneven hardness. Conversely, low temperatures can slow down the curing process, potentially resulting in a weaker bond between the epoxy and the wood. Humidity fluctuations also play a crucial role. High humidity can lead to moisture absorption by the wood, causing it to swell. This swelling can create stress at the interface between the wood and the epoxy coating, leading to adhesion failure. On the other hand, low humidity can cause the wood to shrink, which may result in gaps between the wood and the epoxy, compromising its protective properties. Additionally, moisture trapped within the wood can lead to blistering or bubbling of the epoxy coating as it tries to escape. Maintaining a stable environment with controlled temperature and humidity levels is essential for ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of epoxy-coated wood surfaces. Ideally, temperatures should be kept within a narrow range (typically between 60°F to 80°F or 15°C to 27°C) during application and curing, while humidity levels should be maintained below 60%. Proper ventilation and drying times must also be adhered to, ensuring that any moisture present in the wood or air does not interfere with the bonding process. In practical terms, this means that epoxy-coated wood surfaces should be protected from direct sunlight, extreme weather conditions, and areas prone to high humidity such as basements or bathrooms. Regular inspections for signs of damage or deterioration due to environmental factors are also crucial. By understanding and managing these environmental variables, one can mitigate potential issues and ensure that epoxy-coated wood surfaces remain durable and functional over time.
Exposure to Water or Moisture
Exposure to water or moisture is a critical factor that can significantly impact the integrity and longevity of epoxy coatings over wood. When epoxy-coated wood surfaces are exposed to water or high humidity, several adverse effects can occur. Firstly, water can seep into the wood substrate, causing it to swell and potentially leading to delamination of the epoxy coating. This delamination can result in the loss of adhesion between the epoxy and the wood, compromising the protective barrier that the coating is intended to provide. Moreover, moisture can penetrate through any cracks or imperfections in the epoxy layer, reaching the wood beneath. Once inside, it can lead to fungal growth and wood rot, especially in environments with poor ventilation. The presence of moisture also accelerates chemical reactions that degrade both the wood and the epoxy, reducing their structural strength and durability. In addition, exposure to water can cause hydrolysis—a chemical reaction where water molecules break down the polymer chains in the epoxy resin. This process weakens the epoxy's mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and hardness, making it more susceptible to scratches, cracks, and other forms of damage. To mitigate these risks, it is essential to ensure that the wood substrate is properly prepared before applying the epoxy coating. This includes drying the wood thoroughly and sealing any pores or cracks. Regular maintenance is also crucial; inspecting for signs of moisture intrusion and addressing any issues promptly can help extend the lifespan of both the wood and the epoxy coating. In summary, exposure to water or moisture poses significant threats to epoxy-coated wood surfaces by causing delamination, promoting fungal growth, accelerating degradation processes, and weakening the epoxy's mechanical properties. Proper preparation of the wood substrate and regular maintenance are key strategies for minimizing these risks and ensuring a long-lasting protective barrier.
Inadequate Maintenance Practices
Inadequate maintenance practices are a critical factor that can significantly compromise the durability and effectiveness of epoxy coatings over wood. When maintenance is neglected, the protective barrier provided by the epoxy coating can deteriorate, exposing the underlying wood to environmental stresses such as moisture, UV radiation, and physical wear. For instance, failing to inspect and repair cracks or chips in the epoxy coating allows water to penetrate and cause wood rot or warping. Similarly, neglecting to clean the surface regularly can lead to the accumulation of dirt and debris, which can create uneven surfaces and reduce the coating's adhesion. Inadequate maintenance also includes not following manufacturer guidelines for recoating or touch-ups, leading to a weakened protective layer that is more susceptible to damage. Furthermore, ignoring signs of wear such as peeling or flaking can result in costly repairs down the line. Proper maintenance involves regular inspections, timely repairs, and adherence to recommended care procedures to ensure that the epoxy coating remains intact and continues to protect the wood effectively. By prioritizing these practices, individuals can extend the lifespan of their epoxy-coated wood surfaces and maintain their aesthetic and functional integrity. Conversely, neglecting these responsibilities can lead to premature failure of the coating, necessitating costly replacements or extensive repairs. Therefore, it is imperative to integrate rigorous maintenance routines into the care regimen for epoxy-coated wood to prevent such issues and ensure long-term performance.